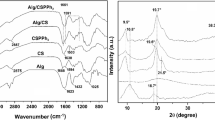
Abstract
The removal and recovery of phosphate from water using adsorption technology require that the adsorbent material is easily separable from treated water. Continuous efforts are still awaited to develop additional efficient phosphate adsorbents that are economical to fabricate. In this study, hydrous zirconia-impregnated chitosan beads (HZCB) containing different Zr/chitosan ratios were synthesized using a facile scheme. We found that HZCB with a Zr/amine molar ratio of ~ 1 (HZCB-1) possessed excellent stability and phosphate removal performance. This optimized material was characterized with XRD, SEM, FTIR, XPS, specific surface area and point of zero charge measurements. The maximum adsorption capacity was 42.02 mg/g (at pH ~ 6.7). The adsorption kinetics were best described by a pseudosecond-order model, and the rate constant of HZCB-1 was much lower than that of its powder but was similar to the commercial bead product Ferrolox. The removal of phosphate depended substantially upon pH and was enhanced by lowering the pH. Good selectivity of HZCB-1 for phosphate was observed, although the coexistence of sulfate produced a significant negative effect. Direct coordination of phosphate to Zr atoms by replacing hydroxyls was the dominant adsorption mechanism (~ 85%), while chitosan also contributed to phosphate removal (~ 15%). Adsorbed phosphate was successfully eluted by an NaOH solution, and the material obtained after desorption and regeneration was able to be repeatedly used. The results of column studies indicated that this material could be implemented in long-term application.










Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abdellaoui Y, Oualid HA, Hsini A, El Ibrahimi B, Laabd M, El Ouardi M, Giácoman-Vallejos G, Gamero-Melo P (2021) Synthesis of zirconium-modified Merlinoite from fly ash for enhanced removal of phosphate in aqueous medium: experimental studies supported by Monte Carlo/SA simulations. Chem Eng J 404:126600
Acelas NY, Martin BD, López D, Jefferson B (2015) Selective removal of phosphate from wastewater using hydrated metal oxides dispersed within anionic exchange media. Chemosphere 119:1353–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.024
Arias CA, Del Bubba M, Brix H (2001) Phosphorus removal by sands for use as media in subsurface flow constructed reed beds. Water Res 35:1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00368-7
Awual MR, Jyo A, Ihara T, Seko N, Tamada M, Lim KT (2011) Enhanced trace phosphate removal from water by zirconium(IV) loaded fibrous adsorbent. Water Res 45:4592–4600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.009
Awual MR, Shenashen MA, Jyo A, Shiwaku H, Yaita T (2014) Preparing of novel fibrous ligand exchange adsorbent for rapid column-mode trace phosphate removal from water. J Ind Eng Chem 20:2840–2847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.11.016
Bacelo H, Pintor AMA, Santos SCR, Boaventura RAR, Botelho CMS (2020) Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem Eng J 381:122566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122566
Biswas BK, Inoue K, Ghimire KN, Harada H, Ohto K, Kawakita H (2008) Removal and recovery of phosphorus from water by means of adsorption onto orange waste gel loaded with zirconium. Bioresour Technol 99:8685–8690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.04.015
Bui TH, Hong SP, Yoon J (2018) Development of nanoscale zirconium molybdate embedded anion exchange resin for selective removal of phosphate. Water Res 134:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.061
Bui TH, Hong SP, Kim C, Yoon J (2021) Performance analysis of hydrated Zr(IV) oxide nanoparticle-impregnated anion exchange resin for selective phosphate removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 586:741–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.143
Chen J, Yang R, Zhang Z, Wu D (2022) Removal of fluoride from water using aluminum hydroxide-loaded zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash. J Hazard Mater 421:126817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126817
Chinese Environmental Protection Administration (2002) Analysis Methods for Water and Wastewater, 4th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Bei**g
Cho DW, Jeon BH, Jeong Y, Nam IH, Choi UK, Kumar R, Song H (2016) Synthesis of hydrous zirconium oxide-impregnated chitosan beads and their application for removal of fluoride and lead. Appl Surf Sci 372:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.068
Cooke DG, Welch EB, Peterson SA, Nicholas SA (2005) Restoration and management of lakes and reservoirs. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Change 19:292–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.10.009
Cordell D, Rosemarin A, Schröder JJ, Smit AL (2011) Towards global phosphorus security: a systems framework for phosphorus recovery and reuse options. Chemosphere 84:747–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.032
