Abstract
The present article demonstrates a simple method for synthesizing the highly stabilized Pd(0) nanoparticles by using supported 12-tungstophosphoric acid as a stabilizer as well as a carrier. The obtained material was characterized by different methods and the presence of nanoparticles on the surface of the carrier was confirmed, especially by TEM and XPS. As an application, the use of material was explored for the well-known fascinating organic transformation, Suzuki–Miyaura cross coupling reaction in aqueous medium as well as in neat H2O. It was found that the material shows an outstanding activity as the heterogeneous catalyst (0.0096 mol% of Pd) for both aqueous medium (99% conversion, TOF 96958 h−1) and in neat H2O (89% conversion, TOF 46390 h−1) towards biphenyl. The catalyst was recovered by filtration only, regenerated and reused without any significant loss in conversion. Study shows that the present catalyst is truly heterogeneous and sustainable for the said reaction, in either of the medium. The viability of the catalyst was learned toward different substrates and found to be excellent in almost all cases.
Graphical Abstract
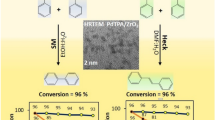
Pd nanoparticles stabilized by supported 12-tungstophosphoric acid is proved to be sustainable and excellent for Suzuki–Miyaura reaction with very high catalyst to substrate ratio as well as TOF.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astruc D, Lu F, Aranzaes JR (2005) Nanoparticles as recyclable catalysts: the frontier between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 44(48):7852–7872
Deshmukh RR, Rajagopal R, Srinivasan KV (2001) Ultrasound promoted C–C bond formation: Heck reaction at ambient conditions in room temperature ionic liquids. Chem Commun 17:1544–1545
Hamill NA, Hardacre C, McMath SEJ (2002) In situ XAFS investigation of palladium species present during the Heck reaction in room temperature ionic liquids. Green Chem 4(2):139–142
Reetz MT, Breinbauer R, Wanninger K (1996) Suzuki and Heck reactions catalyzed by preformed palladium clusters and palladiumnickel bimetallic clusters. Tetrahedron Lett 37(26):4499–4502
Li Y, Hong XM, Collard DM, El-Sayed MA (2000) Suzuki cross-coupling reactions catalyzed by palladium nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Org Lett 2(15):2385–2388
Li Y, Boone E, El-Sayed MA (2002) Size effects of PVP–Pd nanoparticles on the catalytic Suzuki reactions in aqueous solution. Langmuir 18(12):4921–4925
Li Y, El-Sayed MA (2001) The effect of stabilizers on the catalytic activity and stability of Pd colloidal nanoparticles in the Suzuki reactions in aqueous solution†. J Phys Chem B 105(37):8938–8943
Moreno-Mañas M, Pleixats R, Villarroya S (2001) Fluorous phase soluble palladium nanoparticles as recoverable catalysts for Suzuki cross-coupling and Heck reactions. Organometallics 20(22):4524–4528
Strimbu L, Liu J, Kaifer AE (2003) Cyclodextrin-capped palladium nanoparticles as catalysts for the Suzuki reaction. Langmuir 19(2):483–485
Pathak S, Greci MT, Kwong RC, Mercado K, Prakash GKS, Olah GA et al (2000) Synthesis and applications of palladium-coated poly(vinylpyridine) nanospheres. Chem Mater 12(7):1985–1989
Rocaboy C, Gladysz JA (2002) Highly active thermomorphic fluorous palladacycle catalyst precursors for the Heck reaction; evidence for a palladium nanoparticle pathway. Org Lett 4(12):1993–1996
Jana NR, Wang ZL, Pal T (2000) Redox catalytic properties of palladium nanoparticles: surfactant and electron donor–acceptor effects. Langmuir 16(6):2457–2463
Özkar S, Finke RG (2016) Palladium(0) nanoparticle formation, stabilization, and mechanistic studies: Pd(acac)2 as a preferred precursor, [Bu4N]2HPO4 stabilizer, plus the stoichiometry, kinetics, and minimal, four-step mechanism of the palladium nanoparticle formation and subsequent agglomeration reactions. Langmuir 32(15):3699–3716
