Abstract
A kind of hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT) hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer (AT/MA-HMIPs) with high selectivity and hard silicon skeleton was successfully prepared based on double hybrid monomers. The relationship between templates and functional monomers was studied through computer molecular simulation and experiments. Three single-monomer molecularly imprinted polymers were prepared as controls. The Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic models were found to fit well with the adsorption results. The maximum adsorption capacity was 18.79 mg/g, and equilibrium was reached within 20 min. Moreover, it shows excellent selectivity (imprinting factor is 10.73) and good recoverability (after 10 adsorption-desorption cycles, the adsorption capacity only decreases by 7.75%) for HCPT. The purity of HCPT can reach 80.86% after being put into a solid phase extraction column and used in an actual sample, and the yield was 61.43%. This study lays the fundament for the development of excellent HCPT molecularly imprinted composites.
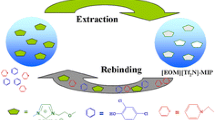
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao CJ, Zhang YK, Li CY, He X, Yang L, Fu Y et al (2016) Development of an ionic liquid-based ultrasonic/microwave-assisted simultaneous distillation and extraction method for separation of camptothecin, 10-hydroxycamptothecin, vincoside-lactam, and essential oils from the fruits of Camptotheca acuminata Decne. Appl Sci 6(10):293
Wang T, Li PF, Sun Y, Song XM, Li H, Qin LT et al (2020) Camptothecin-imprinted polymer microspheres with rosin-based cross-linker for separation of camptothecin from Camptotheca acuminata fruit. Sep Purif Technol 234:116085
Hu WC, Zhao YQ, Yang Y, Zhang HF, Ding CB, Hu C et al (2019) Microwave-assisted extraction, physicochemical characterization and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Camptotheca acuminata fruits. Int J Biol Macromol 133:127–136
Guo YY, Gao T, Fang F, Sun S, Yang DY, Li YJ et al (2021) A novel polymer micelle as a targeted drug delivery system for 10-hydroxycamptothecin with high drug-loading properties and anti-tumor efficacy. Biophys Chem 279:106679
Zhang QL, Liu LH, Ni YN (2022) Magnetic reduced graphene oxide (MrGO) nanocomposites as nano carries for loading and transferring of 10-hydroxycamptothecin. J Mol Liq 362:119680
Wang YT, Xuan JJ, Zhao GC, Wang DD, Ying N, Zhuang J (2021) Improving stability and oral bioavailability of hydroxycamptothecin via nanocrystals in microparticles (NCs/MPs) technology. Int J Pharm 604:120729
Cui GQ, Yang XB, Liu TT, Liu ZZ, Yang L (2018) An efficient approach for the enzyme-enhanced extraction of camptothecin and 10-hydroxycamptothecin from the samara of Camptotheca acuminata using an ionic liquid solution. Sep Purif Technol 200:102–111
Teixeira SPB, Reis RL, Peppas NA, Gomes ME, Domingues RMA (2021) Epitope-imprinted polymers: design principles of synthetic binding partners for natural biomacromolecules. Sci Adv 7(44):eabi9884
Li CY, Nie F, Feng CY, Tian MF, Yu MT, Zhao CJ et al (2022) Magnetic dual-template molecularly imprinted polymers for separation and enrichment of echinacoside and acteoside from Cistanche deserticola YC Ma. Chem Eng Res Des 182:719–732
Li XT, Wan JQ, Wang Y, Yan ZC, Chi HY, Ding S (2020) Mechanism of accurate recognition and catalysis of diethyl phthalate (DEP) in wastewater by novel MIL100 molecularly imprinted materials. Appl Catal B-Environ 266:118591
Nie F, Li CY, Ahmad N, Yuan ZY, Tan YL, Xu YW et al (2022) Molecularly imprinted polymer based on carboxymethylcellulose/graphene oxide composites for selective adsorption of hydroxycamptothecin. Acs Appl Polym Mater 4(12):9294–9304
Ayankojo AG, Reut J, Öpik A, Furchner A, Syritski V (2018) Hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer for amoxicillin detection. Biosens Bioelectron 118:102–107
Wei ZH, Zhang RR, Mu LN, Huang YP, Liu ZS (2019) Fabrication of core-shell sol-gel hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer based on metal–organic framework. Eur Polym J 121:109301
Da Silva AS, De Oliveira HL, Da Silva ATM, Do Nascimento TA, Borges KB (2017) Preparation of an organic–inorganic hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer for effective removal of albendazole sulfoxide enantiomers from aqueous medium. J Environ Chem Eng 5(6):6179–6187
Tang WY, Li GZ, Row KH, Zhu T (2016) Preparation of hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer with double-templates for rapid simultaneous purification of theophylline and chlorogenic acid in green tea. Talanta 152:1–8
