Abstract
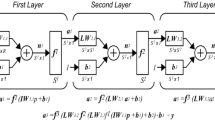
Earthquake-induced landslides are destructive and hazardous geological disasters, and mountainous areas are prone to earthquakes. Therefore, it is essential to establish an earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility prediction model with good accuracy, robustness, and generalization capability for the southwestern mountainous areas of China. In this study, the 2008 Wenchuan Ms 8.0, 2010 Yushu Ms 7.1, 2013 Ya’an Ms 7.0, 2014 Ludian Ms 6.5, 2017 Jiuzhaigou Ms 7.0, and 81,513 landslide sites were analyzed. Thirteen influencing factors were selected: PGA, elevation, slope, aspect, curvature, fault type, distance to faults, distance to rivers, NDVI, TWI, lithology, land cover type, and distance to road. Weight and spatial distribution analyses were also performed. Based on a backpropagation (BP) neural network, a regional earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility prediction model was constructed for southwest China. Various methods have been used to evaluate the accuracy of the model. The results showed that the model had excellent prediction accuracy and applicability and that the AUC, accuracy, recall, F1-score, and precision of the model could be stabilized at approximately 0.9. The inclusion of more landslide events in the model can further improve its accuracy and robustness. The constructed model was applied to the fault intersection area, and it was found that most of the actual landslides fell in the predicted medium-high susceptibility area. The research results can enrich the theory of earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility assessment and provide valuable information regarding the location of landslide-prone areas for rapid post-earthquake emergency response in Southwest China.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato G, Fiorucci M, Martino S, Lombardo L (2021) Earthquake-triggered landslide susceptibility in Italy by means of Artificial neural network. Earth 31(25). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03163-x
Chang KT, Merghadi A, Yunus AP, Pham BT, Dou J (2019) Evaluating scale effects of topographic variables in landslide susceptibility models using GIS-based machine learning techniques. Sci Rep 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48773-2
Chen X, Chen W (2021) GIS-based landslide susceptibility assessment using optimized hybrid machine learning methods. CATENA 196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104833
Chen S, Miao Z, Wu L, Zhang A, Li Q, He Y (2021) Front Earth Sci 9(122). https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.609896. A One-Class-Classifier-Based Negative Data Generation Method for Rapid Earthquake-Induced Landslide Susceptibility Map**
Cristianini (2020) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods
Ding S-f, Qi B-j, Tan H-y (2011) An overview on theory and algorithm of support Vector machines. J Univ Electron Sci Technol China 40(01):2–10. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2011.01.001
Ding Y-N, Li D-Q, Zarei C, Yi B-L, Liu Y (2021) Probabilistically quantifying the effect of geotechnical anisotropy on landslide susceptibility. B Eng Geol Environ 80(8):6615–6627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02197-3
Du GL, Zhang YS, Iqbal J, Yang ZH, Yao X (2017) Landslide susceptibility map** using an integrated model of information value method and logistic regression in the Bailongjiang watershed, Gansu Province, China. J Mt Sci-Engl 14(2):249–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-4126-9
Fan X, Scaringi G, Xu Q, Zhan W, Dai L, Li Y, Pei X, Yang Q, Huang R (2018) Coseismic landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake (Sichuan, China): factors controlling their spatial distribution and implications for the seismogenic blind fault identification. Landslides 15(5):967–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-0960-x
Fan XM, Scaringi G, Korup O, West AJ, van Westen CJ, Tanyas H, Hovius N, Hales TC, Jibson RW, Allstadt KE, Zhang LM, Evans SG, Xu C, Li G, Pei XJ, Xu Q, Huang RQ (2019) Earthquake-Induced Chains of Geologic hazards: patterns, mechanisms, and impacts. Rev Geophys 57(2):421–503. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018RG000626
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett 27(8):861–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Figurnov M, Kirillov A (2012) Linear combination of random forests for the Relevance Prediction Challenge, Proc. of Int. Conf. on Web Service and Data Mining workshop on Web Search Click Data. New York: ACM, pp. 71–75