Veisi H, Faraji AR, Hemmati S, Gil A (2015) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Pistacia atlantica kurdica gum and their catalytic performance in Mizoroki–Heck and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions in aqueous solutions. Appl Organomet Chem 29(8):517–523
Lebaschi S, Hekmati M, Veisi H (2017) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles mediated by black tea leaves (Camellia sinensis) extract: catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction under ligand-free conditions. J Colloid Interface Sci 485:223–231
Veisi H, Mirzaee N (2018) Ligand-free Mizoroki–Heck reaction using reusable modified graphene oxide-supported Pd(0) nanoparticles. Appl Organomet Chem 32(2):e4067
Veisi H, Pirhayati M, Kakanejadifard A (2017) Immobilization of palladium nanoparticles on ionic liquid-triethylammonium chloride functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: as a magnetically separable, stable and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. Tetrahedron Lett 58(45):4269–4276
Farzad E, Veisi H (2018) Fe3O4/SiO2 nanoparticles coated with polydopamine as a novel magnetite reductant and stabilizer sorbent for palladium ions: synthetic application of Fe3O4/SiO2@PDA/Pd for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki reactions. J Ind Eng Chem 60:114–124
Veisi H, Najafi S, Hemmati S (2018) Pd(II)/Pd(0) anchored to magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4) modified with biguanidine-chitosan polymer as a novel nanocatalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. Int J Biol Macromol 113:186–194
Veisi H, Pirhayati M, Kakanejadifard A, Mohammadi P, Abdi MR, Gholami J et al (2018) In situ green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles on tannic acid-modified magnetite nanoparticles as a green reductant and stabilizer agent: its application as a recyclable nanocatalyst (Fe3O4@TA/Pd) for reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki reactions. ChemistrySelect 3(6):1820–1826
Veisi H, Mohammadi Biabri P, Falahi H (2017) l-Arginine as a base and ligand for the palladium-catalyzed C-C and C-N cross-coupling reactions in aqueous media. Tetrahedron Lett 58(35):3482–3486
Veisi H, Nasrabadi NH, Mohammadi P (2016) Biosynthesis of palladium nanoparticles as a heterogeneous and reusable nanocatalyst for reduction of nitroarenes and Suzuki coupling reactions. Appl Organomet Chem 30(11):890–896
Veisi H, Mirshokraie SA, Ahmadian H (2018) Synthesis of biaryls using palladium nanoparticles immobilized on metformine-functionalized polystyrene resin as a reusable and efficient nanocatalyst. Int J Biol Macromol 108:419–425
Heidari F, Hekmati M, Veisi H (2017) Magnetically separable and recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2/isoniazide/Pd nanocatalyst for highly efficient synthesis of biaryls by Suzuki coupling reactions. J Colloid Interface Sci 501:175–184
Kogan V, Aizenshtat Z, Popovitz-Biro R, Neumann R (2002) Carbon–carbon and carbon–nitrogen coupling reactions catalyzed by palladium nanoparticles derived from a palladium substituted keggin-type polyoxometalate. Org Lett 4(20):3529–3532
Zhang J, Keita B, Nadjo L, Mbomekalle IM, Liu T (2008) Self-assembly of polyoxometalate macroanion-capped Pd0 nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Langmuir 24(10):5277–5283
D’Souza L, Noeske M, Richards RM, Kortz U (2013) Palladium (0) metal clusters: novel Krebs type polyoxoanions stabilized, extremely active hydrogenation catalyst. Appl Catal A 453:262–271
Villanneau R, Roucoux A, Beaunier P, Brouri D, Proust A (2014) Simple procedure for vacant POM-stabilized palladium (0) nanoparticles in water: structural and dispersive effects of lacunary polyoxometalates. RSC Adv 4(50):26491–26498
Izumi Y, Tanaka Y, Urabe K (1982) Selective catalytic hydrogenation of, propargyl alcohol with heteropoly acid-modified palladium. Chem Lett 11(5):679–682
