Abstract
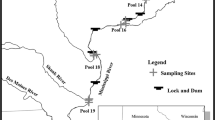
Silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and bighead carp H. nobilis (collectively bigheaded carp) are abundant planktivorous invasive species in North America that negatively affect adult native fishes. It is hypothesized bigheaded carp may also compete with native fish larvae but these potential interactions have not been investigated. We investigated larval freshwater drum Aplodinotus grunniens length-at-age (i.e., growth) across a gradient of adult bigheaded carp relative abundance in the Upper Mississippi River. We sampled fish larvae and zooplankton every 10 days (May–August, 2017 and 2018) from UMR Pools 14-20, collected environmental data from nearby gaging stations, and indexed adult bigheaded carp relative abundance during fall with boat electrofishing. We removed larval freshwater drum otoliths and two independent readers estimated daily ages. We then evaluated the effects of environmental covariates on larval freshwater drum length-at-age using linear mixed-effects models. Larval freshwater drum length-at-age was negatively related to adult bigheaded carp relative abundance and positively associated with water temperature. Negative effects of adult bigheaded carp relative abundance were observed at the 25th and 50th water temperature percentiles but not at the 75th percentile, indicating warmer temperatures may outweigh the effect of bigheaded carp. We did not detect effects of river discharge, larval hatch date, taxa-specific zooplankton abundance, or larval fish abundance on larval freshwater drum length-at-age. Our results indicate adult bigheaded carp abundance and larval freshwater drum length-at-age co-vary, suggesting bigheaded carp abundance can reduce freshwater drum growth during early life stages and may have similar effects on larvae of other fishes with implications for larval survival and recruitment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data used for these analyses can be made available under a reasonable request.
Change history
28 June 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-024-03375-6
References
Auer NA (1982) Identification of larval fishes of the Great Lakes basin with emphasis on the Lake Michigan drainage. Special Pub 82–3. Great Lakes Fishery Commission, Ann Arbor MI
Betsill R, Van Den Avyle M (1997) Effect of temperature and zooplankton abundance on growth and survival of larval threadfin shad. Trans Am Fish Soc 126:999–1011
Bosley TR, Conner JV (1984) Geographic and temporal variation in numbers of myomeres in fish larvae from the lower Mississippi River. Trans Am Fish Soc 113:238–242
Bremigan MT, Stein RA (1994) Gape-dependent larval foraging and zooplankton size: implications for fish recruitment across systems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:913–922
Buijse AD, Houthuijzen RP (1992) Piscivory, growth, and size-selective mortality of age 0 Pikeperch (Stizostedion lucioperca). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49:894–902
Bunnell DB, González MJ, Stein RA (2003) Zooplankton biomass enhances growth, but not survival, of first-feeding Pomoxis spp. larvae. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 60:1314–1323
Burdis RM, Hoxmeier RJH (2011) Seasonal zooplankton dynamics in main channel and backwater habitats of the Upper Mississippi River. Hydrobiologia 667:69–87
Butler RL (1965) Freshwater drum, Aplodinotus grunniens, in the navigational impoundments of the upper Mississippi River. Trans Am Fish Soc 94:339–349
Calkins HA, Tripp SJ, Garvey JE (2012) Linking silver carp habitat selection to flow and phytoplankton in the Mississippi River. Biol Invasions 14:949–958
Carlson BD, Propst D, Synes D (1995) Economic impact of recreation on the Upper Mississippi River System. Technical report EL-95-16. USACE Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, MS
Chick JH, Pegg MA (2001) Invasive carp in the Mississippi River basin. Science 292:2250–2251
Chick JH, Gibson-Reinemer DK, Soeken-Gittinger L et al (2020) Invasive silver carp is empirically linked to declines of native sport fish in the Upper Mississippi River System. Biol Invasions 22:723–734
China V, Levy L, Liberzon A et al (2017) Hydrodynamic regime determines the feeding success of larval fish through the modulation of strike kinematics. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 284:20170235
Claramunt RM, Wahl DH (2000) The effects of abiotic and biotic factors in determining larval fish growth rates: a comparison across species and reservoirs. Trans Am Fish Soc 129:835–851
Collins SC, Wahl DK. 2018. Size-specific effects of bighead carp predation across teh zooplankton size spectra. Freshw Biol 63:700–708
Cooke SL, Hill WR, Meyer KP (2009). Feeding at different plankton densities alters invasive bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) growth and zooplankton species composition. Hydrobiologia 625:185–193
Crecco VA, Savoy TF (1985) Effects of biotic and abiotic factors on growth and relative survival of young American shad, Alosa sapidissima, in the Connecticut River. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:1640–1648