Gorum T, Carranza EJM (2015) Control of style-of-faulting on spatial pattern of earthquake-triggered landslides. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(10):3189–3212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0752-y
Guo FT, Zhang LJ, ** S, Tigabu M, Su ZW, Wang WH (2016) Modeling anthropogenic fire occurrence in the Boreal Forest of China using logistic regression and Random forests. FORESTS 7(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/f7110250
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2009) Random forests. In: Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (eds) The elements of statistical learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction. Springer New York, New York, pp 587–604
He Q, Wang M, Liu K (2021) Rapidly assessing earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility on a global scale using random forest. Geomorphology 391:107889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107889
Huang RQ, Li WL (2009) Analysis of the geo-hazards triggered by the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. B Eng Geol Environ 68(3):363–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-009-0207-0
Huang Y, Zhao L (2018) Review on landslide susceptibility map** using support vector machines. CATENA 165:520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.03.003
Huang F, Pan L, Fan X, Jiang S-H, Huang J, Zhou C (2022) The uncertainty of landslide susceptibility prediction modeling: suitability of linear conditioning factors. B Eng Geol Environ 81(5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02672-5
Jibson RW, Keeper DK (1993) Analysis of the seismic origin of landslides: examples from the New Madrid seismic zone. Geol Soc Am Bull 105(4):521–536. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1993)105<0521:AOTSOO>2.3.CO;2
Jibson RW, Harp EL, Michael JA (2000) A method for producing digital probabilistic seismic landslide hazard maps. Eng Geol 58(3):271–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00039-9
Juliev M, Mergili M, Mondal I, Nurtaev B, Pulatov A, Hubl J (2019) Comparative analysis of statistical methods for landslide susceptibility map** in the Bostanlik District, Uzbekistan. Sci Total Environ 653:801–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.431
Keefer DK (2002) Investigating landslides caused by earthquakes - a historical review. Surv Geophys 23(6):473–510. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021274710840
Lee CT, Huang CC, Lee JF, Pan KL, Lin ML, Dong JJ (2008) Statistical approach to earthquake-induced landslide susceptibility. Eng Geol 100(1–2):43–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.004
Lin L, Lin QG, Wang Y (2017) Landslide susceptibility map** on a global scale using the method of logistic regression. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 17(8):1411–1424. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-17-1411-2017
Liu J, Zhang Y, Wei J, **ang C, Wang Q, Xu P, Fu H (2021a) Hazard assessment of earthquake-induced landslides by using permanent displacement model considering near-fault pulse-like ground motions. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80(11):8503–8518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02464-3
Liu R, Li L, Pirasteh S, Lai Z, Yang X, Shahabi H (2021b) The performance quality of LR, SVM, and RF for earthquake-induced landslides susceptibility map** incorporating remote sensing imagery. Arab J Geosci 14(4):259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06573-x
Liu J, Fu H-y, Zhang Y-b, Xu P-y, Hao R-d, Yu H-h, He Y-y, Deng H-y, Zheng L (2023) Effects of the probability of pulse-like ground motions on landslide susceptibility assessment in near-fault areas. J Mt Sci 20(1):31–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7527-y
Marano KD, Wald DJ, Allen TI (2010) Global earthquake casualties due to secondary effects: a quantitative analysis for improving rapid loss analyses. Nat Hazards 52(2):319–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-009-9372-5
Markus R, Gustau C-V, Bjorn S, Martin J, Joachim D, Nuno C, Prabhat (2019) Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 566(7743). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0912-1
Merghadi A, Yunus AP, Dou J, Whiteley J, ThaiPham B, Bui DT, Avtar R, Abderrahmane B (2020) Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies: a comparative overview of algorithm performance. EARTH-SCIENCE REVIEWS, p 207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103225
