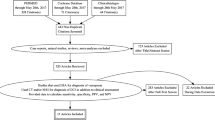
Abstract
Cerebral vasospasm is a life-threatening complication following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH). While digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the current gold standard for detection, the diagnostic performance of computed tomography angiography (CTA) and transcranial Doppler (TCD) remains controversial. We aimed to summarize the available evidence and provide recommendations for their use based on GRADE criteria. A literature search was conducted for studies comparing CTA or TCD to DSA for adults ≥ 18 years with aSAH for radiographic vasospasm detection. The DerSimonian–Laird random-effects model was used to pool sensitivity and specificity and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) and derive positive and negative pooled likelihood ratios (LR + /LR −). Out of 2070 studies, seven studies (1646 arterial segments) met inclusion criteria and were meta-analyzed. Compared to the gold standard (DSA), CTA had a pooled sensitivity of 82% (95%CI, 68–91%) and a specificity of 97% (95%CI, 93–98%), while TCD had lower sensitivity 38% (95%CI, 19–62%) and specificity of 91% (95%CI, 87–94%). Only the LR + for CTA (27.3) reached clinical significance to rule in diagnosis. LR − for CTA (0.19) and TCD (0.68) approached clinical significance (< 0.1) to rule out diagnosis. CTA showed higher LR + and lower LR − than TCD for diagnosing radiographic vasospasm, thereby achieving a strong recommendation for its use in ruling in or out vasospasm, based on the high quality of evidence. TCDs had very low LR + and a reasonably low LR − , thereby achieving a weak recommendation against its use in ruling in vasospasm and weak recommendation for its use in ruling out vasospasm.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Most of the data, including the complete search string and study selection process that is relevant for study selection, is presented within supplementary files. Complete data used for the meta-analysis in this study is available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Carr KR, Zuckerman SL, Mocco J (2013) Inflammation, cerebral vasospasm, and evolving theories of delayed cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res Int 2013:506584. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/506584
Findlay JM, Nisar J, Darsaut T (2016) Cerebral vasospasm: a review. Can J Neurol Sci 43(1):15–32. https://doi.org/10.1017/cjn.2015.288
Kolias AG, Sen J, Belli A (2009) Pathogenesis of cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: putative mechanisms and novel approaches. J Neurosci Res 87(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21823
Nassar HGE, Ghali AA, Bahnasy WS, Elawady MM (2019) Vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: prediction, detection, and intervention. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg 55(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41983-018-0050-y
Zacharia BE, Hickman ZL, Grobelny BT et al (2010) Epidemiology of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Clin N Am 21(2):221–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2009.10.002
Kassell NF, Boarini DJ, Adams HP et al (1981) Overall management of ruptured aneurysm: comparison of early and late operation. Neurosurgery 9(2):120–128. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198108000-00002
Bauer AM, Rasmussen PA (2014) Treatment of intracranial vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Neurol 5:72. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2014.00072
Vergouwen MD, Vermeulen M, van Gijn J et al (2010) Definition of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage as an outcome event in clinical trials and observational studies: proposal of a multidisciplinary research group. Stroke 41(10):2391–2395. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.110.589275
Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR et al (2012) Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke 43(6):1711–1737. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839
Dodd WS, Laurent D, Dumont AS et al (2021) Pathophysiology of delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a review. J Am Heart Assoc. 10(15):e021845. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.121.021845
Francoeur CL, Mayer SA (2016) Management of delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit Care 20(1):277. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-016-1447-6
Wintermark M, Ko NU, Smith WS, Liu S, Higashida RT, Dillon WP (2006) Vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: utility of perfusion CT and CT angiography on diagnosis and management. Am J Neuroradiol 27(1):26–34
Kühn AL, Balami JS, Grunwald IQ (2013) Current management and treatment of cerebral vasospasm complicating SAH. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 12(2):233–241. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527311312020010
Shankar JJ, Tan IY, Krings T, Terbrugge K, Agid R (2012) CT angiography for evaluation of cerebral vasospasm following acute subarachnoid haemorrhage. Neuroradiology 54(3):197–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0876-9
