Abstract
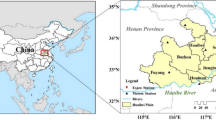
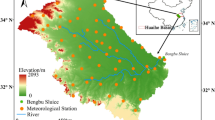
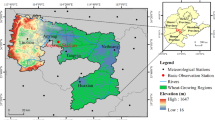
Agricultural drought (AGD) is one of the most impactful natural disasters for rain-fed agricultural regions worldwide, including those in China. Spatiotemporal characteristics of the winter wheat drought season on the Huang-Huai-Hai (HHH) Plain, China, were studied by employing the Penman-Monteith (P-M) equation and a crop coefficient model based on daily meteorological datasets from 57 stations from 1980 to 2011. The crop water deficit index (CWDI) was employed as an index of AGD appraisal to depict the spatiotemporal changes in drought during the winter wheat growth stages in the HHH Plain, China. Besides, this study also intends to develop a drought disaster risk index (DDRI) of winter wheat for various growth stages based on risk formation theory. The spatial distribution patterns indicated higher CWDI values in the northern and middle parts of the HHH Plain and lower in the southern region throughout the wheat growth stages. Of the winter wheat growth stages on the northern HHH Plain, the drought frequency was the highest during the heading-mature stage, when it reached up to 80–100%. The high drought hazard was obvious during the heading-mature growth stage, with a more severe high drought hazard in the northern region of the HHH Plain than in the southern region. Spatially, the high DDRI values were distributed in the northern and central regions of the HHH Plain. The outcomes suggest that the DDRI model provides accurate spatiotemporal appraisals in both temporal and spatial scales, and these findings are important for enhancing the adaptability and mitigation ability of AGD risk on the HHH Plain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
AghaKouchak A, Farahmand A, Melton FS, Teixeira J, Anderson MC, Wardlow BD, Hain CR (2015) Remote sensing of drought: progress, challenges and opportunities. Rev Geophys 53(2):452–480
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration–guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Rome
Campana PE, Zhang J, Yao T, Andersson S, Landelius T, Melton F, Yan J (2018) Managing agricultural drought in Sweden using a novel spatially-explicit model from the perspective of water-food-energy nexus. J Clean Prod 197:1382–1393
Chang J, Li Y, Wang Y, Yuan M, Yuan M (2016) Copula-based drought risk assessment combined with an integrated index in the Wei River Basin, China. J Hydrol 540:824–834
Chen T, **a G, Liu T, Chen W, Chi D (2016) Assessment of drought impact on main cereal crops using a standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index in Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 8(10):1–16
Chiogna G, Skrobanek P, Narany TS, Ludwig R, Stumpp C (2018) Effects of the 2017 drought on isotopic and geochemical gradients in the Adige catchment, Italy. Sci Total Environ 645:924–936
Çolak YB, Yazar A, Çolak İ, AkÇa H, Duraktekin G (2015) Evaluation of crop water stress index (CWSI) for eggplant under varying irrigation regimes using surface and subsurface drip systems. Agric Agric Sci Proc 4:372–382
Dai A (2011) Drought under global warming: a review. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Clim Change 2(1):45–65
Dina RA, Islam ARMT (2020) Assessment of drought disaster risk in Boro rice cultivated areas of northwestern Bangladesh. Eur J Geosci 2(1):19–29
Esfahanian E, Nejadhashemi AP, Abouali M, Adhikari U, Zhang Z, Daneshvar F, Herman MR (2017) Development and evaluation of a comprehensive drought index. J Environ Manag 185:31–43
Gadge SB, Gorantiwar SD, Kumar V, Kothari M (2011) Estimation of crop water requirement based on Penman-monteith approach under micro-irrgation system. J Agrometeorol 13(1):58–61
Gao C, Li XW, Sun YW, Zhou T, Luo G, Chen C (2019) Water requirement of summer maize at different growth stages and the spatiotemporal characteristics of agricultural drought in the Huaihe River Basin, China. Theor Appl Climatol 136:1289–1302
Guenang GM, Kamga FM (2014) Computation of the standardized precipitation index (SPI) and its use to assess drought occurrences in Cameroon over recent decades. J Appl Meteorol Clim 53:2310–2324
He B, Wu J, Lu A, Cui X, Zhou L, Liu M, Zhao L (2013) Quantitative assessment and spatial characteristic analysis of agricultural drought risk in China. Nat Hazards 66:155–166