Yang X, Wang RL, Wang WH, Yan HY, Qiu MD, Song YX (2014) Synthesis of a novel molecularly imprinted organic–inorganic hybrid polymer for the selective isolation and determination of fluoroquinolones in tilapia. J Chromatogr B 945-946:127–134
Yan HY, Wang MY, Han YH, Qiao FX, Row KH (2014) Hybrid molecularly imprinted polymers synthesized with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane-methacrylic acid monomer for miniaturized solid-phase extraction: a new and economical sample preparation strategy for determination of acyclovir in urine. J Chromatogr A 1346:16–24
Gao J, Yan L, Yan Y, Chen L, Lu J, **ng WD et al (2022) Solvent-driven controllable molecularly imprinted membrane with switched selectivity and fast regenerability enabled by customized bifunctional monomers. Chem Eng J 446:136991
Lu H, Liu MM, Cui HY, Huang Y, Li L, Ding YP (2022) An advanced molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based bifunctional monomers for highly sensitive detection of nitrofurazone. Electrochim Acta 427:140858
Li YG, Zhang L, Dang YY, Chen ZQ, Zhang RY, Li YC et al (2019) A robust electrochemical sensing of molecularly imprinted polymer prepared by using bifunctional monomer and its application in detection of cypermethrin. Biosens Bioelectron 127:207–214
Zhang JW, Tan L, Yuan JB, Qiao RF, Wang CZ, Yang FQ et al (2020) Extraction of activated epimedium glycosides in vivo and in vitro by using bifunctional-monomer chitosan magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers and identification by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Talanta 219:121350
Huang YF, Li YY, Wu YF, Huang XJ (2023) Computer-aided design-based green fabrication of magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for specific extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Chem Eng J 452:139440
Pan D, Zhu KF, Zhang YZ, Sun LX, Hao XH (2022) First principles and molecular dynamics simulation investigation of mechanical properties of the PTFE/graphene composites. Compos Part B-Eng 242:110050
Zhang PA, Yuan JM, Pang AM, Tang G, Deng JR (2020) A novel UV-curing liner for NEPE propellant: insight from molecular simulations. Compos Part B-Eng 195:108087
Frisch A, Hratchian HP, Dennington RD, Keith TA, Millam J, Nielsen B, et al. (2009) Gaussview 6.0. 8.
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR et al (2016) Gaussian 16. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT
Grimme S, Ehrlich S, Goerigk L (2011) Effect of the dam** function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J Comput Chem 32(7):1456–1465
Lu T, Chen FW (2012) Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J Comput Chem 33(5):580–592
Lu T, Chen QX (2022) Independent gradient model based on Hirshfeld partition: a new method for visual study of interactions in chemical systems. J Comput Chem 43(8):539–555
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph Model 14(1):33–38
Zu YG, Zhao CJ, Fu YJ, Li QY, Li CY (2004) Determination of camptothecin and hydroxycamptothecin by high performance liquid chromatography with changing detection wavelength. Anal Chem 32(11):1441–1444
Ma YM, Jiang MW, Liu XJ, Xu XY, Jiang XX, Chen LG et al (2022) Functionally modified cross-linked molecularly imprinted resins: separation and purification of camptothecin and its theoretical study. Ind Crop Prod 184:115078
He YQ, Fudickar W, Tang JH, Wang H, Stang PJ (2020) Capture and release of singlet oxygen in coordination-driven self-assembled organoplatinum(II) metallacycles. J Am Chem Soc 142(5):2601–2608
**an WW, Yi K, Jun PJ, Bin L, Fei XH (2022) Probing the mechanism of green solvent solubilization of hemicellulose based on molecular dynamics simulations. Ind Crop Prod 186(186):115159
Ling X (2009) Synthesis, characterization and application of molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres. Sichuan Normal University
Wang XG, Liu ZX, Lu J, Teng HH, Fukuda H, Qin WD et al (2022) Highly selective membrane for efficient separation of environmental determinands: enhanced molecular imprinting in polydopamine-embedded porous sleeve. Chem Eng J 449:137825
Tan L, Guo ML, Tan J, Geng YY, Huang SY, Tang YW et al (2019) Development of high-luminescence perovskite quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymers for pesticide detection by slowly hydrolysing the organosilicon monomers in situ. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 291:226–234
