Abstract
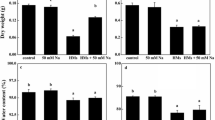
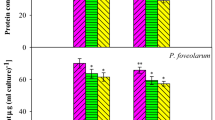
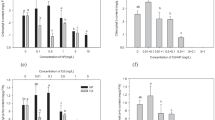
Cadmium pollution and harmful cyanobacterial blooms are two prominent environmental problems. The interactive effects of cadmium(II) and harmful cyanobacteria on rice seedlings remain unknown. In order to elucidate this issue, the interactive effects of cadmium(II) and Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB905 on the growth and antioxidant responses of rice seedling were investigated in this study, as well as the accumulation of cadmium(II) and microcystins. The results showed that the growth of rice seedlings was inhibited by cadmium(II) stress but promoted by inoculation of M. aeruginosa FACHB905. cadmium(II) stress induced oxidative damage on rice seedlings. Inoculation of M. aeruginosa FACHB905 alleviated the toxicity of cadmium(II) on rice seedlings. The accumulation of cadmium(II) in rice seedlings was decreased by M. aeruginosa FACHB905, but the translocation of cadmium(II) from root to shoot was increased by this cyanobacterium. The accumulation of microcystins in rice seedlings was decreased by cadmium(II). Results presented in this study indicated that cadmium(II) and M. aeruginosa had antagonistic toxicity on rice seedlings. The findings of this study throw new light on evaluation of ecological- and public health-risks for the co-contamination of cadmium(II) and harmful cyanobacteria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Lawson T, Weyers JDB, Codd GA (1996) Microcystin-LR inhibits photosynthesis of Phaseolus vulgaris primary leaves: implications for current spray irrigation practice. New Phytol 133:651–658. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1996.tb01934.x
Atafar Z, Mesdaghinia A, Nouri J, Homaee M, Yunesian M, Ahmadimoghaddam M, Mahvi AH (2010) Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environ Monit Assess 160:83–89. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0659-x
Azevedo CC, Azevedo J, Osório H, Vasconcelos V, Campos A (2014) Early physiological and biochemical responses of rice seedlings to low concentration of microcystin-LR. Ecotoxicology 23:107–121. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1156-8
Bauda P, Block JC (1990) Role of envelopes of gram-negative bacteria in cadmium binding and toxicity. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 5(1):47–60. doi:10.1002/tox.2540050105
Carmichael WW (1995) Toxic Microcystis in the environment, In: Watanabe MF, Harada K, Carmichael WW, & Fujiki H (eds) Toxic Microcystis, CRC Press, New York, pp 1–12
Chen J, Han FX, Wang F, Zhang H, Shi Z (2012) Accumulation and phytotoxicity of microcystin-LR in rice (Oryza sativa). Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 76:193–199. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.09.022
Chen J, Song L, Dai J, Gan N, Liu Z (2004) Effects of microcystins on the growth and the activity of superoxide dismutase and peroxidase of rape (Brassica napus L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.). Toxicon 43:393–400. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.01.011
Choo KS, Snoeijs P, Pedersen M (2004) Oxidative stress tolerance in the filamentous green algae Cladophora glomerata and Enteromorpha ahlneriana. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 298:111–123. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2003.08.007
Corbel S, Mougin C, Martin-Laurent F, Crouzet O, Bru D, Nélieu S, Bouaïcha N (2015) Evaluation of phytotoxicity and ecotoxicity potentials of a cyanobacterial extract containing microcystins under realistic environmental concentrations and in a soil-plant system. Chemosphere 128:332–340. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.008
Fasahat P (2015) Recent progress in understanding cadmium toxicity and tolerance in rice. Emir J Food Agric 27:94–105. doi:10.9755/ejfa.v27i1.17870
Fu J, Zhou Q, Liu J, Liu W, Wang T, Zhang Q, Jiang G (2008) High levels of heavy metals in rice (Oryza sativa L.) from a typical E-waste recycling area in southeast China and its potential risk to human health. Chemosphere 71:1269–1275. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.065