Nowicki MA, Wald DJ, Hamburger MW, Hearne M, Thompson EM (2014) Development of a globally applicable model for near real-time prediction of seismically induced landslides. Eng Geol 173:54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.02.002
Nowicki Jessee MA, Hamburger MW, Allstadt K, Wald DJ, Robeson SM, Tanyas H, Hearne M, Thompson EM (2018) A global empirical model for Near-Real-Time Assessment of Seismically Induced landslides. J Geophys Research: Earth Surf 123(8):1835–1859. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JF004494
Pan Q-J, Leung Y-F, Hsu S-C (2021) Stochastic seismic slope stability assessment using polynomial chaos expansions combined with relevance vector machine Geoscience Frontiers. 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.03.016
Peng L, Niu RQ, Huang B, Wu XL, Zhao YN, Ye RQ (2014) Landslide susceptibility map** based on rough set theory and support vector machines: a case of the Three Gorges area, China. Geomorphology 204:287–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.08.013
Pradel D, Smith Patrick M, Stewart Jonathan P, Raad G (2005) Case History of Landslide Movement during the Northridge Earthquake. J Geotech GeoEnviron Eng 131(11):1360–1369. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:11(1360)
Pradhan B, Lee S (2010) Landslide susceptibility assessment and factor effect analysis: backpropagation artificial neural networks and their comparison with frequency ratio and bivariate logistic regression modelling. Environ Model Softw 25(6):747–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2009.10.016
Rajabi AM, Khodaparast M, Mohammadi M (2021) Earthquake-induced landslide prediction using back-propagation type artificial neural network: case study in northern Iran. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04963-8
Razifard M, Shoaei G, Zare M (2019) Application of fuzzy logic in the preparation of hazard maps of landslides triggered by the twin ahar-varzeghan earthquakes (2012). B Eng Geol Environ 78(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1235-4
Reichenbach P, Rossi M, Malamud BD, Mihir M, Guzzetti F (2018) A review of statistically-based landslide susceptibility models. Earth Sci Rev 180:60–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.03.001
Sato HP, Hasegawa H, Fujiwara S, Tobita M, Koarai M, Une H, Iwahashi J (2007) Interpretation of landslide distribution triggered by the 2005 Northern Pakistan earthquake using SPOT 5 imagery. LANDSLIDES 4(2):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-006-0069-5
Shafizadeh-Moghadam H, Minaei M, Shahabi H, Hagenauer J (2019) Big data in Geohazard; pattern mining and large scale analysis of landslides in Iran. Earth Sci Inf 12(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-018-0354-6
Shao X-y, Xu C, Ma S-y, Xu X-w, Shyu JBH, Zhou Q (2021) Calculation of landslide occurrence probability in Taiwan region under different ground motion conditions. J Mt Sci-Engl 18(4):1003–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6540-2
Shirani K, Pasandi M, Arabameri A (2018) Landslide susceptibility assessment by Dempster-Shafer and Index of Entropy models, Sarkhoun basin. Southwest Iran Nat HAZARDS 93(3):1379–1418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3356-2
Sun D, Shi S, Wen H, Xu J, Zhou X, Wu J (2021) A hybrid optimization method of factor screening predicated on GeoDetector and Random Forest for Landslide susceptibility map**. Geomorphology 379:107623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107623
Tanyas H, Rossi M, Alvioli M, van Westen CJ, Marchesini I (2019) A global slope unit-based method for the near real-time prediction of earthquake-induced landslides. Geomorphology 327:126–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.10.022
Tanyaş H, van Westen CJ, Allstadt KE, Nowicki Jessee A, Görüm M, Jibson T, Godt RW, Sato JW, Schmitt HP, Marc RG, Hovius O, N (2017) Presentation and analysis of a Worldwide Database of Earthquake-Induced landslide inventories. J Geophys Research: Earth Surf 122(10):1991–2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JF004236
Wang Y, Song C, Lin Q, Li J (2016) Occurrence probability assessment of earthquake-triggered landslides with Newmark displacement values and logistic regression: the Wenchuan earthquake, China. Geomorphology 258:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.01.004
Wen HJ, ** of earthquake-triggered slope geohazards in Lushan County by combining remote sensing with the AHP model developed for the Wenchuan earthquake. B Eng Geol Environ 76(3):909–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0957-4
