Abstract
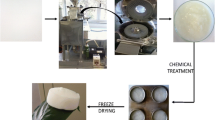
In this study, low density and high porosity aerogels were produced through freeze drying of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) dispersions with 0.6, 0.9 and 1.2 wt% concentration and modified via chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of hexadecyltrimethoxylan (HDTMS) to absorb and remove oil and organic pollutants from the water. Aergels were evaluated by density and porosity measurement, BET analysis, scanning electron microscopy, contact angle, oil absorption capacity and mechanical tests. The densities of unmodified and modified aerogels were in the range of 8.0–13.8 and 11–17.5 mg cm−3, respectively. The porosities of aerogels, before and after modification, were 99.1–99.5 and 98.8–99.3%, respectively. The porous structure formation via successful self assembling of CNF was also evidenced by the scanning electron microscopy images. All of the modified aerogels, regardless of the initial CNF concentration, had contact angle values greater than 90° and were classified as hydrophobic materials. The 0.6% sample revealed the highest adsorption capacities of 78.8 and 162.4 g g−1 for motor and cooking oils, respectively and the 1.2% aerogel exhibited the maximum values of stress and Young’s modulus in compression test. The results of this investigation indicated that ultra-light, hydrophob and superabsorbent materials based on chemically modified cellulosic aerogels with this type of silanated material were successfully produced.
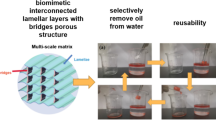
Graphical abstract



(Reproduced with permission from Bordeanu et al. 2010)











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah M, Rahmah AU, Man Z (2010) Physicochemical and sorption characteristics of Malaysian Ceiba pentandra (L.) Gaertn. as a natural oil sorbent. J Hazard Mater 177(1):683–691
Bordeanu N, Eyholzer C, Zimmermann T (2010) Surface modified cellulose nanofibrils. EP2196478 A1, Patent
Cervin NT, Aulin C, Larsson PT, Wågberg L (2012) Ultra porous nanocellulose aerogels as separation medium for mixtures of oil/water liquids. Cellulose 19(2):401–410
Dash R, Li Y, Ragauskas AJ (2012) Cellulose nanowhisker foams by freeze casting. Carbohydr Polym 88(2):789–792
Fan M, Dai D, Huang B (2012) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for natural fibers, chap 3. In: Salih SM (ed) Fourier transform—materials analysis. In Tech. ISBN 978-953-51-0594-7. http://www.intechopen.com/books/fourier-transform-materials-analysis/fourier-transform-infraredspectroscopy-for-natural-fibres
Feng J, Nguyen ST, Fan Z, Duong HM (2015) Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chem Eng J 270:168–175
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Heath L, Thielemans W (2010) Cellulose nanowhisker aerogels. Green Chem 12(8):1448–1453
Jian L, Caichao W, Yun L, Qingfeng S (2014) Fabrication of cellulose aerogel from wheat straw with strong absorptive capacity. Front Agric Sci Eng 1(1):46–52
Jiang F, Hsieh Y-L (2014a) Amphiphilic superabsorbent cellulose nanofibril aerogels. J Mater Chem A 2(18):6337–6342
Jiang F, Hsieh Y-L (2014b) Super water absorbing and shape memory nanocellulose aerogels from TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils via cyclic freezing–thawing. J Mater Chem A 2(2):350–359
Laitinen O, Suopajärvi T, Österberg M, Liimatainen H (2017) Hydrophobic, superabsorbing aerogels from choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent pretreated and silylated cellulose nanofibrils for selective oil removal. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:25029–25037
Nguyen ST, Feng J, Le NT, Le AT, Hoang N, Tan VB, Duong HM (2013) Cellulose aerogel from paper waste for crude oil spill cleaning. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(51):18386–18391
Nguyen ST, Feng J, Ng SK, Wong JP, Tan VB, Duong HM (2014) Advanced thermal insulation and absorption properties of recycled cellulose aerogels. Colloid Surf A 445:128–134
Ozmen N, Çetin NS, Tingaut P, Sèbe G (2007) Transesterification reaction between acetylated wood and trialkoxysilane coupling agents. J Appl Polym Sci 115:570–575
Paralikar SA, Simonsen J, Lombardi J (2008) Poly (vinyl alcohol)/cellulose nanocrystal barrier membranes. J Memb Sci 320:248–258
Rengasamy R, Das D, Karan CP (2011) Study of oil sorption behavior of filled and structured fiber assemblies made from polypropylene, kapok and milkweed fibers. J Hazard Mater 186(1):526–532
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794
Sehaqui H, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2011) High-porosity aerogels of high specific surface area prepared from nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC). Compos Sci Technol 71(13):1593–1599
Tansel B, Pascual B (2011) Removal of emulsified fuel oils from brackish and pond water by dissolved air flotation with and without polyelectrolyte use: pilot-scale investigation for estuarine and near shore applications. Chemosphere 85(7):1182–1186
Wan C, Lu Y, Cao J, Sun Q, Li J (2015) Preparation, characterization and oil adsorption properties of cellulose aerogels from four kinds of plant materials via a NAOH/PEG aqueous solution. Fiber Polym 16(2):302–307
Wang J, Zheng Y, Wang A (2012) Superhydrophobic kapok fiber oil-absorbent: preparation and high oil absorbency. Chem Eng J 213:1–7
Wang J, Zheng Y, Wang A (2013) Coated kapok fiber for removal of spilled oil. Mar Pollut Bull 69(1):91–96
Wu ZY, Li C, Liang HW, Chen JF, Yu SH (2013) Ultralight, flexible, and fire-resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels from bacterial cellulose. Angew Chem-Ger Edit 125(10):2997–3001
Xue Z, Cao Y, Liu N, Feng L, Jiang L (2014) Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J Mater Chem A 2(8):2445–2460
Yang X, Cranston ED (2014) Chemically cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels with shape recovery and superabsorbent properties. Chem Mater 26(20):6016–6025
Yu Y, Wu X, Fang J (2015) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic “sponge-like” aerogels for oil/water separation. J Mater Sci 50(15):5115–5124
Zanini M, Lavoratti A, Lazzari LK, Galiotto D, Pagnocelli M, Baldasso C, Zattera AJ (2017) Producing aerogels from silanized cellulose nanofiber suspension. Cellulose 24(2):769–779
Zhai T, Zheng Q, Cai Z, **a H, Gong S (2016) Synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanofibril hybrid aerogel microspheres and their use as oil/solvent superabsorbents. Carbohydr Polym 148:300–308
Zhang Z, Sèbe G, Rentsch D, Zimmermann T, Tingaut P (2014) Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem Mater 26:2659–2668
Zhou S, Liu P, Wang M, Zhao H, Yang J, Xu F (2016) Sustainable, reusable, and superhydrophobic aerogels from microfibrillated cellulose for highly effective oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(12):6409–6416
Acknowledgments
This article was the result of M.Sc. dissertation approved by the University of Shahreza. The authors wish to acknowledge to the Iranian National Science Foundation for the financial support Research Project # 92043921.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafieian, F., Hosseini, M., Jonoobi, M. et al. Development of hydrophobic nanocellulose-based aerogel via chemical vapor deposition for oil separation for water treatment. Cellulose 25, 4695–4710 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1867-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1867-3