Abstract
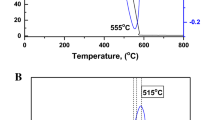
The utilization of bagasse as a raw material to prepare activated carbon adsorbents is an effective way to solve the water pollution problem, while achieving the goal of treating waste simultaneously. An effective activated carbon-based adsorbent was prepared from sugar cane bagasse with a one-step method of pyrolysis and ZnCl2 activation for efficient Cr(VI) removal from water. Morphology, physicochemical properties and structure of the adsorbent samples were studied by Scanning Electron Microscope, Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy, X-ray Diffraction, N2 adsorption and desorption, Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. The batch and fixed bed adsorption experiments were adopted to confirm the one-step preparation of pyrolysis and ZnCl2 during the activation process and to investigate the adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI). The maximum adsorption capacity was 80.880 mg g−1, while the adsorption behavior fitted better with Freundlich equation and pseudo-second-order kinetics. These results confirmed that chemical adsorption is the strongest adsorption interaction during the adsorbing process of Cr(VI), and the adsorbents could effectively capture Cr(VI) to form monodentate and bidentate complexes.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SBET :
-
Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area (m2 g−1)
- Vmic :
-
Micropore volume (cm3 g−1)
- Dp :
-
Average pore diameter (nm)
- C0 :
-
Initial concentration of Cr(VI) (mg L−1)
- Ce :
-
Equilibrium concentration of Cr(VI) (mg L−1)
- qm :
-
Maximum adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) per unit mass of ZBAC (mg g−1)
- w:
-
Weight of the adsorbent (g)
- V:
-
Volume of Cr(VI) solution (L)
- H:
-
Bed height in fixed bed column adsorption
- qt :
-
Amounts of Cr(VI) adsorbed at contact time (mg g−1)
- qe :
-
Amounts of Cr(VI) adsorbed at equilibrium time (mg g−1)
- k1 :
-
Rate constant for first order kinetic (min−1)
- k2 :
-
Rate constant for second order kinetic (g mg−1 min−1)
- k0 :
-
Initial adsorption rate (g mg−1 min−1)
- R2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- K:
-
Langmuir adsorption constant (L mg−1)
- RL :
-
Dimensionless constant separation factor
- kf :
-
Freundlich constant which indicates the adsorption capacity
- n:
-
Freundlich constant which related to the adsorption strength of the adsorbent
- ε:
-
Polanyi potential
- K′:
-
Constant of the adsorption energy (mol2 kJ−2)
- Ki :
-
Rate constant of the intraparticle diffusion (mg g−1 min−1/2)
- E:
-
Adsorption energy (kJ mol−1)
- pHpzc :
-
pH at point of zero charge
References
Acharya J, Sahu JN, Mohanty CR, Meikap BC (2009a) Removal of lead(II) from wastewater by activated carbon developed from Tamarind wood by zinc chloride activation. Chem Eng J 149:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.10.029
Acharya J, Sahu JN, Sahoo BK, Mohanty CR, Meikap BC (2009b) Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater by activated carbon developed from Tamarind wood activated with zinc chloride. Chem Eng J 150:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.11.035
Ahmadpour A, Do DD (1997) The preparation of activated carbon from macadamia nutshell by chemical activation. Carbon 35:1723–1732. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(97)00127-9
Bhattacharya A, Naiya T, Mandal S, Das S (2007) Adsorption, kinetics and equilibrium studies on removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using different low-cost adsorbents. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.05.021
Biniak S, Świątkowski A, Pakuła M, Sankowska M, Kuśmierek K, Trykowski G (2013) Cyclic voltammetric and FTIR studies of powdered carbon electrodes in the electrosorption of 4-chlorophenols from aqueous electrolytes. Carbon 51:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.08.057
Brauer SL, Wetterhahn KE (1991) Chromium(VI) forms a thiolate complex with glutathione. J Am Chem Soc 113:3001–3007. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00008a031
Burg P, Fydrych P, Cagniant D, Nanse G, Bimer J, Jankowska A (2002) The characterization of nitrogen-enriched activated carbons by IR. XPS LSER Methods Carbon 40:1521–1531. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00004-0
Cai Y, Liu C, Lu Y, Luo X, Zeng J (2019) Bagasse-based adsorbent with nitric acid esterification and Fe(iii) chelation for the highly efficient removal of low concentration phosphate from water. New J Chem 43:2966–2973. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj05446k
Chen Y, Wang B, **n J, Sun P, Wu D (2018) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cr(VI) by modified biochar derived from Enteromorpha prolifera. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:440–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.024