Huang WH, Yang XG, Qu HH, Feng LP, Huang BX, Wang J, Shi SJ, Wu YF, Zhang XY, **ao XP, Yang GL, Li MS (2009) Analysis of spatio-temporal characteristic on seasonal drought of spring maize based on crop water deficit index. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 25(8):28–34
Huang Y, Wang J, Jiang D, Zhou K, Ding X, Fu J (2014) Surface water deficiency zoning of China based on surface water deficit index (SWDI). Water Resour 41:372–378
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability contribution of working group 2 to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Islam ARMT, Shen SH, Hu ZH, Atiqur Rahman M (2017) Drought hazard evaluation in Boro paddy cultivated areas of western Bangladesh at current and future climate change conditions. Adv Meteorol ID: 3514381
Islam ARMT, Shen S, Yang SB, Hu Z, Chu R (2019) Assessing recent impacts of climate change on design water requirement of Boro rice season in Bangladesh. Theor Appl Climatol 138:97–113
Islam ARMT, Rahman MS, Khatun R, Hu Z (2020) Spatiotemporal trends in the frequency of daily rainfall in Bangladesh during 1975-2017. Theor Appl Climatol 141:869–887
Kamruzzaman M, Hwang S, Cho J, Jang M, Jeong H (2019) Evaluating the spatiotemporal characteristics of agricultural drought in Bangladesh using effective drought index. Water 11:2437
Lee SM, Byun HR, Tanaka HL (2012) Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought occurrences over Japan. J Appl Meteorol Clim 51:1087–1098
Li XX, Ju H, Sarah G, Yan CR, William DB, Liu Q (2017) Spatiotemporal variation of drought characteristics in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China under the climate change scenario. J Integr Agr 16(10):2308–2322
Liao H, Chang WY (2014) Integrated assessment of air quality and climate change for policy-making: highlights of IPCC AR5 and research challenges. Natl Sci Rev 1(2):176–179
Liu XF, Zhu XF, Pan YZ, Li S, Liu Y, Ma Y (2016) Agricultural drought monitoring: progress, challenges, and prospects. J Geogr Sci 26(6):750–767
Ma X, Wu WY, Zhang H (2009) The agricultural drought and flood index and its operational application to monitoring and early-warning in Jianghuai area. J Appl Meteorol Sci 20(2):186–194 (in Chinese)
Murthy CS, Laxman B, Sai MS (2015) Geospatial analysis of agricultural drought vulnerability using a composite index based on exposure, sensitivity and adaptive capacity. Inter J Disaster Risk Reduct 12:163–171
Narasimhan B, Srinivasan R (2005) Development and evaluation of soil moisture deficit index (SMDI) and evapotranspiration deficit index (ETDI) for agricultural drought monitoring. Agric For Meteorol 133(1–4):69–88
Páscoa P, Gouveia CM, Russo A, Trigo RM (2017) The role of drought on wheat yield interannual variability in the Iberian Peninsula from 1929 to 2012. Int J Biometeorol 61(3):439–451
Pei W, Fu Q, Liu D, Li TX, Cheng K, Cui S (2017) Spatiotemporal analysis of the agricultural drought risk in Heilongjiang Province, China. Theor Appl Climatol 133:151–164
Piao S, Ciais P, Huang Y, Shen Z, Peng S, Li J, Zhou L, Liu H, Ma Y, Ding Y, Friedlingstein P, Liu C, Tan Y, Zhang T, Fang J (2010) The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 467(7311):43–51
Potopová V, Boroneanţ C, Boincean B, Soukup J (2016) Impact of agricultural drought on main crop yields in the Republic of Moldova. Int J Climatol 36(4):2063–2082
Sui Y, Huang WH, Yang XG, Li MS (2012) Characteristics and adaption of seasonal drought in southern China under the background of global climate change. II. Spatio-temporal characteristics of drought for wintering grain and oil crops based on crop water deficit index. Chin J Appl Ecol 23:2467–2476
Sun F, Yang S, Ren G (2007) Decade variations of precipitation event frequency, intensity and duration in the northeast China. J Appl Meteor Sci 18:610–618
Uddin MJ, Hu J, Islam ARMT, Eibek KU, Zahan MN (2020) A comprehensive statistical assessment of drought indices to monitor drought status in Bangladesh. Arab J Geosci 13:323
Wang Q, Wu J, Li X, Zhou H, Yang J, Geng G, An X, Liu L, Tang Z (2017) A comprehensively quantitative method of evaluating the impact of drought on crop yield using daily multi-scale SPEI and crop growth process model. Int J Biometeorol 61(4):685e699
Wang LJ, Liao SH, Huang SB, Ming B, Meng QF, Wang P (2018) Increasing concurrent drought and heat during the summer maize season in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Int J Climatol 38:3177–3190