Crowder LB, McDonald ME, Rice JA (1987) Understanding recruitment of Lake Michigan fishes: the importance of size-based interactions between fish and zooplankton. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:141–147
Dettmers JM, Wahl DH, Soluk DA et al (2001) Life in the fast lane: fish and foodweb structure in the main channel of large rivers. J N Am Benthol Soc 20:255–265
Fletcher CM, Collins SF, Nannini MA et al (2019) Competition during early ontogeny: effects of native and invasive planktivores on the growth, survival, and habitat use of Bluegill. Freshw Biol 64:697–707
Frank KT, Leggett WC (1982) Environmental regulation of growth rate, efficiency, and swimming performance in larval Capelin (Mallotus villosus), and its application to the match/mismatch hypothesis. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 39:691–699
Fritts AK, Knights BC, Stanton JC et al (2020) Lock operations influence upstream passages of invasive and native fishes at a Mississippi River high-head dam. Biol Invasions 23:771–794
Garvey JE, Herra TP, Leggett WC (2002) Protracted reproduction in sunfish: the temporal dimension in fish recruitment revisited. Ecol Appl 12:194–205
Ghan D, Sprules W (1993) Diet, prey selection, and growth of larval and juvenile Burbot Lota lota (L.). J Fish Biol 42:47–64
Heyer CJ, Miller TJ, Binkowski FP et al (2001) Maternal effects as a recruitment mechanism in Lake Michigan yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:1477–1487
Houde ED (1987) Fish early life dynamics and recruitment variability. Am Fish Soc Symp 2:17–29
Houde ED (1989) Comparative growth, mortality, and energetics of marine fish larvae: temperature and implied latitudinal effects. Fish Bull 87:471–495
Houde ED (1994) Differences between marine and freshwater fish larvae: implications for recruitment. ICES J Mar Sci 51:91–97
Huss M, Byström P, Persson L (2008) Resource heterogeneity, diet shifts and intra-cohort competition: effects on size divergence in YOY fish. Oecologia 158:249–257
Irons KS, Sass G, McClelland M et al (2007) Reduced condition factor of two native fish species coincident with invasion of non-native Asian carps in the Illinois River, USA. Is this evidence for competition and reduced fitness? J Fish Biol 71:258–273
Jacquemin SJ, Doll JC, Pyron M et al (2014) Effects of flow regime on growth rate in freshwater drum, Aplodinotus grunniens. Environ Biol Fishes 98:993–1003
Kamimura Y, Takahashi M, Yamashita N et al (2015) Larval and juvenile growth of Chub Mackerel Scomber japonicus in relation to recruitment in the western North Pacific. Fish Sci 81:505–513
Ludsin SA, DeVries DR (1997) First-year recruitment of largemouth bass: the interdependence of early life stages. Ecol Appl 7:1024–1038
Ludsin SA, DeVanna KM, Smith RE (2014) Physical–biological coupling and the challenge of understanding fish recruitment in freshwater lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 71:775–794
Miller TJ, Crowder LB, Rice JA et al (1988) Larval size and recruitment mechanisms in fishes: toward a conceptual framework. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:1657–1670
Mion JB, Stein RA, Marschall EA (1998) River discharge drives survival of larval walleye. Ecol Appl 8:88–103
Nunn A, Harvey J, Cowx I (2007a) The food and feeding relationships of larval and 0+ year juvenile fishes in lowland rivers and connected waterbodies. I. Ontogenetic shifts and interspecific diet similarity. J Fish Biol 70:726–742
Nunn A, Harvey J, Cowx I (2007b) The food and feeding relationships of larval and 0+ year juvenile fishes in lowland rivers and connected waterbodies. II. Prey selection and the influence of gape. J Fish Biol 70:743–757
Opuszyński K (1981) Comparison of the usefulness of the silver carp and the bighead carp as additional fish in carp ponds. Aquaculture 25:223–233
Opuszynski K, Shireman JV, Cichra CE (1991) Food assimilation and filtering rate of bighead carp kept in cages. Hydrobiologia 220:49–56
Partridge DG, DeVries DR (1999) Regulation of growth and mortality in larval Bluegills: implications for juvenile recruitment. Trans Am Fish Soc 128:625–638
Pendleton RM, Schwinghamer C, Solomon LE et al (2017) Competition among river planktivores: are native planktivores still fewer and skinnier in response to the silver carp invasion? Environ Biol Fishes 100:1213–1222
Phelps QE, Tripp SJ, Bales KR et al (2017) Incorporating basic and applied approaches to evaluate the effects of invasive Asian Carp on native fishes: a necessary first step for integrated pest management. PLoS ONE 12:e0184081
Post DM (2003) Individual variation in the timing of ontogenetic niche shifts in largemouth bdass. Ecology 84:1298–1310
Post JR, Prankevicius AB (1987) Size-selective mortality in young-of-the-year yellow perch (Perca flavescens): evidence from otolith microstructure. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:1840–1847
Rutherford ES, Houde ED (1995) The influence of temperature on cohort-specific growth, survival, and recruitment of Striped Bass, Morone saxatilis, larvae in Chesapeake Bay. Fish Bull 93:315–332
