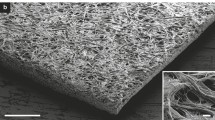
Abstract
Preconcentration of organic analytes from an aqueous solution onto a substrate surface can significantly improve trace level analyte detection by Raman spectroscopy. Nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC)-based three dimensional (3D) substrates have great potential for this application since they can readily absorb water when exposed to an aqueous analyte solution while adsorbing organic molecules from the solution. However, the transport of organic analytes inside the substrate along with water, loss of mechanical robustness, and disintegration of the 3D structure in water limit the use of porous NFC substrates in aqueous environments. To overcome these deficiencies, a chemically crosslinked network of methacrylated carboxymethyl cellulose was incorporated into the NFC matrices, which improves the stability and robustness of the substrates in water. Application of a polydimethyl siloxane-based hydrophobic coating on four of the five analyte exposed surfaces further improves preconcentration efficiency by forcing the analyte solutions to pass through one hydrophilic surface only. Samples with a range of porosities were investigated to optimize sampling time, solution uptake volume, and substrate robustness in water. Using this substrate, parts-per-million detection sensitivity for organic probe molecules in aqueous solution was possible. Incorporation of silver nanoparticles within the substrates further enhanced substrate sensitivity to parts-per-trillion level detection of probe molecules, due to the Raman signal enhancement by surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect. A model is presented here which describes the linearity, saturation, and depletion of the SERS signal.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas A, Brimer A, Slocik JM et al (2013) Multifunctional analytical platform on a paper strip: separation, preconcentration, and subattomolar detection. Anal Chem 85:3977–3983. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac303567g
Alahmadi NS, Betts JW, Heinze T et al (2018) Synthesis and antimicrobial effects of highly dispersed, cellulose-stabilized silver/cellulose nanocomposites. RSC Adv 8:3646–3656. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra12280b
Altun AO, Youn SK, Yazdani N et al (2013) Metal-dielectric-CNT nanowires for femtomolar chemical detection by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Adv Mater 25:4431–4436. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201300571
Altun AO, Bond T, Pronk W, Park HG (2017) Sensitive detection of competitive molecular adsorption by surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Langmuir 33:6999–7006. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b01186
Audunsson G (1986) Aqueous/aqueous extraction by means of a liquid membrane for sample cleanup and preconcentration of amines in a flow system. Anal Chem 58:2714–2723. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00126a030
Barud HS, Barrios C, Regiani T et al (2008) Self-supported silver nanoparticles containing bacterial cellulose membranes. Mater Sci Eng C 28:515–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2007.05.001
Barud HS, Regiani T, Marques RFC et al (2011) Antimicrobial bacterial cellulose-silver nanoparticles composite membranes. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/721631
Bell JP, Tsezos M (1987) Removal of hazardous organic pollutants by biomass adsorption. J Water Pollut Control Fed 59:191–198
Bumbrah GS, Sharma RM (2016) Raman spectroscopy—basic principle, instrumentation and selected applications for the characterization of drugs of abuse. Egypt J Forensic Sci 6:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejfs.2015.06.001
Cervin NT, Johansson E, Larsson PA, Wågberg L (2016) Strong, water-durable, and wet-resilient cellulose nanofibril-stabilized foams from oven drying. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:11682–11689. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b00924
Chen S, Lin X, Yuen C et al (2014) Recovery of Raman spectra with low signal-to-noise ratio using Wiener estimation. Opt Express 22:12102. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.22.012102
Cheng ML, Tsai BC, Yang J (2011) Silver nanoparticle-treated filter paper as a highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate for detection of tyrosine in aqueous solution. Anal Chim Acta 708:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.10.013
Doherty B, Brunetti BG, Sgamellotti A, Miliani C (2011) A detachable SERS active cellulose film: a minimally invasive approach to the study of painting lakes. J Raman Spectrosc 42:1932–1938. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2942