Xu C, Xu X (2014) The spatial distribution pattern of landslides triggered by the 20 April 2013 Lushan earthquake of China and its implication to identification of the seismogenic fault. Chin Sci Bull 59(13):1416–1424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0202-0
Xu C, Dai F, Xu X, Lee YH (2012) GIS-based support vector machine modeling of earthquake-triggered landslide susceptibility in the Jianjiang River watershed, China. Geomorphology 145:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.12.040
Xu C, Xu X, Dai F, Wu Z, He H, Shi F, Wu X, Xu S (2013a) Application of an incomplete landslide inventory, logistic regression model and its validation for landslide susceptibility map** related to the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan earthquake of China. Nat Hazards 68(2):883–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0661-7
Xu C, Xu X, Yao Q, Wang Y (2013b) GIS-based bivariate statistical modelling for earthquake-triggered landslides susceptibility map** related to the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, China. Q J Eng GeolHydrogeol 46(2):221–236. https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2012-006
Youssef AM, Pourghasemi HR, Pourtaghi ZS, Al-Katheeri MM (2016) Landslide susceptibility map** using random forest, boosted regression tree, classification and regression tree, and general linear models and comparison of their performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia (vol 13, pg 839, 2016). LANDSLIDES, 13(5), 1315–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0667-1
Zhang W, Li H, Li Y, Liu H, Chen Y, Ding X (2021a) Application of deep learning algorithms in geotechnical engineering: a short critical review. Artif Intell Rev 54(8):5633–5673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-09967-1
Zhang W, Wu AC, Zhong AH, Li AY, Wang AL (2021b) Prediction of undrained shear strength using extreme gradient boosting and random forest based on bayesian optimization. Geosci Front 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.03.007
Zhang WG, Li HR, Wu CZ, Li YQ, Liu ZQ, Liu HL (2021c) Soft computing approach for prediction of surface settlement induced by earth pressure balance shield tunneling. Undergr Space 6(4):353–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2019.12.003
Zhang W, Li H, Han L, Chen L, Wang L (2022a) Slope stability prediction using ensemble learning techniques: a case study in Yunyang County, Chongqing, China. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 14(4):1089–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.12.011
Zhang Y, Liu J, Cheng Q, **ao L, Zhao L, **ang C, Buah PA, Yu H, He Y (2022b) A new permanent displacement model considering pulse-like ground motions and its application in landslide hazard assessment. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 163:107556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107556
Zhang Y, Liu J, Cheng Q, **ao L, Zhao L, **ang C, Buah PA, Yu H, He YJSD, Engineering E (2022c) A new permanent displacement model considering pulse-like ground motions and its application in landslide hazard assessment. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 163:107556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107556
Zhang Y, Xu P, Liu J, He J, Yang H, Zeng Y, He Y, Yang C (2023) Comparison of LR, 5-CV SVM, GA SVM, and PSO SVM for Landslide Susceptibility Assessment in Tibetan Plateau Area, China. J Mt Sci 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7685-y
Zhou S, Fang L (2015) Support vector machine modeling of earthquake-induced landslides susceptibility in central part of Sichuan Province. China Geoenvironmental Disasters 2(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-014-0006-1
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977213, 52378370, 52278372), National Ten Thousand Talent Program for Young Top-notch Talents, Sichuan Provincial Transportation Science and Technology Project (2021-A-03), and China Road & Bridge Corporation (P220447). The financial support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, H., Lin, J. et al. Susceptibility assessment of earthquake-induced landslide by using back-propagation neural network in the Southwest mountainous area of China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 187 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03687-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03687-w