Abstract
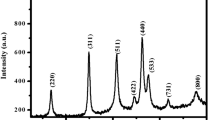
Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) were synthesized via an affordable and environmentally friendly route using waste banana peel extract. The polyphenol-rich extract acted as a stabilizing and reducing agent resulting in formation of α-Fe2O3 with a particle size of around 60 nm. The composition, phase, morphology and size of the nanoparticles were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and a Zetasizer. The efficiency of the IONPs was assessed in terms of arsenic(V) remediation from contaminated water within the range of 0.1–2.0 mg/L. Batch study showed that IONPs had a high As(V) adsorption capacity of about 2.715 mg/g at 40 °C. A statistical approach, viz. an artificial neural network, was adapted for modeling and optimization of the process parameters for achieving maximum As(V) removal efficiency. A set of 54 experimental sets were conducted and the predicted model generated showed an R2 value of 0.9971 and the corresponding mean squared error value was 0.0000601. Surface binding of the As(V) phenomenon on the green synthesized IONPs was explained on the basis of FTIR spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy of the control and the As(V)-loaded IONPs.The spent adsorbent was successfully immobilized in phosphate glass matrix with an objective to provide a complete and sustainable solution for arsenic contamination.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali I (2012) New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem Rev 112:5073–5091. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300133d
An C, Yang S, Huang G et al (2016) Removal of sulfonated humic acid from aqueous phase by modified coal fly ash waste: equilibrium and kinetic adsorption studies. Fuel 165:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2015.10.069
Andrade AL, Souza DM, Pereira MC, Fabris JD, Domingues RZ (2009) Synthesis andcharacterization of magnetic nanoparticles coated with silica through a sol-gel approach. Cerâmica 55:420–424. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0366-69132009000400013
Brunson LR, Sabatini DA (2009) An evaluation of fish bone char as an appropriate arsenic and fluoride removal technology for emerging regions. Environ Eng Sci 26:1777–1784. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2009.0222
Bundschuh J, Maity JP (2015) Geothermal arsenic: occurrence, mobility and environmental implications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 42:1214–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2014.10.092
Chakraborti D, Rahman MM, Ahamed S et al (2016) Arsenic groundwater contamination and its health effects in Patna district (capital of Bihar) in the middle Ganga plain, India. Chemosphere 152:520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2016.02.119
Cheng W, Zhang W, Hu L, et al (2016) Etching synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles for adsorption of arsenic from water †. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra26143k
Chenu S, Lebullenger R, Rocherullé J (2010) Characterization of NaPO3–SnO–WO3 glasses prepared by microwave heating. J Mater Sci 45:6505–6510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4739-2
Chiban M, Zerbet M, Carja G, Sinan F (2012) Application of low-cost adsorbents for arsenic removal: a review. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 4:91–102. https://doi.org/10.5897/JECE11.013
Chowdhury SR, Yanful EK, Pratt AR (2011) Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by mixed magnetite–maghemite nanoparticles. Environ Earth Sci 64:411–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0865-z
Debnath A, Deb K, Chattopadhyay KK, Saha B (2016a) Methyl orange adsorption onto simple chemical route synthesized crystalline α-Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles: kinetic, equilibrium isotherm, and neural network modeling. Desalin Water Treat 57:13549–13560. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1060540
Debnath A, Deb K, Das NS et al (2016b) Simple chemical route synthesis of Fe2O3 nanoparticles and its application for adsorptive removal of Congo red from aqueous media: artificial neural network modeling. J Dispers Sci Technol 37:775–785. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2015.1062772
Devi RR, Umlong IM, Das B et al (2014) Removal of iron and arsenic (III) from drinking water using iron oxide-coated sand and limestone. Appl Water Sci 4:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0139-5
Dhar RK, Zheng Y, Rubenstone J, van Geen A (2004) A rapid colorimetric method for measuring arsenic concentrations in groundwater. Anal Chim Acta 526:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2004.09.045
Fierro V, Muñiz G, Gonzalez-Sánchez G et al (2009) Arsenic removal by iron-doped activated carbons prepared by ferric chloride forced hydrolysis. J Hazard Mater 168:430–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2009.02.055
Gallegos-Garcia M, Ramírez-Muñiz K, Song S (2012) Arsenic removal from water by adsorption using iron oxide minerals as adsorbents: a review. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev 33:301–315. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2011.584219
Ghosal PS, Gupta AK (2016) Enhanced efficiency of ANN using nonlinear regression for modeling adsorptive removal of fluoride by calcined Ca–Al–(NO3)–LDH. J Mol Liq 222:564–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2016.07.070
Ghosal PS, Gupta AK (2017) Development of a generalized adsorption isotherm model at solid-liquid interface: a novel approach. J Mol Liq 240:21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.05.042