Izumi Y, Satoh Y, Kondoh H, Urabe K (1992) Reductive carbonylation of nitrobenzene catalyzed by heteropolyanion-modified palladium. J Mol Catal 72(1):37–46
Liu H, Sun W, Yue B, ** S, Deng J, **e G (1997) Preparation and characterization of keggin type polyoxotungstates containing palladium or iridium. Synth React Inorg Met-Org Chem 27(4):551–566
Maksimov GM, Zaikovskii VI, Matveev KI, Likholobov VA (2000) Preparation of polyoxometalate-stabilized colloidal solutions of palladium metal and catalysts supported on them. Kinet Catal 41(6):844–852
Troupis A, Hiskia A, Papaconstantinou E (2002) Synthesis of metal nanoparticles by using polyoxometalates as photocatalysts and stabilizers. Angew Chem Int Ed 41(11):1911–1914
Kogan V, Aizenshtat Z, Neumann R (2002) Preferential catalytic hydrogenation of aromatic compounds versus ketones with a palladium substituted polyoxometalate as pre-catalyst. New J Chem 26(3):272–274
Mandal S, Das A, Srivastava R, Sastry M (2005) Keggin ion mediated synthesis of hydrophobized Pd nanoparticles for multifunctional catalysis. Langmuir 21(6):2408–2413
De bruyn M, Neumann R (2007) Stabilization of palladium nanoparticles by polyoxometalates appended with alkylthiol tethers and their use as binary catalysts for liquid phase aerobic oxydehydrogenation. Adv Synth Catal 349(10):1624–1628
Keita B, Zhang G, Dolbecq A, Mialane P, Sécheresse F, Miserque F et al (2007) MoV–MoVI mixed valence polyoxometalates for facile synthesis of stabilized metal nanoparticles: electrocatalytic oxidation of alcohols. J Phys Chem C 111(23):8145–8148
Sun M, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Wan H (2009) Polyoxometalate-supported Pd nanoparticles as efficient catalysts for the direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide in the absence of acid or halide promoters. Chem Commun 34:5174–5176
Liu R, Li S, Yu X, Zhang G, Zhang S, Yao J et al (2012) A general green strategy for fabricating metal nanoparticles/polyoxometalate/graphene tri-component nanohybrids: enhanced electrocatalytic properties. J Mater Chem 22(8):3319–3322
Mori K, Furubayashi K, Okada S, Yamashita H (2012) Synthesis of Pd nanoparticles on heteropolyacid-supported silica by a photo-assisted deposition method: an active catalyst for the direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide. RSC Adv 2(3):1047–1054
Rafiee E, Kahrizi M, Joshaghani M, Ghaderi-Sheikhi Abadi P (2016) New strategy by a two-component heterogeneous catalytic system composed of Pd–PVP–Fe and heteropoly acid as co-catalyst for Suzuki coupling reaction. Res Chem Intermed 42(6):5573–5585
He P, Xu B, Xu X, Song L, Wang X (2016) Surfactant encapsulated palladium-polyoxometalates: controlled assembly and their application as single-atom catalysts. Chem Sci 7(2):1011–1015
Patel S, Purohit N, Patel A (2003) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of new solid acid catalysts, H3PW12O40 supported on to hydrous zirconia. J Mol Catal A 192(1):195–202
Bhatt N, Shah C, Patel A (2007) 12-tungstophosphoric and 12-tungstosilicicacid supported onto hydrous zirconia for liquid phase tert-butylation of m-cresol. Catal Lett 117(3):146–152
Pathan S, Patel A (2012) Heck coupling catalyzed by Pd exchanged supported 12-tunstophosphoric acid—an efficient ligand free, low Pd-loading heterogeneous catalyst. RSC Adv 2(1):116–120
Vogel AI, Jeffery GH (1989) Vogel’s textbook of quantitative chemical analysis. Longman, London
Militello MC, Simko SJ (1994) Elemental palladium by XPS. Surf Sci Spectra 3(4):387–394
Röhlich C, Wirth AS, Köhler K (2012) Suzuki coupling reactions in neat water as the solvent: where in the biphasic reaction mixture do the catalytic reaction steps occur? Chem Eur J 18(48):15485–15494
Guan Z, Hu J, Gu Y, Zhang H, Li G, Li T (2012) PdCl2(py)2 encaged in monodispersed zeolitic hollow spheres: a highly efficient and reusable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction in aqueous media. Green Chem 14(7):1964–1970