Fierro-Mercado PM, Hernández-Rivera SP (2012) Highly sensitive filter paper substrate for SERS trace explosives detection. Int J Spectrosc 2012:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/716527
Fu X, Cheng Z, Yu J et al (2016) A SERS-based lateral flow assay biosensor for highly sensitive detection of HIV-1 DNA. Biosens Bioelectron 78:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.099
Glasser WG, Atalla RH, Blackwell J et al (2012) About the structure of cellulose: debating the Lindman hypothesis. Cellulose 19:589–598
Goodacre R, Cheung W, Shadi IT (2009) Quantitative analysis of methyl green using surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering. Anal Bioanal Chem 394:1833–1838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2896-4
Gupta S, Martoïa F, Orgéas L, Dumont P (2018) Ice-templated porous nanocellulose-based materials: current progress and opportunities for materials engineering. Appl Sci 8:2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122463
Haynes CL, McFarland AD, Van Duyne RP (2005) Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 77:338 A–346 A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac053456d
He Y, **ao S, Dong T, Nie P (2019) Gold nanoparticles with different particle sizes for the quantitative determination of chlorpyrifos residues in soil by SERS. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112817
Henglein A, Giersig M (1999) Formation of colloidal silver nanoparticles: cap** action of citrate. J Phys Chem B 103:9533–9539. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9925334
Hoppmann EP, Yu WW, White IM (2013) Highly sensitive and flexible inkjet printed SERS sensors on paper. Methods 63:219–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.07.010
Hoppmann EP, Yu WW, White IM (2014) Inkjet-printed fluidic paper devices for chemical and biological analytics using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2013.2286076
Hossen MR, Dadoo N, Holomakoff DG et al (2018) Wet stable and mechanically robust cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) based hydrogel. Polymer (Guildf). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2018.07.016
Hossen MR, Talbot MW, Kennard R et al (2020) A comparative study of methods for porosity determination of cellulose based porous materials. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03257-9
Jiang F, Hsieh Y-L (2014) Amphiphilic superabsorbent cellulose nanofibril aerogels. J Mater Chem A 2:6337–6342. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA00743C
Johnston ID, McCluskey DK, Tan CKL, Tracey MC (2014) Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J Micromech Microeng. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/24/3/035017
Kim J, Monllor-Satoca D, Choi W (2012) Simultaneous production of hydrogen with the degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2 photocatalyst modified with dual surface components. Energy Environ Sci 5:7647–7656. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee21310a
Kim CH, Youn HJ, Lee HL (2015) Preparation of cross-linked cellulose nanofibril aerogel with water absorbency and shape recovery. Cellulose 22:3715–3724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0745-5
Kosior A, Antošová M, Faber R et al (2013) Single-component adsorption of proteins on a cellulose membrane with the phenyl ligand for hydrophobic interaction chromatography. J Membr Sci 442:216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.04.013
Lasgow GG, Sers SR (2011) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and resonance Raman scattering (SERRS): a review of applications. Appl Spectrosc. https://doi.org/10.1366/11-06365
Lauridsen RK, Rindzevicius T, Molin S et al (2015) Towards quantitative SERS detection of hydrogen cyanide at ppb level for human breath analysis. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 5:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2015.07.002
Li Y, Church JS (2014) Science direct Raman spectroscopy in the analysis of food and pharmaceutical nanomaterials. J Food Drug Anal 22:29–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.003
Li D, Qu L, Zhai W et al (2011) Facile on-site detection of substituted aromatic pollutants in water using thin layer chromatography combined with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 45:4046–4052. https://doi.org/10.1021/es104155r
Li Z, Deen MJ, Kumar S, Selvaganapathy PR (2014) Raman spectroscopy for in-line water quality monitoring—instrumentation and potential. Sensors (Switzerland) 14:17275–17303. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140917275
Links DA (2012) Evaporative preconcentration and cryopreservation of fluorescent analytes using superhydrophobic surfaces †. Soft Matter. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2sm07127d
Lu Y, Wu C, Wu Y et al (2018) Ag-coated cellulose fibers as surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates for adsorptive detection of malachite green. Materials (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071197