Fujiki H, Suganuma M (2011) Tumor promoters–microcystin-LR, nodularin and TNF-alpha and human cancer development. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 11:4–18
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.04.006
Guo B, Liang YC, Zhu YG, Zhao FJ (2007) Role of salicylic acid in alleviating oxidative damage in rice roots (Oryza sativa) subjected to cadmium stress. Environ Pollut 147:743–749. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.09.007
Herbeck LS, UngerD WuY, Jennerjahn TC (2013) Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters in NE Hainan, tropical China. Cont Shelf Res 57:92–104. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2012.05.006
Hu XF, Jiang Y, Shu Y, Hu X, Liu L, Luo F (2014) Effects of mining wastewater discharges on heavy metal pollution and soil enzyme activity of the paddy fields. J Geochem Explor 147:139–150. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.08.001
Huang W, **ng W, Li D, Liu Y (2008) Microcystin-RR induced apoptosis in tobacco BY-2 suspension cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial permeability transition pore status. Toxicol in Vitro 22:328–337. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2007.09.018
Ichimura T (1979) Media for freshwater cyanobacteria. In: Nishizawa K, Chihara M (eds) Methods in Phycology, Kyouritsu Shuppan, Tokyo, pp 295– 296. doi: 10.1007/s10811-013-0213-2
Jarvie HP, Neal C, Withers PJ (2005) Sewage-effluent phosphorus: a greater risk to river eutrophication than agricultural phosphorus? Sci Total Environ 360:246–253. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.08.038
Kuang X, Shao J, Chen A, Luo S, Peng L, Wu G, Gu JD (2016) Effects of bloom-forming cyanobacterial extracellular polymeric substances on the adsorption of cadmium onto kaolinite: behaviors and possible mechanisms. SpringerPlus 5:542. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-2191-8
Kulczycki E, Ferris FG, Fortin D (2002) Impact of cell wall structure on the behavior of bacterial cells as sorbents of cadmium and lead. Geomicrobiol J 19:553–565. doi:10.1080/01490450290098586
Landberg T and Greger M (2003) Influence of N and N supplementation on Cd accumulation in wheat grain. 7th International Conference on the Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements, Uppsala, 15–19 June 2003, pp 90–91
Lei M, Tie B, Williams PN, Zheng Y, Huang Y (2011) Arsenic, cadmium, and lead pollution and uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in greenhouse. J Soils Sediments 11:115–123. doi:10.1007/s11368-010-0280-9
Liang C, Wang W (2015) Response and recovery of rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings to irrigation with microcystin-contaminated water. Environ Earth Sci 73:4573–4580. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3746-z
Liu L, Yan H, **a WB, Li C, Zhang TY (2014) Toxic effect of cadmium on Microcysis aeruginosa and Scenedesmus obliquus. China Environ Sci 34:478–484
Liu Y, Donner E, Lombi E, Li R, Wu Z, Zhao FJ, Wu P (2013) Assessing the contributions of lateral roots to element uptake in rice using an auxin-related lateral root mutant. Plant Soil 372:125–136. doi:10.1007/s11104-012-1582-z
Moulis JM (2010) Cellular mechanisms of cadmium toxicity related to the homeostasis of essential metals. Biometals 23:877–896. doi:10.1007/s10534-010-9336-y
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27:31–36
Nakanishi H, Ogawa I, Ishimaru Y, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006) Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 52:464–469. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0765.2006.00055.x
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Masood A, Khan MIR, Syeed S, Khan NA (2012) Cadmium toxicity in plants and role of mineral nutrients in its alleviation. Am J Plant Sci 3:1476–1489. doi:10.4236/ajps.2012.310178