Zhang L, Su Z, Jiang F, Zhou Y, Xu W, Hong M (2013) Catalytic palladium nanoparticles supported on nanoscale MOFs: a highly active catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Tetrahedron 69(44):9237–9244
Shi Z, Bai X-F (2015) Novel Pd nanocubes supported on activated carbon as a catalyst for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Open Mater Sci J 9:173–177
Isfahani AL, Mohammadpoor-Baltork I, Mirkhani V, Khosropour AR, Moghadam M, Tangestaninejad S et al (2013) Palladium nanoparticles immobilized on nano-silica triazine dendritic polymer (Pdnp-nSTDP): an efficient and reusable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling and Heck reactions. Adv Synth Catal 355(5):957–972
Gholinejad M, Razeghi M, Najera C (2015) Magnetic nanoparticles supported oxime palladacycle as a highly efficient and separable catalyst for room temperature Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction in aqueous media. RSC Adv 5(61):49568–49576
Abbas Khakiani B, Pourshamsian K, Veisi H (2015) A highly stable and efficient magnetically recoverable and reusable Pd nanocatalyst in aqueous media heterogeneously catalysed Suzuki C–C cross-coupling reactions. Appl Organomet Chem 29(5):259–265
Sarvestani M, Azadi R (2016) Palladium nanoparticles deposited on a graphene–benzimidazole support as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for aqueous-phase Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction. Appl Organomet Chem 31(8):e3667
Karimi B, Mansouri F, Vali H (2014) A highly water-dispersible/magnetically separable palladium catalyst based on a Fe3O4@SiO2 anchored TEG-imidazolium ionic liquid for the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction in water. Green Chem 16(5):2587–2596
Borah BJ, Borah SJ, Saikia K, Dutta DK (2014) Efficient Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction in water: stabilized Pdo-montmorillonite clay composites catalyzed reaction. Appl Catal A 469:350–356
Dutt S, Kumar R, Siril PF (2015) Green synthesis of a palladium–polyaniline nanocomposite for green Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions. RSC Adv 5(43):33786–33791
Yang F, Chi C, Dong S, Wang C, Jia X, Ren L et al (2015) Pd/PdO nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes: a highly effective catalyst for promoting Suzuki reaction in water. Catal Today 256:186–192
Ghazali-Esfahani S, Păunescu E, Bagherzadeh M, Fei Z, Laurenczy G, Dyson PJ (2016) A simple catalyst for aqueous phase Suzuki reactions based on palladium nanoparticles immobilized on an ionic polymer. Sci China Chem 59(4):482–486
Sabounchei SJ, Hosseinzadeh M, Panahimehr M, Nematollahi D, Khavasi HR, Khazalpour S (2015) A palladium–phosphine catalytic system as an active and recycable precatalyst for Suzuki coupling in water. Transition Met Chem 40(6):657–663
Miyaura N, Suzuki A (1995) Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organoboron compounds. Chem Rev 95(7):2457–2483
Das P, Linert W (2016) Schiff base-derived homogeneous and heterogeneous palladium catalysts for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Coord Chem Rev 311:1–23
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Board of Research in Nuclear Science (BRNS), Project No. 37(2)/14/34/2014-BRNS, Mumbai, for the financial support. One of the authors Mr. Anish Patel is thankful to the same for the grant of JRF. We are also thankful to Department of Chemistry, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda for BET surface area analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, A., Patel, A. Stabilized Palladium Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Multi-spectroscopic Characterization and Application for Suzuki–Miyaura Reaction. Catal Lett 148, 3534–3547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2559-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2559-1