Crini G (2005) Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Prog Polym Sci 30:38–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.11.002
De-Bashan LE, Bashan Y (2004) Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res 38:4222–4246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.07.014
Del Nero M, Galindo C, Barillon R, Halter E, Madé B (2010) Surface reactivity of α-Al2O3 and mechanisms of phosphate sorption: in situ ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and ζ potential studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 342:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.10.057
Díaz-Flores PE, Arcibar-Orozco JA, Rangel-Méndez F-R, JR, (2021) Synthesis of a chitosan-zeolite composite modified with La(III): characterization and its application in the removal of fluoride from aqueous systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 232:235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05185-1
Eltaweil AS, Omer AM, El-Aqapa HG, Gaber NM, Attia NF, El-Subruiti GM, Mohy-Eldin MS, El-Monaem EMA (2021) Chitosan based adsorbents for the removal of phosphate and nitrate: a critical review. Carbohydr Polym 274:118671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118671
Guan T, Kuang Y, Li X, Fang J, Fang W, Wu D (2020) The recovery of phosphorus from source-separated urine by repeatedly usable magnetic Fe3O4@ZrO2 nanoparticles under acidic conditions. Environ Int 134:105322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105322
Guibal E (2004) Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: a review. Sep Purif Technol 38:43–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2003.10.004
Huang W, Zhang Y, Li D (2017) Adsorptive removal of phosphate from water using mesoporous materials: a review. J Environ Manag 193:470–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.02.030
Huang X, Wu W, **a Y, Li W, Gong Y, Li Z (2019) Alkali resistant nanocomposite gel beads as renewable adsorbents for water phosphate recovery. Sci Total Environ 685:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.296
Jang J, Lee DS (2019) Effective phosphorus removal using chitosan/Ca-organically modified montmorillonite beads in batch and fixed-bed column studies. J Hazard Mater 375:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.070
Johir MAH, Pradhan M, Loganathan P, Kandasamy J, Vigneswaran S (2016) Phosphate adsorption from wastewater using zirconium (IV) hydroxide: Kinetics, thermodynamics and membrane filtration adsorption hybrid system studies. J Environ Manag 167:167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.11.048
Jung KW, Jeong TU, Kang HJ, Ahn KH (2016) Characteristics of biochar derived from marine macroalgae and fabrication of granular biochar by entrapment in calcium-alginate beads for phosphate removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 211:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.066
Karageorgiou K, Paschalis M, Anastassakis GN (2007) Removal of phosphate species from solution by adsorption onto calcite used as natural adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 139:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.038
Kumar IA, Viswanathan N (2017) Fabrication of metal ions cross-linked alginate assisted biocomposite beads for selective phosphate removal. J Environ Chem Eng 5:1438–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.02.005
Lin J, Jiang B, Zhan Y (2018) Effect of pre-treatment of bentonite with sodium and calcium ions on phosphate adsorption onto zirconium-modified bentonite. J Environ Manag 217:183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.079
Lin X, **e Y, Lu H, **n Y, Altaf R, Zhu S, Liu D (2021) Facile preparation of dual La-Zr modified magnetite adsorbents for efficient and selective phosphorus recovery. Chem Eng J 413:127530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127530
Liu X, Zhang L (2015) Removal of phosphate anions using the modified chitosan beads: adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism studies. Powder Technol 277:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.02.055
Liu Q, Hu P, Wang J, Zhang L, Huang R (2016) Phosphate adsorption from aqueous solutions by Zirconium (IV) loaded cross-linked chitosan particles. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 59:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.08.012
Loganathan P, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, Bolan NS (2014) Removal and recovery of phosphate from water using sorption. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:847–907. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2012.741311
Luo H, Rong H, Zhang TC, Zeng X, Wan J (2019) Amino-functionalized magnetic zirconium alginate beads for phosphate removal and recovery from aqueous solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 136:46897. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46897
