Abstract
Objective
Conventional single-echo spin-echo T2 map** used for liver iron quantification is too long for breath-holding. This study investigated a short TR (~100 ms) single-echo spin-echo T2 map** technique wherein each image (corresponding to a single TE) could be acquired in ~17 s–short enough for a breath-hold. TE images were combined for T2 fitting. To avoid T1 bias, each TE acquisition incremented TR to maintain a constant TR-TE.
Materials and methods
Experiments at 1.5T validated the technique’s accuracy in phantoms, 9 healthy volunteers, and 5 iron overload patients. In phantoms and healthy volunteers, the technique was compared to the conventional approach of constant TR for all TEs. Iron overload results were compared to FerriScan.
Results
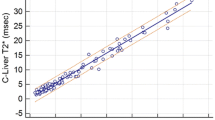
In phantoms, the constant TR-TE technique provided unbiased estimates of T2, while the conventional constant TR approach underestimated it. In healthy volunteers, there was no significant discrepancy at the 95% confidence level between constant TR-TE and reference T2 values, whereas there was for constant TR scans. In iron overload patients, there was a high correlation between constant TR-TE and FerriScan T2 values (r2 = 0.95), with a discrepancy of 0.6+/− 1.4 ms.
Discussion
The short-TR single-echo breath-hold spin-echo technique provided unbiased estimates of T2 in phantoms and livers.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Due to privacy concerns, data is not publicly available.
References
Olivieri NF, Brittenham GM (1997) Iron-chelating therapy and the treatment of thalassemia. Blood 89(3):739–761
Hernando D, Levin YS, Sirlin CB, Reeder SB (2014) Quantification of Liver Iron With MRI: State of the Art and Remaining Challenges. J Magn Reson Imaging 40(5):1003–1021
Runge JH, Akkerman EM, Troelstra MA, Nederveen AJ, Beuers U, Stoker J (2016) Comparison of clinical MRI liver iron content measurements using signal intensity ratios, R (2) and R (2)*. Abdom Radiol 41(11):2123–2131
Wood JC, Enriquez C, Ghugre N, Tyzka JM, Carson S, Nelson MD, Coates TD (2005) MRI R2 and R2* map** accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients. Blood 106(4):1460–1465
Jhaveri KS, Kannengiesser SAR, Ward R, Kuo K, Sussman MS (2019) Prospective Evaluation of an R2*Method for Assessing Liver Iron Concentration (LIC) Against FerriScan: Derivation of the Calibration Curve and Characterization of the Nature and Source of Uncertainty in the Relationship. J Magn Reson Imaging 49(5):1467–1474
St Pierre TG, Clark PR, Chua-Anusorn W, Fleming AJ, Jeffrey GP, Olynyk JK, Pootrakul P, Robins E, Lindeman R (2005) Noninvasive measurement and imaging of liver iron concentrations using proton magnetic resonance. Blood 105(2):855–861
Sharma SD, Hernando D, Horng DE, Reeder SB (2015) Quantitative susceptibility map** in the abdomen as an imaging biomarker of hepatic iron overload. Magn Reson Med 74(3):673–683
Clark PR, Chua-anusorn W, St Pierre TG (2004) Reduction of respiratory motion artifacts in transverse relaxation rate (R-2) images of the liver. Comput Med Imaging Graph 28(1–2):69–76
Pavitt HL, Aydinok Y, El-Beshlawy A, Bayraktaroglu S, Ibrahim AS, Hamdy MM, Pang WJ, Sharples C, St Pierre TG (2011) The Effect of Reducing Repetition Time TR on the Measurement of Liver R2 for the Purpose of Measuring Liver Iron Concentration. Magn Reson Med 65(5):1346–1351
Sussman MS, Vidarsson L, Pauly JM, Cheng HLM (2010) A Technique for Rapid Single-Echo Spin-Echo T(2) Map**. Magn Reson Med 64(2):536–545
Henninger B, Kremser C, Rauch S, Eder R, Zoller H, Finkenstedt A, Michaely HJ, Schocke M (2012) Evaluation of MR imaging with T1 and T2*map** for the determination of hepatic iron overload. Eur Radiol 22(11):2478–2486
Banerjee R, Pavlides M, Tunnicliffe EM, Piechnik SK, Sarania N, Philips R, Collier JD, Booth JC, Schneider JE, Wang LM, Delaney DW, Fleming KA, Robson MD, Barnes E, Neubauer S (2014) Multiparametric magnetic resonance for the non-invasive diagnosis of liver disease. J Hepatol 60(1):69–77
Tofts PS (2003) Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Measuring Changes Caused by Disease. Wiley, Chichester, West Sussex
Tofts PS, Shuter B, Pope JM (1993) NI-DTPA DOPED AGAROSE-GEL - A PHANTOM MATERIAL FOR GD-DTPA ENHANCEMENT MEASUREMENTS. Magn Reson Imaging 11(1):125–133
Gudbjartsson H, Patz S (1995) THE RICIAN DISTRIBUTION OF NOISY MRI DATA. Magn Reson Med 34(6):910–914
Taylor JR (1982) Taylor JR (1982) An Introduction to Error Analysis: The Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements A Series of Books in Physics. University Science Books, Mill Valley, California
