Abstract
Background
Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) carries adverse impact. Heart rate variability (HRV) represents autonomic cardiac regulation which influences intradialytic blood pressure. We aimed to evaluate the association between IDH and HRV.
Methods
This prospective study was carried out in a teaching hospital in Taiwan from June to August 2010. Adult patients on chronic hemodialysis without active medical conditions were enrolled and received HRV measurements for 4 times (before and during an index hemodialysis session). Patients were categorized by the changes of systolic blood pressure during the index hemodialysis into Group 1 (elevation >20 mmHg), Group 2 (decrease >20 mmHg), and Group 3 (others). Then we compared HRV indices among the three groups, and determined the indicators for IDH.
Results
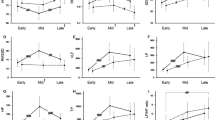
One hundred and seventy-one patients (96 women, mean age 64.9 years) were enrolled and categorized into Group 1 (n = 47, 27.5 %), Group 2 (n = 45, 26.3 %) and Group 3 (n = 79, 46.2 %). Comparing with Group 1 and/or Group 3, Group 2 had significantly higher blood pressure at hemodialysis initiation (most p < 0.001) and statistically lower levels of HRV indices including variance, total power, very low-frequency, low-frequency and high-frequency since the middle phase of the hemodialysis. By logistic regression method, higher systemic blood pressure [odds ratio (OR) 1.048; p < 0.001], heart rate (OR 1.093; p = 0.021), low-frequency/high-frequency ratio (OR 1.715; p = 0.022), as well as lower variance (OR 0.639; p = 0.048) at hemodialysis initiation were independently associated with intradialytic blood pressure changes.
Conclusions
HRV is a useful indicator for IDH among hemodialysis patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Gp:
-
Group
- HF:
-
High frequency
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- LF:
-
Low frequency
- TP:
-
Total power
- Var:
-
Variance of the R–R interval values
- VLF:
-
Very low frequency
References
K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45(4 Suppl 3):S1–153.
Ewing DJ, Winney R. Autonomic function in patients with chronic renal failure on intermittent haemodialysis. Nephron. 1975;15(6):424–9.
Daul AE, Wang XL, Michel MC, Brodde OE. Arterial hypotension in chronic hemodialyzed patients. Kidney Int. 1987;32(5):728–35.
Converse RL Jr, Jacobsen TN, Jost CM, Toto RD, Grayburn PA, Obregon TM, et al. Paradoxical withdrawal of reflex vasoconstriction as a cause of hemodialysis-induced hypotension. J Clin Investig. 1992;90(5):1657–65. doi:10.1172/JCI116037.
Barnas MG, Boer WH, Koomans HA. Hemodynamic patterns and spectral analysis of heart rate variability during dialysis hypotension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(12):2577–84.
Routledge HC, Chowdhary S, Townend JN. Heart rate variability—a therapeutic target? J Clin Pharm Ther. 2002;27(2):85–92.
Reed MJ, Robertson CE, Addison PS. Heart rate variability measurements and the prediction of ventricular arrhythmias. QJM. 2005;98(2):87–95. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hci018.
Kleiger RE, Stein PK, Bigger JT Jr. Heart rate variability: measurement and clinical utility. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005;10(1):88–101. doi:10.1111/j.1542-474X.2005.10101.x.
Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Euro Heart J. 1996;17(3):354–81.
Elghozi JL, Julien C. Sympathetic control of short-term heart rate variability and its pharmacological modulation. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2007;21(4):337–47. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2007.00502.x.
Pelosi G, Emdin M, Carpeggiani C, Morales MA, Piacenti M, Dattolo P, et al. Impaired sympathetic response before intradialytic hypotension: a study based on spectral analysis of heart rate and pressure variability. Clin Sci (Lond). 1999;96(1):23–31.
Ranpuria R, Hall M, Chan CT, Unruh M. Heart rate variability (HRV) in kidney failure: measurement and consequences of reduced HRV. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23(2):444–9. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm634.
Billman GE. The LF/HF ratio does not accurately measure cardiac sympatho-vagal balance. Front Physiol. 2013;. doi:10.3389/fphys.00026.
Chen KY, Chen CL, Yang CC, Kuo TB. Cardiac autonomic dysregulation in patients with acute hepatitis. Am J Med Sci. 2006;332(4):164–7.
Cavalcanti S, Severi S, Chiari L, Avanzolini G, Enzmann G, Bianco G, et al. Autonomic nervous function during haemodialysis assessed by spectral analysis of heart-rate variability. Clin Sci (Lond). 1997;92(4):351–9.
Rubinger D, Revis N, Pollak A, Luria MH, Sapoznikov D. Predictors of haemodynamic instability and heart rate variability during haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19(8):2053–60. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh306.
Forsstrom J, Heinonen E, Valimaki I, Antila K. Effects of haemodialysis on heart rate variability in chronic renal failure. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1986;46(7):665–70.
Rubinger D, Backenroth R, Sapoznikov D. Sympathetic nervous system function and dysfunction in chronic hemodialysis patients. Semin Dial. 2013;26(3):333–43. doi:10.1111/sdi.12093.