Malka I, Petrushansky A, Rosenwaks S, Bar I (2013) Detection of explosives and latent fingerprint residues utilizing laser pointer-based Raman spectroscopy. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 113:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5500-8
Malm CJ, Genung LB, Fleckenstein JV (1947) Densities of cellulose esters. Ind Eng Chem 39:1499–1504. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50455a022
Maneerung T, Tokura S, Rujiravanit R (2008) Impregnation of silver nanoparticles into bacterial cellulose for antimicrobial wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym 72:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.07.025
Martoïa F, Cochereau T, Dumont PJJ et al (2016) Cellulose nanofibril foams: links between ice-templating conditions, microstructures and mechanical properties. Mater Des 104:376–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.04.088
Matisová E, Škrabáková S (1995) Carbon sorbents and their utilization for the preconcentration of organic pollutants in environmental samples. J Chromatogr A 707:145–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(95)00347-P
Medronho B, Duarte H, Alves L et al (2015) Probing cellulose amphiphilicity. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 30:58–66. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2015-30-01-p058-066
Nazari B, Bousfield DW (2016) Cellulose nanofibers influence on properties and processing of paperboard coatings. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 31:511–520. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2016-31-03-p511-520
Nechyporchuk O, Belgacem MN, Bras J (2016) Production of cellulose nanofibrils: a review of recent advances. Ind Crops Prod 93:2–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.02.016
Ngo YH, Li D, Simon GP, Garnier G (2012) Gold nanoparticle-paper as a three-dimensional surface enhanced Raman scattering substrate. Langmuir 28:8782–8790. https://doi.org/10.1021/la3012734
Oh K, Lee M, Lee SG et al (2018) Cellulose nanofibrils coated paper substrate to detect trace molecules using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Cellulose 25:3339–3350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1806-3
Oreshkin VN, Tsizin GI (2004) Determination of the total trace elements in natural waters by the sorption-atomic absorption method with the fractional evaporation of concentrates in a crucible atomizer. J Anal Chem 59:890–894. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JANC.0000040708.39938.de
Pal A, Gin KYH, Lin AYC, Reinhard M (2010) Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci Total Environ 408:6062–6069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.09.026
Purington E, Bousfield D, Gramlich WM (2019) Fluorescent dye adsorption in aqueous suspension to produce tagged cellulose nanofibers for visualization on paper. Cellulose 26:5117–5131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02439-4
Qi J, Motwani P, Gheewala M et al (2013) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with monolithic nanoporous gold disk substrates. Nanoscale 5:4105–4109. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr33242f
Reza AT, Nicoll SB (2010) Characterization of novel photocrosslinked carboxymethylcellulose hydrogels for encapsulation of nucleus pulposus cells. Acta Biomater 6:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2009.06.004
Rick SW (2001) Simulations of ice and liquid water over a range of temperatures using the fluctuating charge model. J Chem Phys 114:2276–2283. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1336805
Shin S, Lee J, Lee S et al (2017) A droplet-based high-throughput SERS platform on a droplet-guiding-track-engraved superhydrophobic substrate. Small 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201602865
Shrivastava A, Gupta V (2011) Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron Young Sci 2:21. https://doi.org/10.4103/2229-5186.79345
Šileikaite A, Puišo J, Prosyčevas I, Tamulevičius S (2009) Investigation of silver nanoparticles formation kinetics during reduction of silver nitrate with sodium citrate. Mater Sci 15:21–27
Simpson SL, Quirino JP, Terabe S (2008) On-line sample preconcentration in capillary electrophoresis. Fundamentals and applications. J Chromatogr A 1184:504–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.001
Soylak M, Divrikli U, Saracoglu S, Elci L (2007) Membrane filtration—atomic absorption spectrometry combination for copper, cobalt, cadmium, lead and chromium in environmental samples. Environ Monit Assess 127:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9271-0
Stokes RJ, Macaskill A, Johan Lundahl P et al (2007) Quantitative enhanced raman scattering of labeled DNA from gold and silver nanoparticles. Small 3:1593–1601. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200600662
