Abstract
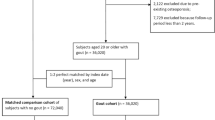
Coexistence of rheumatoid arthritis and gout is considered to be unusual. The current study was designed as a population-based cross-sectional study, utilizing the medical database of Clalit Health Services, the largest healthcare provider organization in Israel. Data of adult patients who were previously diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis was retrieved. For each patient, five age- and sex-matched control patients were randomly selected. Different parameters including BMI, socioeconomic status, and existence of gout as well as smoking and hypertension were examined for both groups. The study included 11,540 patients with rheumatoid arthritis and 56,763 controls. The proportion of gout in the study group was high compared to controls (1.61 vs. 0.92%, P < 0.001). In a multivariate analysis, rheumatoid arthritis was associated with gout (OR = 1.72, 95% CI 1.45–2.05, P = 0.00). The proportion of gout in rheumatoid arthritis patients is not lower than in the general population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Houri LE, Watad A, Whitby A, Tiosano S, Comaneshter D, Cohen AD et al (2016) Coexistence of ischemic heart disease and rheumatoid arthritis patients—a case control study. Autoimmun Rev 15(4):393–396
Gabriel SE, Michaud K (2009) Epidemiological studies in incidence, prevalence, mortality, and comorbidity of the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 11(3):229
Dehlin M, Drivelegka P, Sigurdardottir V, Svard A, Jacobsson LT (2016) Incidence and prevalence of gout in Western Sweden. Arthritis Res Ther 18:164
Liu R, Han C, Wu D, **a X, Gu J, Guan H et al (2015) Prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout in mainland China from 2000 to 2014: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2015:762820
Zandman-Goddard G, Amital H, Shamrayevsky N, Raz R, Shalev V, Chodick G (2013) Rates of adherence and persistence with allopurinol therapy among gout patients in Israel. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52(6):1126–1131
Kuo CF, Tsai WP, Liou LB (2008) Rare copresent rheumatoid arthritis and gout: comparison with pure rheumatoid arthritis and a literature review. Clin Rheumatol 27(2):231–235
Jebakumar AJ, Udayakumar PD, Crowson CS, Matteson EL (2013) Occurrence of gout in rheumatoid arthritis: it does happen! A population-based study. Int J Clin Rheumtol 8(4):433–437
Bieber V, Cohen AD, Freud T, Agmon-Levin N, Gertel S, Amital H (2013) Autoimmune smoke and fire—coexisting rheumatoid arthritis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional analysis. Immunol Res 56(2–3):261–266
Dahan S, Shor DB, Comaneshter D, Tekes-Manova D, Shovman O, Amital H et al (2016) All disease begins in the gut: celiac disease co-existence with SLE. Autoimmun Rev 15(8):848–853
Guy A, Tiosano S, Comaneshter D, Tekes-Manova D, Shovman O, Cohen AD et al. (2016) Aortic aneurysm association with lupus
Watad A, Cohen AD, Comaneshter D, Tekes-Manova D, Amital H (2016) Hyperthyroidism association with SLE, lessons from real-life data—a case-control study. Autoimmunity 49(1):17–20
MacFarlane LA, Kim SC (2014) Gout: a review of nonmodifiable and modifiable risk factors. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 40(4):581–604
Schlesinger N (2014) Treatment of acute gout. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 40(2):329–341
Yardim-Akaydin S, Sepici A, Ozkan Y, Torun M, Simsek B, Sepici V (2004) Oxidation of uric acid in rheumatoid arthritis: is allantoin a marker of oxidative stress? Free Radic Res 38(6):623–628
Shovman O, Tiosano S, Comaneshter D, Cohen AD, Amital H, Sherf M (2016) Aortic aneurysm associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cross-sectional study. Clin Rheumatol
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the institutional review board of the Clalit Health Services at the Soroka Medical Center, in Beer Sheva, Israel.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Rona Merdler-Rabinowicz and Shmuel Tiosano contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merdler-Rabinowicz, R., Tiosano, S., Comaneshter, D. et al. Comorbidity of gout and rheumatoid arthritis in a large population database. Clin Rheumatol 36, 657–660 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3477-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3477-5