Lürling M, Van Oosterhout F (2013) Controlling eutrophication by combined bloom precipitation and sediment phosphorus inactivation. Water Res 47:6527–6537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.08.019
National Health and Family Planning Commission of China (2013) National standard for the safety of chitosan as a food additive. The national standard of the Peoples Republic of China GB 29941–2013, Bei**g
Prabhu SM, Subaramanian M, Meenakshi S (2016) A simple one-pot in-situ method for the synthesis of aluminum and lanthanum binary oxyhydroxides in chitosan template towards defluoridation of water. Chem Eng J 283:1081–1089
Qu XL, Alvarez PJJ, Li QL (2013) Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res 47:3931–3946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.058
Salehi S, Hosseinifard M (2020) Optimized removal of phosphate and nitrate from aqueous media using zirconium functionalized nanochitosan-graphene oxide composite. Cellulose 27:8859–8883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03382-5
Schindler DW, Carpenter SR, Chapra SC, Hecky RE, Orihel DM (2016) Reducing phosphorus to curb lake eutrophication is a success. Environ Sci Technol 50:8923–8929. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02204
Shan S, Tang H, Zhao Y, Wang W, Cui F (2019) Highly porous zirconium-crosslinked graphene oxide/alginate aerogel beads for enhanced phosphate removal. Chem Eng J 359:779–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.033
Shang Y, Guo K, Xu X, Ren Z, Gao B (2018) Cellulose based multifunctional hybrid material for sequestering phosphate in stratified water purification columns. Cellulose 25:5877–5892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1954-5
Sowmya A, Meenakshi S (2014) Zr(IV) loaded cross-linked chitosan beads with enhanced surface area for the removal of nitrate and phosphate. Int J Biol Macromol 69:336–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.05.043
Wan J, Zhu C, Hu J, Zhang TC, Richter-Egger D, Feng X, Zhou A, Tao T (2017) Zirconium-loaded magnetic interpenetrating network chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for phosphorus recovery from the aquatic environment. Appl Surf Sci 423:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.201
Wang Z, **ng M, Fang W, Wu D (2016) One-step synthesis of magnetite core/zirconia shell nanocomposite for high efficiency removal of phosphate from water. Appl Surf Sci 366:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.059
Wang Z, Fang W, **ng M, Wu D (2017) A bench-scale study on the removal and recovery of phosphate by hydrous zirconia-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 424:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.067
Wu FC, Tseng RL, Juang RS (2010) A review and experimental verification of using chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for selected heavy metals. J Environ Manag 91:798–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.10.018
Wu B, Wan J, Zhang Y, Pan B, Lo IMC (2020) Selective phosphate removal from water and wastewater using sorption: process fundamentals and removal mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 54:50–66. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05569
Xu X, Cheng Y, Wu X, Fan P, Song R (2020) La(III)-bentonite/chitosan composite: A new type adsorbent for rapid removal of phosphate from water bodies. Appl Clay Sci 190:105547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105547
Zhang Y, Qin J, Wang X, Chen Z, Zheng X, Chen Y (2021) Advanced treatment of phosphorus-containing tail water by Fe–Mg–Zr layered double hydroxide beads: Performance and mechanism. J Environ Manag 296:113203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113203
Zhou K, Wu B, Su L, **n W, Chai X (2018) Enhanced phosphate removal using nanostructured hydrated ferric-zirconium binary oxide confined in a polymeric anion exchanger. Chem Eng J 345:640–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.091
Zhu X, Jyo A (2005) Column-mode phosphate removal by a novel highly selective adsorbent. Water Res 39:2301–2308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.033
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation Project (52170166) and the HITACHI Chemical Co., Ltd (Grant No 2020-07).
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52170166) and the HITACHI Chemical Co., Ltd of Japan (Grant No. 2020-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZ: conceptualization, investigation, writing-original draft; TL: investigation, validation; DW: supervision, writing-reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
“The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.”
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Liu, T. & Wu, D. Facile synthesis of hydrous zirconia-impregnated chitosan beads as a filter medium for efficient removal of phosphate from water. Cellulose 29, 8749–8768 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04813-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04813-1