Ellis AS, Johnson TM, Bullen TD (2002) Chromium isotopes and the fate of hexavalent chromium in the environment. Science 295:2060–2062
Gottipati R, Mishra S (2016) Preparation of microporous activated carbon from Aegle Marmelos fruit shell and its application in removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous phase. J Ind Eng Chem 36:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.03.005
Guimarães Gusmão KA, Alves Gurgel LV, Sacramento Melo TM, Gil LF (2012) Application of succinylated sugarcane bagasse as adsorbent to remove methylene blue and gentian violet from aqueous solutions—Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Dyes Pigments 92:967–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2011.09.005
Haldorai Y, Voit W, Shim J-J (2014) Nano ZnO@reduced graphene oxide composite for high performance supercapacitor: Green synthesis in supercritical fluid. Electrochim Acta 120:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.12.063
Hamadi NK, Chen XD, Farid MM, Lu MGQ (2001) Adsorption kinetics for the removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorbents derived from used tyres and sawdust. Chem Eng J 84:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1385-8947(01)00194-2
Huang Y, Ma E, Zhao G (2015) Thermal and structure analysis on reaction mechanisms during the preparation of activated carbon fibers by KOH activation from liquefied wood-based fibers. Ind Crops Prod 69:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.03.002
Kalderis D, Bethanis S, Paraskeva P, Diamadopoulos E (2008) Production of activated carbon from bagasse and rice husk by a single-stage chemical activation method at low retention times. Bioresour Technol 99:6809–6816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.041
Kul AR, Koyuncu H (2010) Adsorption of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by native and activated bentonite: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. J Hazard Mater 179:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.009
Kumar A, Mohan Jena H (2015) High surface area microporous activated carbons prepared from Fox nut (Euryale ferox) shell by zinc chloride activation. Appl Surf Sci 356:753–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.074
Luo X, Lei X, Cai N, **e X, Xue Y, Yu F (2016a) Removal of heavy metal ions from water by magnetic cellulose-based beads with embedded chemically modified magnetite nanoparticles and activated carbon. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:3960–3969. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00790
Luo X, Lei X, ** activated bentonite. Carbohydr Polym 151:640–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.003
Luo X, Liu C, Yuan J, Zhu X, Liu S (2017a) Interfacial solid-phase chemical modification with Mannich reaction and Fe(III) chelation for designing lignin-based spherical nanoparticle adsorbents for highly efficient removal of low concentration phosphate from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:6539–6547. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00674
Luo X et al (2017b) Improved solid-phase synthesis of phosphorylated cellulose microsphere adsorbents for highly effective Pb2 + removal from water: batch and fixed-bed column performance and adsorption mechanism. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:5108–5117. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00472
Luo Y, Li D, Chen Y, Sun X, Cao Q, Liu X (2019) The performance of phosphoric acid in the preparation of activated carbon-containing phosphorus species from rice husk residue. J Mater Sci 54:5008–5021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-03220-x
Naeem A, Westerhoff P, Mustafa S (2007) Vanadium removal by metal (hydr)oxide adsorbents. Water Res 41:1596–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.01.002
Pap S, Šolević Knudsen T, Radonić J, Maletić S, Igić SM, Turk Sekulić M (2017) Utilization of fruit processing industry waste as green activated carbon for the treatment of heavy metals and chlorophenols contaminated water. J Clean Prod 162:958–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.083
Peng N et al (2019) Novel dual responsive alginate-based magnetic nanogels for onco-theranostics. Carbohydr Polym 204:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.084
Pitakteeratham N, Hafuka A, Satoh H, Watanabe Y (2013) High efficiency removal of phosphate from water by zirconium sulfate-surfactant micelle mesostructure immobilized on polymer matrix. Water Res 47:3583–3590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.006
