Abstract
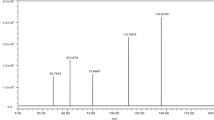
A simple and rapid reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous separation and determination of erlotinib, an antineoplastic agent, which is used in the therapy of advanced or metastatic pancreatic or non-small cell lung cancer, and its metabolites has been developed. This method has been applied to urine and serum samples of patients under erlotinib treatment. After a dilution step, erlotinib and its metabolites have been separated on an Ultrabase 120 Å C18 column (4.6 mm i.d. × 150 mm, 5 μm) using methanol: 20 mM phosphate buffer pH 5.0 (60:40; v:v) as mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.4 mL min−1 and detected at 248 nm with a diode array detector. The limits of detection were between 2.1 and 5.1 ng mL−1. Within- and between-day accuracy and precision of the validated method were below the acceptable limits of 15% relative standard deviation at all concentrations tested. The quantitation method was successfully applied for the simultaneous determination of erlotinib and its metabolites in urine and serum samples from patients under clinical treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. The concentration ranges of erlotinib and desmethyl erlotinib in serum were 380–6510 and 66–558 ng mL−1, respectively, in patients under treatment. The objective is to propose a fast and simple method for a direct and reliable quantification of erlotinib and its metabolites in human urine and serum without previous sample treatment steps. The direct injection of diluted urine and serum can be highlighted as the greatest advantage that can be achieved by this method.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grunwald V, Hidalgo M (2002) The epidermal growth factor receptor: a new target for anticancer therapy. Curr Probl Cancer 26:109–164
American Society of Clinical Oncology (1997) Clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of unresectable nonsmall-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 15:2996–3018
Baselga J, Hammond LA (2002) HER-targeted tyrosinekinase inhibitors. Oncology 63(Suppl 1):6–16
Hidalgo M, Siu LL, Nemunaitis J (2001) Phase I and pharmacologic study of OSI-774, an epidermalgrowth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 19:3267–3279
Hidalgo M, Bloedow D (2003) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: maximizing the clinical potentialof erlotinib (Tarceva). Semin Oncol 303(Suppl 7):25–33
Birner A (2003) Pharmacology of oral chemotherapy agents. Clin J Oncol Nurs 7:11–19
Abbas R, Fettner S, Riek M (2003) A drug–drug interaction study to evaluate the effect of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of the EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib, in healthy subjects. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:137
Zielinski SL (2004) Tarceva wins approval from FDA. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1811
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanul T (2005) Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353:123–132
Ling J, Johnson KA, Miao Z, Rakhit A, Pantze MP, Hamilton M, Lum BL, Prakash C (2006) Metabolism and excretion of erlotinib, a small molecule inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in healthy male volunteers. Drug Metab Dispos 34:420–426
Zhanga W, Siub LL, Moorea MJ, Chenb EX (2005) Simultaneous determination of OSI-774 and its major metabolite OSI-420 in human plasma by using HPLC with UV detection. J Chromatogr B 814:143–147
Faivrea L, Gomoa C, Mirb O, Taieba F, Schoemann-Thomasa A, Ropertb S, Vidala M, Dusserd D, Dauphina A, Goldwasserb F, Blanchet B (2011) A simple HPLC-UV method for the simultaneous quantification of gefitinib and erlotinib in human plasma. J Chromatogr B 879:2345–2350
Lepper ER, Swain SM, Tan AR, Figg WD, Sparreboom A (2003) Liquid-chromatographic determination of erlotinib (OSI-774), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J Chromatogr B 796:181–188
Dziadosza M, Lessiga R, Bartelsa H (2012) HPLC-DAD protein kinase inhibitor analysis in human serum. J Chromatogr B 893–894:77–81
Masters AR, Sweeney CJ, Jones DJ (2007) The quantification of erlotinib (OSI-774) and OSI-420 in human plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 848:379–383
Zhaoa M, Hea P, Rudekb MA, Hidalgo M, Baker SD (2003) Specific method for determination of OSI-774 and its metabolite OSI-420 in human plasma by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 793:413–420
Ishida T, Naito J, Kawakami J (2015) Simultaneous determination of erlotinib and its isomeric major metabolites in human plasma using isocratic liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and its clinical application. Chromatography 29:643–646
Honeywella R, Yarzadaha K, Giovannettia E, Losekoota N, Smitb EF, Walravena M, Lindb JSW, Tibaldic C, Verheula HM, Petersa GJ (2010) Simple and selective method for the determination of various tyrosine kinase inhibitors used in the clinical setting by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 878:1059–1068
Bouchet S, Chauzit E, Ducint D, Castaing N, Canal-Raffin M, Moore N, Titier K, Molimard M (2011) Simultaneous determination of nine tyrosine kinase inhibitors by 96-well solid-phase extraction and ultra performance LC/MS-MS. Clin Chim Acta 412:1060–1067
Gotze L, Hegele A, Metzelder SK, Renz H, Nockher WA (2012) Development and clinical application of a LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of various tyrosine kinase inhibitors in human plasma. Clin Chim Acta 413:143–149
Rodriguez J, Castañeda G, Muñoz L, Navarro D, Villa JC (2014) Simultaneous determination of erlotinib and metabolites in human urine using capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 35:1489–1495
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Ministerio of Competitividad of Spain for financial support of this work (CTQ 2016-78793-P).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All human urine and serum samples used in this study were obtained after the subjects gave written informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, J., Castañeda, G., Muñoz, L. et al. Simultaneous Determination of Erlotinib and its Metabolites in Human Urine and Serum Samples by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chromatographia 80, 409–415 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3258-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-017-3258-6