Abstract
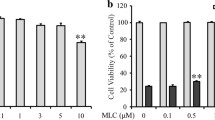
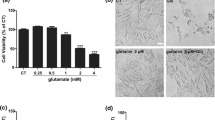
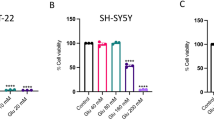
Oxidative glutamate toxicity plays a vital role in the neurodegeneration diseases, including Alzheimer’s diseases (AD). This study set out with the aim to investigate the beneficial effects of fangchinoline (FAN), a natural alkaloid, against glutamate-induced oxidative damage, and to clarify the underlying cellular and biochemical mechanisms. FAN prevented HT22 cells death from oxidative glutamate cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner, and significantly attenuated the overproduction of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reversed the reduction of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity induced by glutamate. Further investigations on the underlying mechanisms demonstrated that FAN potently up-regulated the protein level of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase (HO-1), in glutamate-exposed HT22 cells. The protective effects of FAN were almost completely antagonized by inhibitor of Nrf2. Subsequent studies revealed that FAN could down-regulate Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) in both mRNA level and protein level. To sum up, our result demonstrated the protective effects of FAN against glutamate-induced oxidative neuronal damage, and for the first time clarified the anti-oxidative mechanisms of FAN involve activating endogenous antioxidant defense system including enhancing SOD activity and regulating Keap1/Nrf-2 antioxidation signaling through modulation of Keap1 expression. Above results shed more light on the molecular mechanisms of FAN’s neuroprotective effects, and may provide important clues for the drug development in preventing oxidative stress-associated neurodegenerative diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht P, Lewerenz J, Dittmer S, Noack R, Maher P, Methner A (2010) Mechanisms of oxidative glutamate toxicity the glutamate cystine antiporter system xc-as a neuroprotective drug target. CNS Neurol Disord: Drug Targets 9:373–382. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152710791292567
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset C (1995) Use of a free-radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Sci Technol-Leb 28:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5
Bryan HK, Olayanju A, Goldring CE, Park BK (2013) The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and -independent mechanisms of regulation. Biochem Pharmacol 85:705–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.11.016
Chao XJ, Chen ZW, Liu AM, He XX, Wang SG, Wang YT, Liu PQ, Ramassamy C, Mak SH, Cui W, Kong AN, Yu ZL, Han YF, Pi RB (2014) Effect of tacrine-3-caffeic acid, a novel multifunctional anti-Alzheimer’s dimer, against oxidative-stress-induced cell death in HT22 hippocampal neurons: involvement of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 20:840–850. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12286
Choi HS, Kim HS, Min KR, Kim Y, Lim HK, Chang YK, Chung MW (2000) Anti-inflammatory effects of fangchinoline and tetrandrine. J Ethnopharmacol 69:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(99)00141-5
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7901908
Dodson M, de la Vega MR, Cholanians AB, Schmidlin CJ, Chapman E, Zhang DD (2018) Modulating NRF2 in disease: timing is everything. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 59:555–575. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010818-021856
Fan B, Zhang X, Ma Y, Zhang A (2017a) Fangchinoline induces apoptosis, autophagy and energetic impairment in bladder cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1159/000481698
Fan H, Shu Q, Guan X, Zhao J, Yan J, Li X, Liu J, Jia Z, Shi J, Li J (2017b) Sinomenine protects PC12 neuronal cells against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress via a ROS-dependent up-regulation of endogenous antioxidant system. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:1387–1398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0469-1
Feng HX, Li CP, Shu SJ, Liu H, Zhang HY (2019) A11, a novel diaryl acylhydrazone derivative, exerts neuroprotection against ischemic injury in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0028-4
Fukui M, Choi HJ, Zhu BT (2010) Mechanism for the protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death. Free Radic Biol Med 49:800–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.06.002
Gulcin I, Elias R, Gepdiremen A, Chea A, Topal F (2010) Antioxidant activity of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids from Stephania rotunda: cepharanthine and fangchinoline. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 25:44–53. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756360902932792
Harvey AL, Cree IA (2010) High-throughput screening of natural products for cancer therapy. Planta Med 76:1080–1086. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1250162
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Engel JD, Yamamoto M (1999) Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev 13:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.1.76
Jeong EJ, Hwang L, Lee M, Lee KY, Ahn MJ, Sung SH (2014) Neuroprotective biflavonoids of Chamaecyparis obtusa leaves against glutamate-induced oxidative stress in HT22 hippocampal cells. Food Chem Toxicol 64:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.12.003
Jiang S, Deng C, Lv J, Fan C, Hu W, Di S, Yan X, Ma Z, Liang Z, Yang Y (2017) Nrf2 weaves an elaborate network of neuroprotection against stroke. Mol Neurobiol 54:1440–1455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9707-7
Kang Y, Tiziani S, Park G, Kaul M, Paternostro G (2014) Cellular protection using Flt3 and PI3Kα inhibitors demonstrates multiple mechanisms of oxidative glutamate toxicity. Nat Commun 5:3672. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4672
Kim SD, Oh SK, Kim HS, Seong YH (2001) Inhibitory effect of fangchinoline on excitatory amino acids-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat cerebellar granule cells. Arch Pharm Res 24:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/Bf02976485
Kim NT, Lee DS, Chowdhury A, Lee H, Cha BY, Woo JT, Woo ER, Jang JH (2017) Acerogenin C from Acer nikoense exhibits a neuroprotective effect in mouse hippocampal HT22 cell lines through the upregulation of Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep 16:1537–1543. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6682