Sur UK (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 77:338A–346A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac053456d
Tang HR, Covington AD, Hancock RA (2003) Structure-activity relationships in the hydrophobic interactions of polyphenols with cellulose and collagen. Biopolymers 70:403–413. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.10499
Tian ZQ, Ren B, Wu DY (2002) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: from noble to transition metals and from rough surfaces to ordered nanostructures. J Phys Chem B 106:9463–9483. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0257449
Tian L, Jiang Q, Liu KK et al (2016) Bacterial nanocellulose-based flexible surface enhanced raman scattering substrate. Adv Mater Interfaces 3:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201600214
Wang Z, Volinsky AA, Gallant ND (2014) Crosslinking effect on polydimethylsiloxane elastic modulus measured by custom-built compression instrument. J Appl Polym Sci 131:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41050
Wang H, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2016) β-Cyclodextrin modified graphitic carbon nitride for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solution: experimental and theoretical calculation study. J Mater Chem A. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta05958a
Wei D, Chen S, Liu Q (2015) Review of fluorescence suppression techniques in Raman spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc Rev 50:387–406. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2014.999936
Wong SY, Cabodi M, Rolland J, Klapperich CM (2014) Evaporative concentration on a paper-based device to concentrate analytes in a biological fluid. Anal Chem 86:11981–11985. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503751a
Wong SY, Cabodi M, Rolland J et al (2016) Evaporative concentration on a paper-based device to concentrate analytes in a biological fluid. Anal Chem 86:11981–11985. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503751a.Evaporative
Xue L, Steinhart M, **e W et al (2017) Advanced SERS sensor based on capillarity-assisted preconcentration through gold nanoparticle-decorated porous nanorods. Small 13:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201603947
Yang S, Dai X, Stogin BB, Wong T-S (2016) Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:268–273. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1518980113
Yu WW, White IM (2012) A simple filter-based approach to surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for trace chemical detection. Analyst 137:1168–1173. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an15947c
Zhang Q, Chuang KT (2001) Adsorption of organic pollutants from effluents of a Kraft pulp mill on activated carbon and polymer resin. Adv Environ Res 5:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(00)00059-9
Zhang R, Bin XuB, Liu XQ et al (2012) Highly efficient SERS test strips. Chem Commun 48:5913–5915. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc31604h
Zhang L, Li X, Ong L et al (2015) Cellulose nanofibre textured SERS substrate. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 468:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.12.056
Zhang C, You T, Yang N et al (2019) Hydrophobic paper-based SERS platform for direct-droplet quantitative determination of melamine. Food Chem 287:363–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.094
Zhao X-H, Yu L-Y, Chen X-Q et al (2014) Aqueous adsorption and removal of organic contaminants by carbon nanotubes. Sci Total Environ 482–483:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.129
Zhou B, Mao M, Cao X et al (2018) Amphiphilic functionalized acupuncture needle as SERS sensor for in situ multiphase detection. Anal Chem 90:3826–3832. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04348
Zhu Y, Fang Q (2013) Analytical detection techniques for droplet microfluidics—a review. Anal Chim Acta 787:24–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.04.064
Zhu Y, Zhang L, Yang L (2015) Designing of the functional paper-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates for colorants detection. Mater Res Bull 63:199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.12.004
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge support from University of Maine System’s Research Reinvestment Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossen, M.R., Talbot, M.W., Gramlich, W.M. et al. Robust nanofibrillated cellulose composite SERS substrate for capillary preconcentration and trace level detection of organic molecules. Cellulose 27, 10119–10137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03478-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03478-y