Mastantuono JM, Combescure C, Elia N, Tramèr MR, Lysakowski C (2018) Transcranial Doppler in the diagnosis of cerebral vasospasm: an updated meta-analysis. Crit Care Med 46(10):1665–1672. https://doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0000000000003297
Kumar G, Shahripour RB, Harrigan MR (2016) Vasospasm on transcranial Doppler is predictive of delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg 124(5):1257–1264. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.4.Jns15428
Connolly ES, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR et al (2012) Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 43(6):1711–1737. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839
Diringer MN, Bleck TP, Claude Hemphill J et al (2011) Critical care management of patients following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: recommendations from the Neurocritical Care Society’s Multidisciplinary Consensus Conference. Neurocrit Care. 15(2):211–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-011-9605-9
Greenberg ED, Gold R, Reichman M et al (2010) Diagnostic accuracy of CT angiography and CT perfusion for cerebral vasospasm: a meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(10):1853–1860. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2246
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA et al (2004) Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 328(7454):1490. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1490
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
Windschall D, Hoekstra K, Haase R (2016) Doppler sonography of blood flow velocity in the vertebral arteries of preterm and term neonates. J Ultrasound Med 35(9):1941–1947. https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.15.09061
Kofke WA, Brauer P, Policare R, Penthany S, Barker D, Horton J (1995) Middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity and stable xenon-enhanced computed tomographic blood flow during balloon test occlusion of the internal carotid artery. Stroke 26(9):1603–1606. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.26.9.1603
Chang JJ, Triano M, Corbin MJ et al (2020) Transcranial Doppler velocity and associations with delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurol Sci. 415:116934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2020.116934
Velat GJ, Kimball MM, Mocco JD, Hoh BL (2011) Vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: review of randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses in the literature. World Neurosurg 76(5):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2011.02.030
Frontera JA, Fernandez A, Schmidt JM et al (2009) Defining vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: what is the most clinically relevant definition? Stroke 40(6):1963–1968. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.108.544700
Samagh N, Bhagat H, Jangra K (2019) Monitoring cerebral vasospasm: how much can we rely on transcranial Doppler. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 35(1):12–18. https://doi.org/10.4103/joacp.JOACP_192_17
Sviri GE, Ghodke B, Britz GW et al (2006) Transcranial Doppler grading criteria for basilar artery vasospasm. Neurosurgery 59(2):360–6. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.Neu.0000223502.93013.6e (discussion 360-6)
Soustiel JF, Bruk B, Shik B, Hadani M, Feinsod M (1998) Transcranial Doppler in vertebrobasilar vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 43(2):282–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199808000-00061 (discussion 291-3)
Janjua N, Qureshi AI, Kirmani JF et al (2005) A 70-year-old woman with poor grade subarachnoid hemorrhage complicated by carotid stenosis, cerebral vasospasm, and cerebral rebleed. Neurocrit Care 3(2):183–188. https://doi.org/10.1385/ncc:3:2:183
Aralasmak A, Akyuz M, Ozkaynak C, Sindel T, Tuncer R (2009) CT angiography and perfusion imaging in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: correlation of vasospasm to perfusion abnormality. Neuroradiology 51(2):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0466-7
Kathy T. Data extraction in meta-analysis. University of Oxford. Accessed on July 24, 2022 https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/data-extraction-tips-meta-analysis
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
Uricchio M, Gupta S, Jakowenko N et al (2019) Computed tomography angiography versus digital subtraction angiography for postclip** aneurysm obliteration detection. Stroke 50(2):381–388. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.118.023614
Takwoingi Y, Guo B, Riley RD, Deeks JJ (2017) Performance of methods for meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy with few studies or sparse data. Stat Methods Med Res 26(4):1896–1911. https://doi.org/10.1177/0962280215592269
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME et al (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155(8):529–536
Laslo AM, Eastwood JD, Pakkiri P, Chen F, Lee TY (2008) CT perfusion-derived mean transit time predicts early mortality and delayed vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(1):79–85. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0747