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M, Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K, Yamamoto M (2004) Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol 24:7130–7139. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.24.16.7130-7139.2004
Koh SB, Ban JY, Lee BY, Seong YH (2003) Protective effects of fangchinoline and tetrandrine on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative neuronal cell damage in cultured rat cerebellar granule cells. Planta Med 69:506–512. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-40647
Lavrovsky Y, Chatterjee B, Clark RA, Roy AK (2000) Role of redox-regulated transcription factors in inflammation, aging and age-related diseases. Exp Gerontol 35:521–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0531-5565(00)00118-2
Lee DS, Jeong GS (2016) Butein provides neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects through Nrf2/ARE-dependent haem oxygenase 1 expression by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Br J Pharmacol 173:2894–2909. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13569
Li Z, Chen X, Lu W, Zhang S, Guan X, Li Z, Wang D (2017) Anti-oxidative stress activity is essential for Amanita caesarea mediated neuroprotection on glutamate-induced apoptotic HT22 cells and an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Int J Mol Sci 18:1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081623
Lin TY, Lu CW, Tien LT, Chuang SH, Wang YR, Chang WH, Wang SJ (2009) Fangchinoline inhibits glutamate release from rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals (synaptosomes). Neurochem Int 54:506–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2009.02.001
Merarchi M, Sethi G, Fan L, Mishra S, Arfuso F, Ahn KS (2018) Molecular targets modulated by fangchinoline in tumor cells and preclinical models. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 23:2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102538
Morroni F, Sita G, Graziosi A, Turrini E, Fimognari C, Tarozzi A, Hrelia P (2018) Neuroprotective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease involves Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Aging Dis 9:605–622. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2017.0903
Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2004) Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med 10:549–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2004.09.003
Murphy TH, Miyamoto M, Sastre A, Schnaar RL, Coyle JT (1989) Glutamate toxicity in a neuronal cell line involves inhibition of cystine transport leading to oxidative stress. Neuron 2:1547–1558. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(89)90043-3
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 284:13291–13295. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R900010200
Olayanju A, Copple IM, Bryan HK, Edge GT, Sison RL, Wong MW, Lai ZQ, Lin ZX, Dunn K, Sanderson CM, Alghanem AF, Cross MJ, Ellis EC, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Malik HZ, Kitteringham NR, Goldring CE, Park BK (2015) Brusatol provokes a rapid and transient inhibition of Nrf2 signaling and sensitizes mammalian cells to chemical toxicity-implications for therapeutic targeting of Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med 78:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.11.003
Pae HO, Kim EC, Chung HT (2008) Integrative survival response evoked by heme oxygenase-1 and heme metabolites. J Clin Biochem Nutr 42:197–203. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.2008029
Prasad KN (2016) Simultaneous activation of Nrf2 and elevation of antioxidant compounds for reducing oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in human Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 153:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.01.002
Prasansuklab A, Tencomnao T (2018) Acanthus ebracteatus leaf extract provides neuronal cell protection against oxidative stress injury induced by glutamate. BMC Complement Altern Med 18:278. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2340-4
Prasansuklab A, Meemon K, Sobhon P, Tencomnao T (2017) Ethanolic extract of Streblus asper leaves protects against glutamate-induced toxicity in HT22 hippocampal neuronal cells and extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:551. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-2050-3
Sandberg M, Patil J, D’Angelo B, Weber SG, Mallard C (2014) NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease: implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology 79:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.004
Tan SL, Wood M, Maher P (1998) Oxidative stress induces a form of programmed cell death with characteristics of both apoptosis and necrosis in neuronal cells. J Neurochem 71:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71010095.x
Tan S, Schubert D, Maher P (2001) Oxytosis: a novel form of programmed cell death. Curr Top Med Chem 1:497–506. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394741
Velichkova M, Hasson T (2005) Keap1 regulates the oxidation-sensitive shuttling of Nrf2 into and out of the nucleus via a Crm1-dependent nuclear export mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 25:4501–4513. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.25.11.4501-4513.2005
Wei Y, Liu D, Zheng Y, Hao C, Li H, Ouyang W (2018) Neuroprotective effects of kinetin against glutamate-induced oxidative cytotoxicity in HT22 cells: involvement of Nrf2 and heme oxygenase-1. Neurotox Res 33:725–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9811-0
**ang Y, Ye W, Huang C, Yu D, Chen H, Deng T, Zhang F, Lou B, Zhang J, Shi K, Chen B, Zhou M (2018) Brusatol enhances the chemotherapy efficacy of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer via the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:2360427. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2360427
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support of this work by Grant Nos. 81872859, 81703507, 81522045 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FB, LT, and HZ designed the study; FB performed all the study; FB and LT analyzed pharmacological data; FB, LT, and HZ wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, F., Tao, L. & Zhang, H. Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Alkaloid Fangchinoline Against Oxidative Glutamate Toxicity: Involvement of Keap1-Nrf2 Axis Regulation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39, 1177–1186 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00711-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00711-6