Ogawa T, Kobayashi E, Okubo Y, Suwazono Y, Kido T, Nogawa K (2004) Relationship among prevalence of patients with Itai-itai disease, prevalence of abnormal urinary findings, and cadmium concentrations in rice of individual hamlets in the **zu River basin, Toyama prefecture of Japan. Int J Environ Health Res 14:243–52. doi:10.1080/09603120410001725586
Pishchik VN, Vorobyev NI, Chernyaeva II, Timofeeva SV, Kozhemyakov AP, Alexeev YV, Lukin SM (2002) Experimental and mathematical simulation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and plant interaction under cadmium stress. Plant Soil 243:173–186. doi:10.1023/A:1019941525758
Prasad CH, Vineeta S (2014) Effect of induced mutation on sheath blight disease resistance in pusa basmati-1rice. Trends Biosci 7:2742–2745
Prieto A, Campos A, Cameán A, Vasconcelos V (2011) Effects on growth and oxidative stress status of rice plants (Oryza sativa) exposed to two extracts of toxin-producing cyanobacteria (Aphanizomenon ovalisporum and Microcystis aeruginosa). Ecotox Environ Safe 74:1973–1980. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.06.009
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sengupta DN (2012) Antioxidants and stress-related metabolites in the seedlings of two indica rice varieties exposed to cadmium chloride toxicity. Acta Physiol Plant 34:835–847. doi:10.1007/s11738-011-0881-y
Schatz D, Keren Y, Vardi A, Sukenik A, Carmeli S, Börner T, Dittmann E, Kaplan A (2007) Towards clarification of the biological role of microcystins, a family of cyanobacterial toxins. Environ Microbiol 9:965–970. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01218.x
Sedmak JJ, Grossberg SE (1977) A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem 79:544–552. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(77)90088-4
Seregin IV, Kozhevnikova AD (2011) Histochemical methods for detection of heavy metals and strontium in the tissues of higher plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 58:721–727. doi:10.1134/S1021443711040133
Shah K, Kumar RG, Verma S, Dubey RS (2001) Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide anion generation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Sci 161:1135–1144. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00517-9
Shen YW, Liu YD, Wu GQ, Ao HY, Qiu CQ (2005) Efficiency test on organic and inorganic fertilizes with cyanobacteria (Microcystis) in several crops. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 29:399–405
Soares CRFS, Oswaldo JO, de Carvalho JG, Guilherme RG (2007) Phosphate nutrition and Arbuscular Mycorrhiza on amelioration of cadmium toxicity in Trema [Trema micrantha (L.) Blum.]. Revista Árvore 31:783–792. doi:10.1590/S0100-67622007000500002
Son YO, Wang L, Poyil P, Budhraja A, Hitron JA, Zhang Z, Lee JC, Shi X (2012) Cadmium induces carcinogenesis in BEAS-2B cells through ROS-dependent activation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharm 264:153–160. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2012.07.028
Tran TA, Popova LP (2013) Functions and toxicity of cadmium in plants: recent advances and future prospects. Turk J Bot 37:1–13
Uchimaya M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278
Umar S, Diva I, Anjum NA, Iqbal M (2008) Research findings II: potassium nutrition reduces cadmium accumulation and oxidative burst in mustard (Brassica campestris L.). e-ifc 16:6–9
Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T (2012) Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice 5:5. doi: 10.1186/1939-8433-5-5
Uraguchi S, Kamiya T, Clemens S, Fujiwara T (2014) Characterization of OsLCT1, a cadmium transporter from indica rice (Oryza sativa). Physiol Plantarum 151:339–347. doi:10.1111/ppl.12189
Valentine JS, Wertz DL, Lyons TJ, Liou LL, Goto JJ, Gralla EB (1998) The dark side of dioxygen biochemistry. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2:253–262. doi:10.1016/S1367-5931(98)80067-7
Wang K, Colica G, Philippis RD, Liu Y, Li D (2010) Biosorption of copper by cyanobacterial bloom-derived biomass harvested from the eutrophic lake Dianchi in China. Curr Microbiol 61:340–345. doi:10.1007/s00284-010-9805-0