Wu J, Zhou L, Mo X, Zhou H, Zhang J, Jia R (2015) Drought monitoring and analysis in China based on the Integrated Surface Drought Index (ISDI). Int J Appl Earth Obs 41:23–33
Wu X, Wang PJ, Huo ZG, Wu DR, Yang JY (2018) Crop drought identification index for winter wheat based on evapotranspiration in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 263:18–30
**e WJ, Yang XG, Yang J, Liu LM, Ye Q, Dong CY, Liu ZJ, Zhao J (2014) Spatio-temporal characteristics of drought for soybean under climate change in the three provinces of northeast China. Acta Ecol Sin 34:6232–6243 (in Chinese)
Xu K, Yang D, Yang H, Li Z, Qin Y, Shen Y (2015) Spatiotemporal variation of drought in China during 1961–2012: a climatic perspective. J Hydrol 526:253–264
Xue CY, Ma ZH, Hu CD (2016) Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought during summer maize growing season in Huang-Huai-Hai area for recent 40 years. J Nat Disasters 25(2):1–14 (in Chinese)
Yang XL, Gao WS, Shi QH, Chen F, Chu Q (2013) Impact of climate change on the water requirement of summer maize in the Huang Huai Hai farming region. Agr Water Manage 124(2):20–27
Yang J, Mei X, Huo Z, Yan C, Ju H, Zhao F, Liu Q (2015) Water consumption in summer maize and winter wheat crop** system based on SEBAL model in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. J Integr Agr 14:2065–2076
Yang T, Xu Y, Sun X, Zhang J (2016) Design and application of the drought weather index insurance of summer corn in Anhui Province. Meteorol Mon 42(2):450–455 (in Chinese)
Yang X, Liu X, Bai W, Liu B (2017) Spatiotemporal assessment of soybean drought and sensitivity analysis in Northeast China. J Appl Meteorol Clim 56(4):937–952
Zhang Q, Zhang JQ (2016) Drought hazard assessment in typical corn cultivated areas of China at present and potential climate change. Nat Hazards 81(2):1323–1331
Zhang JJ, Wang XD (2014) Spatial-temporal analysis of the water surplus deficit index for the summer corn’s key period in the Huaihe Basin. Chin Agric Sci Bull 7(1):596–599 (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Lu H, Li S (2008) Applicability of crop water deficit index in agricultural drought monitoring. Meteorol Sci Technol 36:596–600 (in Chinese)
Zhang S, Zhang Y, Ji R, Cai F, Wu J (2011) Analysis of spatio-temporal characteristics of drought for maize in northeast China. Agric Res Arid Areas 29:231–236
Zhang Q, Qi T, Singh VP, Chen YD, **ao M (2015) Regional frequency analysis of droughts in china: a multivariate perspective. Water Resour Manag 29(6):1767–1787
Zhang Q, Zhang JQ, Wang CY (2017) Risk assessment of drought disaster in typical area of corn cultivation in China. Theor Appl Climatol 128:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1723-4
Zhang F, Chen Y, Zhang J, Guo E, Wang R, Li D (2019a) Dynamic drought risk assessment for maize based on crop simulation model and multi-source drought indices. J Clean Prod 233:100–114
Zhang Q, Yao Y, Wang Y, Wang S, Wang J, Yang J, Wang J, Li Y, Shang J, Li W (2019b) Characteristics of drought in Southern China under climatic warming, the risk, and countermeasures for prevention and control. Theor Appl Climatol 136:1157–1173
Zinat MRM, Salam R, Badhan MA, Islam ARMT (2020) Appraising drought hazard during Boro rice growing period in western Bangladesh. Int J Biometeorol 64(10):1697–1697
Funding
This study was jointly financed by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (grant no. 2019YFD1002202), the Special Scientific Research Fund of Meteorological Public Welfare Profession of China (grant no. GYHY201506001-06), and the Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Agricultural Meteorology Foundation (grant no. KYQ1404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZH Hu and ARM Towfiqul Islam designed the study. ZR Wu, XY You, C Liu, Q Li, and XS Zhang analyzed data and made figures. ZH Hu wrote original draft, and ARM Towfiqul Islam revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 639 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Z., Wu, Z., Islam, A.R.M.T. et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics and risk assessment of agricultural drought disasters during the winter wheat-growing season on the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Theor Appl Climatol 143, 1393–1407 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03506-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03506-8