Abstract
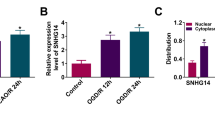
Stroke is a cerebrovascular disease with impaired nerve function. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is considered to be an important regulator of various diseases. Nevertheless, the role of lncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15) in cerebral ischemia injury induced by stroke is still unclear. Cell-counting kit 8 assay and flow cytometry were used to detect cell viability and apoptosis, respectively. The caspase3 activity of cells was measured using Caspase3 Activity Assay Kit. Besides, the protein levels of apoptosis markers and TCCD-induced poly (ADP)-ribose polymerase (TIPARP) were determined using western blot analysis. Moreover, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was employed to examine the relative expression of SNHG15 and miR-9-5p. Furthermore, dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to assess the interaction between miR-9-5p and SNHG15 or TIPARP. In addition, biotin-labeled RNA pull-down assay was performed to evaluate the interaction between miR-9-5p and SNHG15 further. Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was constructed to further explore the role of SNHG15 in neuronal injury in vivo. Our data showed that oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) could induce N-2a cell injury and enhance SNHG15 expression. Silenced SNHG15 could promote the viability and suppress the apoptosis of OGD-induced N-2a cells. Also, SNHG15 knockdown also could alleviate the neuronal injury of MCAO mice. Mechanistically, SNHG15 could sponge miR-9-5p, and miR-9-5p could target TIPARP. Further experiments revealed that miR-9-5p inhibition or TIPARP overexpression could reverse the suppressive effect of SNHG15 knockdown on OGD-induced N-2a cell injury. Our findings indicated that SNHG15 knockdown inhibited neuronal injury through the miR-9-5p/TIPARP axis, suggesting that SNHG15 might be a potential target for cerebral ischemia injury induced by stroke.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Abbreviations
- SNHG15:
-
Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 15
- TIPARP:
-
TCCD-induced Poly (ADP)-Ribose Polymerase
- OGD:
-
Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation
- MCAO:
-
Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
References
Akella A, Bhattarai S, Dharap A (2019) Long noncoding RNAs in the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. Neuromolecular Med 21:474–483
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling FN, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Ferguson JF, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Lutsey PL, Mackey JS, Matchar DB, Matsushita K, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, O’Flaherty M, Palaniappan LP, Pandey A, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Ritchey MD, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sampson UKA, Satou GM, Shah SH, Spartano NL, Tirschwell DL, Tsao CW, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P, American Heart Association Council on E, Prevention Statistics C, Stroke Statistics S (2018) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 137:e67–e492
Bernhardt J, Zorowitz RD, Becker KJ, Keller E, Saposnik G, Strbian D, Dichgans M, Woo D, Reeves M, Thrift A, Kidwell CS, Olivot JM, Goyal M, Pierot L, Bennett DA, Howard G, Ford GA, Goldstein LB, Planas AM, Yenari MA, Greenberg SM, Pantoni L, Amin-Hanjani S, Tymianski M (2018) Advances in stroke 2017. Stroke 49:e174–e199
Chen S, Wang M, Yang H, Mao L, He Q, ** H, Ye ZM, Luo XY, **a YP, Hu B (2017) LncRNA TUG1 sponges microRNA-9 to promote neurons apoptosis by up-regulated Bcl2l11 under ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 485:167–173
Chen F, Zhang L, Wang E, Zhang C, Li X (2018) LncRNA GAS5 regulates ischemic stroke as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-137 to regulate the Notch1 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 496:184–190
Chen Y, Lin Y, Bai Y, Cheng D, Bi Z (2019) A long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-associated competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network identifies eight lncRNA biomarkers in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Med Sci Monit 25:2058–2065
Chi L, Jiao D, Nan G, Yuan H, Shen J, Gao Y (2019) miR-9–5p attenuates ischemic stroke through targeting ERMP1-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Acta Histochem 121:151438
Cucchiara B, George DK, Kasner SE, Knutsson M, Denison H, Ladenvall P, Amarenco P, Johnston SC (2019) Disability after minor stroke and TIA: a secondary analysis of the SOCRATES trial. Neurology 93:e708–e716
Deng QW, Li S, Wang H, Sun HL, Zuo L, Gu ZT, Lu G, Sun CZ, Zhang HQ, Yan FL (2018) Differential long noncoding RNA expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for detection of acute ischemic stroke. Clin Sci (lond) 132:1597–1614
Han B, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Chen X, Huang R, Wu F, Leng S, Chao J, Zhang JH, Hu G, Yao H (2018) Novel insight into circular RNA HECTD1 in astrocyte activation via autophagy by targeting MIR142-TIPARP: implications for cerebral ischemic stroke. Autophagy 14:1164–1184