Wang WM, Deng Y, Zou H, Liang CJ (2014b) Effects of microcystins on growth and antioxidant system of rice roots. Environ Sic 35:1468–1472
Wang Y, Jiang X, Li K, Wu M, Zhang R, Zhang L, Chen G (2014a) Photosynthetic responses of Oryza sativa L. seedlings to cadmium stress: physiological, biochemical and ultrastructural analyses. Biometals 27:389–401. doi:10.1007/s10534-014-9720-0
Wei Y, Shohag MJI, Yang X (2012) Biofortification and bioavailability of rice grain zinc as affected by different forms of foliar zinc fertilization. Plos One 7:e45428. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045428
**ong J, Lu H, Lu K, Duan Y, An L, Zhu C (2009) Cadmium decreases crown root number by decreasing endogenous nitric oxide, which is indispensable for crown root primordia initiation in rice seedlings. Planta 230:599–610. doi:10.1007/s00425-009-0970-y
Ye W, Tan J, Liu X, Lin S, Pan J, Li D, Yang H (2011) Temporal variability of cyanobacterial populations in the water and sediment samples of Lake Taihu as determined by DGGE and real-time PCR. Harmful Algae 10:472–479. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2011.03.002
Yin L, Huang J, Huang W, Li D, Liu Y (2005) Responses of antioxidant system in Arabidopsis thaliana suspension cells to the toxicity of microcystin-RR. Toxicon 46:859–864. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.12.025
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice. IRRI, Los Banos, Philippines, pp 61–65
Yu F, Liu K, Li M, Zhou Z, Deng H, Chen B (2013) Effects of cadmium on enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidative defences of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Phytoremediation 15:513–521. doi:10.1080/15226514.2012.702807
Yu H, Zhou Y, Fu X, **e L, Ying Y (2007) Discrimination between Chinese rice wines of different geographical origins by NIRS and AAS. Eur Food Res Technol 225:313–320. doi:10.1007/s00217-006-0416-8
Yu XZ, Gu JD, Li L (2008) Assimilation and physiological effects of ferrocyanide on wee** willows. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 71:609–615. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.05.007
Zamocky M, Furtmuller PG, Obinger C (2008) Evolution of catalases from bacteria to humans. Antioxid Redox. Sign 10:1527–1548. doi:10.1089/ars.2008.2046
Zhang WH, Zhang XH, Zhang GM, Xu XQ (2003) Variation of Microcystins in a Lake for Water Supply. J Environ Sci Heal, Part A 38(12):2857–2865. doi:10.1081/ESE-120025836
Zhang X, Chen H, Jiang H, Lu W, Pan J, Qian Q, Xue D (2015) Measuring the damage of heavy metal cadmium in rice seedlings by SRAP analysis combined with physiological and biochemical parameters. J Sci Food Agric 95:2292–2298. doi:10.1002/jsfa.6949
Zhang Z, ** F, Wang C, Luo J, Lin H, **ang K, Liu L, Zhao M, Zhang Y, Ding H, Zhou S, Shen Y, Pan G (2012) Difference between Pb and Cd accumulation in 19 elite maize inbred lines and application prospects. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:271485. doi:10.1155/2012/271485
Zhao Y, **e P, Fan H (2012) Genomic profiling of microRNAs and proteomics reveals an early molecular alteration associated with tumorigenesis induced by MC-LR in mice. Environ Sci Technol 46:34–41. doi:10.1021/es201514h
Zhou W, Juneau P, Qiu B (2006) Growth and photosynthetic responses of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to elevated levels of cadmium. Chemosphere 65:1738–1746. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.078
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272248); Foundation from Education Department of Hunan Province (14B084); Joint Foundation of China and Australia (2013DFG91190).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuang, X., Gu, JD., Tie, B. et al. Interactive effects of cadmium and Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanobacterium) on the growth, antioxidative responses and accumulation of cadmium and microcystins in rice seedlings. Ecotoxicology 25, 1588–1599 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1714-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1714-y