Glocheux Y, Pasarín MM, Albadarin AB et al (2013) Removal of arsenic from groundwater by adsorption onto an acidified laterite by-product. Chem Eng J 228:565–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2013.05.043
Gu Z, Fang J, Deng B (2005) Preparation and evaluation of GAC-based iron-containing adsorbents for arsenic removal. Environ Sci Technol 39(10):3833–3843. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048179r
Hémono N, Chenu S, Lebullenger R et al (2010) Microwave synthesis and physical characterization of tin(II) phosphate glasses. J Mater Sci 45:2916–2920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4283-0
Herlekar M, Barve S, Kumar R (2014) Plant-mediated green synthesis of iron nanoparticles. J Nanoparticles 2014:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/140614
Ibrahim HMM (2015) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 8:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JRRAS.2015.01.007
**g H, Song H, Liang Z et al (2010) Equilibrium and thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of Methylene Blue onto rectorite. Fresenius Environ Bull 19:2651–2656
Kanel SR, Choi H (2017) Removal of Arsenic from groundwater by industrial byproducts and its comparison with zero-valent iron. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 21:04016028. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000349
Li W-G, Gong X-J, Wang K, Zhang X-R, Fan W-B (2014) Adsorption characteristics of arsenic from micro-polluted water by an innovative coal-based mesoporous activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 165:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2014.02.069
Liu Z, Wan Y, **ong G et al (2015) Three-dimensional porous nanocomposite of highly dispersed Fe3O4 nanoparticles on carbon nanofibers for high-performance microwave absorbents. Mater Express 5:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2015.1216
Mandal AK, Sen S, Mandal S et al (2015) Energy efficient melting of glass for nuclear waste immobilization using microwave radiation. Int J Green Energy 12:1280–1287. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2014.895735
Martínez-Cabanas M, López-García M, Barriada JL et al (2016) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Development of magnetic hybrid materials for efficient As(V) removal. Chem Eng J 301:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2016.04.149
Mercado-Borrayo BM, Schouwenaars R, Litter MI et al (2014) Metallurgical slag as an efficient and economical adsorbent of arsenic. Water Reclam Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-411645-0.00005-5
Mishra PK, De V, Ghongane DE et al (2013) Preparation and characterisation of glass product with modified composition for vitrification of high level radioactive waste. J Therm Anal Calorim 112:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2811-7
Mohan D, Pittman CU (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142:1–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2007.01.006
Mukherjee D, Ghosh S, Majumdar S, Annapurna K (2016) Green synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for arsenic(V) remediation with a novel aspect for sludge management. J Environ Chem Eng 4:639–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2015.12.010
Popescu V, Batin MN, Popescu V (2011) Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide powders. Powder Metall Prog.11:201–205.
Ramrakhiani L, Halder A, Majumder A et al (2017) Industrial waste derived biosorbent for toxic metal remediation: mechanism studies and spent biosorbent management. Chem Eng J 308:1048–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2016.09.145
Salameh Y, Albadarin AB, Allen S et al (2015) Arsenic(III, V) adsorption onto charred dolomite: charring optimization and batch studies. Chem Eng J 259:663–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2014.08.038
Smedley P, Kinniburgh D (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
Solé-Sardans M, Gamisans X, Dorado AD, Lao-Luque C (2016) Exploring arsenic adsorption at low concentration onto modified Leonardite. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2827-x
Vu HT, Scarlett CJ, Vuong QV (2018) Phenolic compounds within banana peel and their potential uses: a review. J Funct Foods 40:238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFF.2017.11.006
Weng C-H, Lin D-F, Chiang P-C (2003) Utilization of sludge as brick materials. Adv Environ Res 7:679–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(02)00037-0
Willis AL, Turro NJ, O’Brien S (2005) Spectroscopic Characterization ofthe Surface of Iron Oxide Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 17:5970–5975. https://doi.org/10.1021/CM051370V
Yu J, **ong W, Zhu J et al (2017) Removal of Congo red from aqueous solution by adsorption onto different amine compounds modified sugarcane bagasse. Clean Technol Environ Policy 19:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1243-7
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Director, CSIR-CGCRI, India, for granting permission to carry out this research work. Author A. Majumder acknowledges the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), India, for providing the GATE fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majumder, A., Ramrakhiani, L., Mukherjee, D. et al. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles for arsenic remediation in water and sludge utilization. Clean Techn Environ Policy 21, 795–813 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01669-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01669-1