Rutherford DA, Kelso WE, Bryan CF et al (1995) Influence of physicochemical characteristics on annual growth increments of four fishes from the lower Mississippi River. Trans Am Fish Soc 124:687–697
Rypel AL (2007) Sexual dimorphism in growth of freshwater drum. Southeast Nat 6:333–342
Sampson SJ, Chick JH, Pegg MA (2009) Diet overlap among two Asian carp and three native fishes in backwater lakes on the Illinois and Mississippi rivers. Biol Invasions 11:483–496
Sass GG, Cook TR, Irons KS et al (2010) A mark-recapture population estimate for invasive silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in the La Grange Reach, Illinois River. Biol Invasions 12:433–436
Schael DM, Rudstam LG, Post JR (1991) Gape limitation and prey selection in larval yellow Perch (Perca flavescens), freshwater drum (Aplodinotus grunniens), and Black Crappie (Pomoxis nigromaculatus). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48:1919–1925
Siefert RE (1972) First food of larval Yellow Perch, White Sucker, Bluegill, Emerald Shiner, and Rainbow Smelt. Trans Am Fish Soc 101:219–225
Sietman BE, Hove MC, Davis JM (2018) Host attraction, brooding phenology, and host specialization on freshwater drum by 4 freshwater mussel species. Freshw Sci 37:96–107
Sogard SM (1997) Size-selective mortality in the juvenile stage of teleost fishes: a review. Bull Mar Sci 60:1129–1157
Solomon LE, Pendleton RM, Chick JH et al (2016) Long-term changes in fish community structure in relation to the establishment of Asian carps in a large floodplain river. Biol Invasions 18:2883–2895
Sullivan CJ, Camacho CA, Weber MJ, Pierce CL (2017) Intra-annual variability of Silver Carp populations in the Des Moines River, USA. North Am J Fish Manag 37:836–849
Tillotson NT, Weber MJ, Pierce CL (2022) Zooplankton community dynamics along the bigheaded carp invasion front in the Upper Mississippi River. Hydrobiologia 849:1659–1675
Tillotson NT, Weber MJ, Pierce CL (2023) Effects of bigheaded carp on larval Freshwater Drum diets. Trans Am Fish Soc 152:530–549
Tripp S, Brooks R, Herzog D et al (2014) Patterns of fish passage in the Upper Mississippi River. River Res Appl 30:1056–1064
Turner TF, Trexler JC, Miller GL et al (1994) Temporal and spatial dynamics of larval and juvenile fish abundance in a temperate floodplain river. Copeia 1:174–183
Vilizzi L, Tarkan AS, Copp GH (2015) Experimental evidence from causal criteria analysis for the effects of common carp Cyprinus carpio on freshwater ecosystems: a global perspective. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 23:253–290
Weber MJ, Brown ML (2009) Effects of common carp on aquatic ecosystems 80 years after “carp as a dominant”: ecological insights for fisheries management. Rev Fish Sci 17:524–537
Weber MJ, Brown ML (2011) Relationships among invasive common carp, natives fishes, and physicochemical characteristics in upper Midwest (USA) lakes. Ecol Freshw Fish 20:270–278
Weber MJ, Dettmers JM, Wahl DH (2011) Growth and survival of age-0 Yellow Perch across habitats in southwestern Lake Michigan: early life history in a large freshwater environment. Trans Am Fish Soc 140:1172–1185
Weber MJ, Ruebush BC, Creque SM et al (2015) Early life history of Alewife Alosa pseudoharengus in southwestern Lake Michigan. J Great Lakes Res 41:436–447
Welker MT, Pierce CL, Wahl DH (1994) Growth and survival of larval fishes: roles of competition and zooplankton abundance. Trans Am Fish Soc 123:703–717
Werner EE, Gilliam JF (1984) The ontogenetic niche and species interactions in size-structured populations. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 15:393–425
Withers JL, Sesterhenn TM, Foley CJ et al (2015) Diets and growth potential of early stage larval Yellow Perch and Alewife in a nearshore region of southeastern Lake Michigan. J Great Lakes Res 41:197–209
Acknowledgements
Partial funding for this project was provided by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources, US Fish and Wildlife Service, and US Geological Survey. We thank the numerous technicians for their time spent assisting with larval fish and zooplankton sample collection and processing. We also thank P. Dixon for his consultation on the analyses for this study and the staff of the Kibbe Field Station for periodically housing us when we conducted sampling events.
Funding
This work was supported by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources, US Fish and Wildlife Service, and US Geological Survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M Weber conceived, designed, and secured financial support for the study. N Tillotson collected and processed data in the field and laboratory. N Tillotson and M Weber analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. M Weber and C Pierce reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised due to the author's name Clay L. Pierce was incorrectly written as Clay L. Piercev.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tillotson, N.A., Weber, M.J. & Pierce, C.L. Effects of invasive bigheaded carp and environmental factors on larval fish growth. Biol Invasions (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-024-03335-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-024-03335-0