Langhammer B, Sunnerhagen KS, Sallstrom S, Becker F, Stanghelle JK (2018) Return to work after specialized rehabilitation—an explorative longitudinal study in a cohort of severely disabled persons with stroke in seven countries: the Sunnaas International Network stroke study. Brain Behav 8:e01055
Ma Q, Baldwin KT, Renzelli AJ, McDaniel A, Dong L (2001) TCDD-inducible poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: a novel response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:499–506
Mortality GBD, Causes of Death C (2016) Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388:1459–1544
Nakamura K, Shichita T (2019) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of sterile inflammation in ischaemic stroke. J Biochem 165:459–464
Nampoothiri SS, Rajanikant GK (2019) miR-9 upregulation integrates post-ischemic neuronal survival and regeneration in vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39:223–240
Parrella E, Porrini V, Benarese M, Pizzi M (2019) The role of mast cells in stroke. Cells 8:437
Qiu Z, Wang K, Jiang C, Su Y, Fan X, Li J, Xue S, Yao L (2020) Trigonelline protects hippocampal neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury through activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Chem Biol Interact 317:108946
Ross S, Pare G (2018) Pharmacogenetics of stroke. Stroke 49:2541–2548
Shuai Y, Ma Z, Lu J, Feng J (2020) LncRNA SNHG15: a new budding star in human cancers. Cell Prolif 53:e12716
Tian T, Zeng J, Zhao G, Zhao W, Gao S, Liu L (2018) Neuroprotective effects of orientin on oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced cell injury in primary culture of rat cortical neurons. Exp Biol Med (maywood) 243:78–86
Tiedt S, Dichgans M (2018) Role of non-coding RNAs in stroke. Stroke 49:3098–3106
Tong J, Ma X, Yu H, Yang J (2019) SNHG15: a promising cancer-related long noncoding RNA. Cancer Manag Res 11:5961–5969
Vyas S, Matic I, Uchima L, Rood J, Zaja R, Hay RT, Ahel I, Chang P (2014) Family-wide analysis of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity. Nat Commun 5:4426
Wang SW, Liu Z, Shi ZS (2018a) Non-coding RNA in acute ischemic stroke: mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cell Transplant 27:1763–1777
Wang Y, Li G, Zhao L, Lv J (2018b) Long noncoding RNA HOTTIP alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal injury via modulating miR-143/hexokinase 2 pathway. J Cell Biochem 119:10107–10117
Wang LX, Wan C, Dong ZB, Wang BH, Liu HY, Li Y (2019) Integrative analysis of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), microRNA (miRNA) and mRNA expression and construction of a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network in metastatic melanoma. Med Sci Monit 25:2896–2907
Wang H, Zheng X, ** J, Zheng L, Guan T, Huo Y, **e S, Wu Y, Chen W (2020) LncRNA MALAT1 silencing protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through miR-145 to regulate AQP4. J Biomed Sci 27:40
Wu F, Han B, Wu S, Yang L, Leng S, Li M, Liao J, Wang G, Ye Q, Zhang Y, Chen H, Chen X, Zhong M, Xu Y, Liu Q, Zhang JH, Yao H (2019) Circular RNA TLK1 aggravates neuronal injury and neurological deficits after ischemic stroke via miR-335-3p/TIPARP. J Neurosci 39:7369–7393
Yuze C, Huixue Z, **aoyu L, Jianjian W, **aoming Z, Shengnan S, Zhonglei B, Wenqi T, Shangwei N, Lihua W, Liying C (2020) Overexpression of microRNA-9a-5p ameliorates NLRP1 inflammasome-mediated ischemic injury in rats following ischemic stroke. Neuroscience 444:106–117
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
This work was funded by Yancheng Development Project of Medical Science and Technology in 2020 (YK2020061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2021_10121_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 1 Selection of candidate miRNA for SNHG15 and candidate targets for miR-9-5p. (A) Biotin-labeled RNA pull-down assay was used to analyze the enrichment of each candidate miRNA in SNHG15 probe and Oligo probe. (B) The mRNA expression was measured by qRT-PCR in N-2a cells transfected with miR-9-5p mimic or miR-NC. ***P < 0.001. Supplementary file1 (TIF 210 KB)
10528_2021_10121_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 2 Effect of SNHG15 knockdown on neuronal injury. (A) The expression of SNHG15 in the brain tissues of each group was measured by qRT-PCR. (B) Infarct volume of each group was assessed. (C) Longa scoring system was used to analyze the neurological scores. (D) The expression of miR-9-5p in the brain tissues of each group was determined by qRT-PCR. (E) TIPARP protein expression in the brain tissues of each group was detected by WB analysis. **P < 0.01. Supplementary file2 (TIF 409 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, B., Wang, L., Xu, Y. et al. Knockdown of lncRNA SNHG15 Ameliorates Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation (OGD)-Induced Neuronal Injury via Regulating the miR-9-5p/TIPARP Axis. Biochem Genet 60, 755–769 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10121-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10121-3