Clark PR, Chua-anusorn W, Pierre TGS (2003) Bi-exponential proton transverse relaxation rate (R2) image analysis using RF field intensity-weighted spin density projection: potential for R2 measurement of iron-loaded liver. Magn Reson Imaging 21(5):519–530
St Pierre TG, Clark PR, Chua-anusorn W (2004) Single spin-echo proton transverse relaxometry of iron-loaded liver. NMR Biomed 17(7):446–458
Bencikova D, Han F, Kannengieser S, Raudner M, Poetter-Lang S, Bastati N, Reiter G, Ambros R, Ba-Ssalamah A, Trattnig S, Krssak M (2022) Evaluation of a single-breath-hold radial turbo-spin-echo sequence for T2 map** of the liver at 3T. Eur Radiol 32(5):3388–3397
Idilman IS, Celik A, Savas B, Idilman R, Karcaaltincaba M (2021) The feasibility of T2 map** in the assessment of hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a preliminary study. Clin Radiol 76(9):709
Hennig J, Weigel M, Scheffler K (2003) Multiecho sequences with variable refocusing flip angles: Optimization of signal behavior using smooth transitions between pseudo steady states (TRAPS). Magn Reson Med 49(3):527–535
Brittain J, Hu BS, Wright GA, Meyer CH, Macovski A, Nishimura DG (1995) Coronary Angiography with Magnetization-Prepared T2 Contrast. Magn Reson Med 33:689–696
Cassinotto C, Feldis M, Vergniol J, Mouries A, Cochet H, Lapuyade B, Hocquelet A, Juanola E, Foucher J, Laurent F, De Ledinghen V (2015) MR relaxometry in chronic liver diseases: Comparison of T1 map**, T2 map**, and diffusion-weighted imaging for assessing cirrhosis diagnosis and severity. Eur J Radiol 84(8):1459–1465
Foltz W, Al-Kwifi O, Sussman MS, Stainsby JA, Wright GA (2003) Optimized Spiral Imaging for Measurement of Myocardial T2 Relaxation. Magn Reson Med 49(6):1089–1097
Jaubert O, Arrieta C, Cruz G, Bustin A, Schneider T, Georgiopoulos G, Masci P-G, Sing-Long C, Botnar RM, Prieto C (2020) Multi-parametric liver tissue characterization using MR fingerprinting: Simultaneous T1, T2, T2*, and fat fraction map**. Magn Reson Med 84(5):2625–2635
Garbowski MW, Carpenter JP, Smith G, Roughton M, Alam MH, He TG, Pennell DJ, Porter JB (2014) Biopsy-based calibration of T2*magnetic resonance for estimation of liver iron concentration and comparison with R2 Ferriscan. J Cardiov Magn Reson. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-16-40
Ghugre NR, Coates TD, Nelson MD, Wood JC (2005) Mechanisms of tissue-iron relaxivity: Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of human liver biopsy specimens. Magn Reson Med 54(5):1185–1193
Doyle EK, Thornton S, Toy KA, Powell AJ, Wood JC (2021) Improving CPMG liver iron estimates with a T-1-corrected proton density estimator. Magn Reson Med 86(6):3348–3359
Jensen JH, Chandra R (2002) Theory of nonexponential NMR signal decay in liver with iron overload or superparamagnetic iron oxide particles. Magn Reson Med 47(6):1131–1138
Wang CQ, Reeder SB, Hernando D (2021) Relaxivity-iron calibration in hepatic iron overload: Reproducibility and extension of a Monte Carlo model. NMR Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4604
Sussman MS A Simple Method for Increasing the Number of Echoes and Decreasing Echo Spacing in T2 Spectrum Analysis. In: ISMRM 19th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Montreal, Quebec, 2011. p 2752.
Wei Z, Ma YJ, Jang H, Yang WH, Du J (2020) To measure T-1 of short T-2 species using an inversion recovery prepared three-dimensional ultrashort echo time (3D IR-UTE) method: A phantom study. J Magn Reson 314:106725
Sussman MS, Lindner U, Haider M, Kucharczyk W, Hlasny E, Trachtenberg J (2013) Optimizing contrast agent concentration and spoiled gradient echo pulse sequence parameters for catheter visualization in MR-guided interventional procedures: An analytic solution. Magn Reson Med 70(2):333–340
Erden A, Oz DK, Peker E, Kul M, Ates FSO, Erden I, Idilman R (2021) MRI quantification techniques in fatty liver: the diagnostic performance of hepatic T1, T2, and stiffness measurements in relation to the proton density fat fraction. Diagn Interv Radiol 27(1):7–14
Funding
Funding for this study was generously provided by GE Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S: Study conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting of manuscript, Critical revision. J: Study conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting of manuscript, Critical revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This research was generously supported by GE Healthcare.
Ethical approval
This prospective study was performed under Research Ethics Board approval at our institution.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sussman, M.S., Jhaveri, K.S. A short-TR single-echo spin-echo breath-hold method for assessing liver T2. Magn Reson Mater Phy 37, 101–113 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-023-01132-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-023-01132-9