Ino-Oka E, Urae J, Sekino M, Satoh M, Takeuchi K, Sekino H, et al. Blood pressure and sympathetic nerve tone relation during hemodialysis may reflect cardiovascular dysfunction. Intern Med. 2011;50(22):2741–8.
Cases A, Coll E. Chronic hypotension in the dialysis patient. J Nephrol. 2002;15(4):331–5.
Lin YH, Chen CY, Lin SH, Liu CH, Weng WH, Kuo TB, et al. Gender differences in cardiac autonomic modulation during medical internship. Psychophysiology. 2013;50(6):521–7. doi:10.1111/psyp.12038.
Yamamoto K, Kobayashi N, Kutsuna T, Ishii A, Matsumoto T, Hara M, et al. Excessive fall of blood pressure during maintenance hemodialysis in patients with chronic renal failure is induced by vascular malfunction and imbalance of autonomic nervous activity. Ther Apher Dial. 2012;16(3):219–25. doi:10.1111/j.1744-9987.2011.01053.x.
Gonzalez H, Infante O, Perez-Grovas H, Jose MV, Lerma C. Nonlinear dynamics of heart rate variability in response to orthostatism and hemodialysis in chronic renal failure patients: recurrence analysis approach. Med Eng Phys. 2013;35(2):178–87. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2012.04.013.
Mazzeo AT, La Monaca E, Di Leo R, Vita G, Santamaria LB. Heart rate variability: a diagnostic and prognostic tool in anesthesia and intensive care. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55(7):797–811. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2011.02466.x.
Grassi G, Quarti-Trevano F, Seravalle G, Arenare F, Volpe M, Furiani S, et al. Early sympathetic activation in the initial clinical stages of chronic renal failure. Hypertension. 2011;57(4):846–51. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.164780.
Masuo K, Lambert GW, Esler MD, Rakugi H, Ogihara T, Schlaich MP. The role of sympathetic nervous activity in renal injury and end-stage renal disease. Hypertens Res. 2010;33(6):521–8. doi:10.1038/hr.2010.35.
Kim YH, Ahmed MW, Kadish AH, Goldberger JJ. Characterization of the factors that determine the effect of sympathetic stimulation on heart rate variability. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol (PACE). 1997;20(8 Pt 1):1936–46.
Zhang LN, Yang G, Cheng C, Shen C, Cui YY, Zhang J, et al. Plasma FGF23 levels and heart rate variability in patients with stage 5 CKD. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(1):395–405. doi:10.1007/s00198-014-2862-7.
Yun JS, Ahn YB, Song KH, Yoo KD, Kim HW, Park YM, et al. The association between abnormal heart rate variability and a new onset of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a ten-year follow-up study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2015.01.031.
Nolan J, Batin PD, Andrews R, Lindsay SJ, Brooksby P, Mullen M, et al. Prospective study of heart rate variability and mortality in chronic heart failure: results of the United Kingdom heart failure evaluation and assessment of risk trial (UK-heart). Circulation. 1998;98(15):1510–6.
Algra A, Tijssen JG, Roelandt JR, Pool J, Lubsen J. Heart rate variability from 24-hour electrocardiography and the 2-year risk for sudden death. Circulation. 1993;88(1):180–5.
Wang YC, Yang CC, Bai YM, Kuo TB. Heart rate variability in schizophrenic patients switched from typical antipsychotic agents to amisulpride and olanzapine. 3-month follow-up. Neuropsychobiology. 2008;57(4):200–5. doi:10.1159/000149818.
Castellanos A, Moleiro F, Chakko S, Acosta H, Huikuri H, Mitrani RD, et al. Heart rate variability in inappropriate sinus tachycardia. Am J Cardiol. 1998;82(4):531–4.
Singh JP, Larson MG, O’Donnell CJ, Wilson PF, Tsuji H, Lloyd-Jones DM, et al. Association of hyperglycemia with reduced heart rate variability (The Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 2000;86(3):309–12.
Malpas SC. Neural influences on cardiovascular variability: possibilities and pitfalls. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;282(1):H6–20.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank staffs in the hemodialysis center of Saint Mary’s Hospital Luodong who performed the measurement of HRV. The research was supported by Saint Mary’s Hospital Research Fund (SMHRF-2010004).
The SMCKD (Saint Mary’s hospital Chronic Kidney Disease) study group includes Chih-Chung Shiao, MD; Yu-Ming Chang, MD; Jsun-Liang Kao, MD; Shih-Ching Tsai, MD; Rong-Na Jhen, MD; Chuan-Lan Yang, RN; Shu-Min Huang, RN; Ching-Hua Huang, RN; Yu-**g Wu, RN; Huei-Ru Chin, RN; I-Ling Chen, RN; Kuai-Sui Hsu, RN; Show-Chin Leu, RN, Hung-Li Su, RN; Mei-Yun Kao, RN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
On behalf of SMCKD (Saint Mary’s hospital Chronic Kidney Disease) study group.
Members of the Saint Mary’s hospital Chronic Kidney Disease study group are given in Acknowledgments.
Y.-M. Chang, C.-C. Shiao and K.-C. Chang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, YM., Shiao, CC., Chang, KC. et al. Heart rate variability is an indicator for intradialytic hypotension among chronic hemodialysis patients. Clin Exp Nephrol 20, 650–659 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1189-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-015-1189-9