Qu R, Feng M, Wang X, Qin L, Wang C, Wang Z, Wang L (2014) Metal accumulation and oxidative stress biomarkers in liver of freshwater fish Carassius auratus following in vivo exposure to waterborne zinc under different pH values. Aquat Toxicol 150:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.02.008
Raveendran K, Ganesh A, Khilar KC (1996) Pyrolysis characteristics of biomass and biomass components. Fuel 75:987–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(96)00030-0
Regmi P, Moscoso JLG, Kumar S, Cao XY, Mao JD, Schafran G (2012) Removal of copper and cadmium from aqueous solution using switchgrass biochar produced via hydrothermal carbonization process. J Environ Manage 109:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.04.047
Sahu UK, Sahu S, Mahapatra SS, Patel RK (2017) Cigarette soot activated carbon modified with Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an effective adsorbent for As(III) and As(V): material preparation, characterization and adsorption mechanism study. J Mol Liq 243:395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.055
Sayğılı H, Güzel F (2016) High surface area mesoporous activated carbon from tomato processing solid waste by zinc chloride activation: process optimization, characterization and dyes adsorption. J Clean Prod 113:995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.055
Shahri FB, Niazi A (2015) Synthesis of modified maghemite nanoparticles and its application for removal of Acridine Orange from aqueous solutions by using Box-Behnken design. J Magn Magn Mater 396:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.08.054
Singh SK, Townsend TG, Mazyck D, Boyer TH (2012) Equilibrium and intra-particle diffusion of stabilized landfill leachate onto micro- and meso-porous activated carbon. Water Res 46:491–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.007
Valix M, Cheung WH, Zhang K (2008) Textural and surface chemistry of activated bagasse and its role in the removal of chromium ions from solution. Adsorption 14:711–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-008-9122-0
Wang L, Zhang J, Zhao R, Li C, Li Y, Zhang C (2010) Adsorption of basic dyes on activated carbon prepared from Polygonum orientale Linn: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 254:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.12.012
**ao H, Peng H, Deng S, Yang X, Zhang Y, Li Y (2012) Preparation of activated carbon from edible fungi residue by microwave assisted K2CO3 activation–application in reactive black 5 adsorption from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 111:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.054
Yang J, Qiu K (2011) Development of high surface area mesoporous activated carbons from herb residues. Chem Eng J 167:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.013
Yang J, Yu M, Chen W (2015) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by activated carbon prepared from longan seed: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. J Ind Eng Chem 21:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.02.054
Zbair M, Anfar Z, Ait Ahsaine H, El Alem N, Ezahri M (2018) Acridine orange adsorption by zinc oxide/almond shell activated carbon composite: operational factors, mechanism and performance optimization using central composite design and surface modeling. J Environ Manag 206:383–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.10.058
Zhang J, Shang T, ** X, Gao J, Zhao Q (2015) Study of chromium(vi) removal from aqueous solution using nitrogen-enriched activated carbon based bamboo processing residues. RSC Adv 5:784–790. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra11016a
Zhang X, Zhang L, Li A (2018) Eucalyptus sawdust derived biochar generated by combining the hydrothermal carbonization and low concentration KOH modification for hexavalent chromium removal. J Environ Manage 206:989–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.079
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51773159, 51303142), the Science and Technology Planning Program of Guangdong (No. 2015A010105018), and Special fund of Guangdong academy of Science (No. 2016GDASPT-0108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Tables S1–S4
: Pseudo-first-order kinetic parameters of Cr(VI) removal; Pseudo-second-order kinetic parameters of Cr(VI) removal; Intraparticle diffusion kinetic parameters of Cr(VI) removal; Constant parameter and correlation coefficients calculated for various adsorption models at different temperatures for Cr(VI). (DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, X., Cai, Y., Liu, L. et al. Cr(VI) adsorption performance and mechanism of an effective activated carbon prepared from bagasse with a one-step pyrolysis and ZnCl2 activation method. Cellulose 26, 4921–4934 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02418-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02418-9