Nabavi DG, LeBlanc LM, Baxter B et al (2001) Monitoring cerebral perfusion after subarachnoid hemorrhage using CT. Neuroradiology 43(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340000434
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. (2019) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of interventions. Version 6.2. Cochrane, 2021. https://www.training.cochrane.org/handbook. Accessed 01 Aug 2021
Anderson GB, Ashforth R, Steinke DE, Findlay JM (2000) CT angiography for the detection of cerebral vasospasm in patients with acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Am J Neuroradiol 21(6):1011–1015
Binaghi S, Colleoni ML, Maeder P et al (2007) CT angiography and perfusion CT in cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Am J Neuroradiol 28(4):750–758
Burch CM, Wozniak MA, Sloan MA et al (1996) Detection of intracranial internal carotid artery and middle cerebral artery vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroimaging 6(1):8–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon1996618
Lennihan L, Petty GW, Fink ME, Solomon RA, Mohr JP (1993) Transcranial Doppler detection of anterior cerebral artery vasospasm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56(8):906–909
Sloan MA, Burch CM, Wozniak MA et al (1994) Transcranial Doppler detection of vertebrobasilar vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 25(11):2187–2197
Yoon DY, Choi CS, Kim KH, Cho BM (2006) Multidetector-row CT angiography of cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: comparison of volume-rendered images and digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 27(2):370–377
Carrera E, Schmidt JM, Oddo M et al (2009) Transcranial Doppler for predicting delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 65(2):316–23. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.Neu.0000349209.69973.88 (discussion 323-4)
Vora YY, Suarez-Almazor M, Steinke DE, Martin ML, Findlay JM (1999) Role of transcranial Doppler monitoring in the diagnosis of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 44(6):1237–47 (discussion 1247-8)
Suarez JI, Qureshi AI, Yahia AB et al (2002) Symptomatic vasospasm diagnosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage: evaluation of transcranial Doppler ultrasound and cerebral angiography as related to compromised vascular distribution. Crit Care Med 30(6):1348–1355. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200206000-00035
Kumar G, Alexandrov AV (2015) Vasospasm surveillance with transcranial Doppler sonography in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Ultrasound Med 34(8):1345–1350. https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.34.8.1345
Letourneau-Guillon L, Farzin B, Darsaut TE et al (2020) Reliability of CT angiography in cerebral vasospasm: a systematic review of the literature and an inter- and intraobserver study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 41(4):612–618. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A6462
van der Harst JJ, Luijckx GR, Elting JWJ et al (2019) Transcranial Doppler versus CT-angiography for detection of cerebral vasospasm in relation to delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a prospective single-center cohort study: the transcranial Doppler and CT-angiography for investigating cerebral vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage (TACTICS) study. Crit Care Explor 1(1):e0001. https://doi.org/10.1097/cce.0000000000000001
Ionita CC, Graffagnino C, Alexander MJ, Zaidat OO (2008) The value of CT angiography and transcranial Doppler sonography in triaging suspected cerebral vasospasm in SAH prior to endovascular therapy. Neurocrit Care 9(1):8–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-007-9029-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. More specific contributions are as follows: Ayaz Khawaja, writing — review and editing. John McNulty, writing — original draft, resources, and investigation. Unnati V. Thakur, writing — original draft, resources, and investigation. Shreya Chawla, resources and investigation. Sharmila Devi, resources and investigation. Aaron Liew, formal analysis. Shervin Mirshahi, validation. Rose Du, conceptualization and writing — review and editing. Rania A. Mekary, formal analysis and supervision. William Gormley, conceptualization and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
As the study involved analyzing already published deidentified data, informed consent and IRB approval were not sought.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ayaz M. Khawaja, Jack McNulty, and Unnati V. Thakur are co-first authors.
Rania A. Mekary and William Gormley are co-senior authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khawaja, A.M., McNulty, J., Thakur, U.V. et al. Transcranial Doppler and computed tomography angiography for detecting cerebral vasospasm post-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Rev 46, 3 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-022-01913-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-022-01913-1