Shao HK, Zhou HB, Zhang TT, Zhao XL, Jiang ZJ, Wang QQ (2019) Preparation of molecularly imprinted hybrid monoliths for the selective detection of fluoroquinolones in infant formula powders. J Chromatogr A 1588:33–40
Cai XQ, Li JH, Zhang Z, Yang FF, Dong RC, Chen LX (2014) Novel Pb2+ ion imprinted polymers based on ionic interaction via synergy of dual functional monomers for selective solid-phase extraction of Pb2+ in water samples. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(1):305–313
da Mata K, Corazza MZ, de Oliveira FM, de Toffoli AL, Tarley CRT, Moreira AB (2014) Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked molecularly imprinted polyacrylamide for the extraction/preconcentration of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid from water samples. React Funct Polym 83:76–83
Li HH, Zhang WC, Wu ZY, Huang XS, Hui AL, He YW et al (2020) Theoretical design, preparation, and evaluation of Ginkgolide B molecularly imprinted polymers. J Sep Sci 43(2):514–523
Ma Y, Mao CY, Du XD, **e CS, Zhou JM, Tao XQ et al (2023) Insight into the application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in soil-washing effluent: selective removal of 4, 4′-dibromodiphenyl ether, high adaptivity of material and efficient recovery of eluent. Chemosphere 334:138990
Nanicuacua DM, Gorla FA, de Almeida SM, Segatelli MG, Tarley CRT (2022) Synthesis of a novel bifunctional hybrid molecularly imprinted poly (methacrylic acid-phenyltrimetoxysilane) for highly effective adsorption of diuron from aqueous medium. React Funct Polym 181:105432
Bhogal S, Mohiuddin I, Kim KH, Malik AK, Kaur K (2023) Restricted access medium magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: validation of their suitability as an effective quantitation tool against phthalates in food products packaged in plastic. Chem Eng J 457:141270
Zhu ZQ, Niu Y, Wang S, Su M, Long Y, Sun HX et al (2022) Magnesium hydroxide coated hollow glass microspheres/chitosan composite aerogels with excellent thermal insulation and flame retardancy. J Colloid Interface Sci 612:35–42
**ng WD, Ma ZF, Wang C, Gao J, Yu C, Yan YS et al (2023) Hierarchically porous molecularly imprinted membranes with multiple transfer channels for micropollutants selective separation. Desalination 547:116226
Fan L, Zhang Q, Wang F, Hf Y (2023) Dummy molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction-SERS determination of AFB1 in peanut. Spectrochim Acta A 288:122130
Qu Y, Qin L, Guo MC, Liu XG, Yang YZ (2022) Multilayered molecularly imprinted composite membrane based on porous carbon nanospheres/pDA cooperative structure for selective adsorption and separation of phenol. Sep Purif Technol 280:119915
Yang XX, Muhammad T, Yang JJ, Yasen A, Chen LX (2020) In-situ kinetic and thermodynamic study of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid adsorption on molecularly imprinted polymer based solid-phase microextraction coatings. Sensor Actuat A-Phys 313:112190
Zheng XD, Sun W, Li A, Zhang YZ, Li ZY (2022) Bacterial cellulose nanofibrous ion imprinted aerogel for highly efficient recognition and adsorption of Dy (III). Process Saf Environ 160:70–79
Wang LH, Zhang CY, Chen YJ, Deng QL, Wang S (2020) Dummy molecularly imprinted silica materials for effective removal of aristolochic acid I from kaempfer dutchmanspipe root extract. Microchem J 152:104463
Shi SY, Fan DX, **ang HY, Li HA (2017) Effective synthesis of magnetic porous molecularly imprinted polymers for efficient and selective extraction of cinnamic acid from apple juices. Food Chem 237:198–204
Yang LL, Li T, Yang DD, Li YJ, He JY, Zhou LD et al (2023) Constructing a dummy-template adsorbent using magnetic molecular-imprinted chitosan for rapid enrichment of flavonoids compounds from Penthorum chinense Pursh. Microchem J 191:108833
Lafarge C, Bitar M, El Hosry L, Cayot P, Bou-Maroun E (2020) Comparison of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) and sol–gel molecularly imprinted silica (MIS) for fungicide in a hydro alcoholic solution. Mater Today Commun 24:101157
Yang JH (2020) Study on extraction of Camptothecin and 10-hydroxycamptothecin from Camptotheca acuminata Decne leaves and new technology for separation and purification of 10-hydroxycamptothecin. Northeast Forestry University
Li JH (2009) Study on extraction and separation of main alkaloids from Camptotheca acuminata. Northeast Forestry University
Acknowledgements
The National Key Research and Development Project of China (2022YFD2200805), the Fundamental Research Fund for Central Universities (2572022DP06), Heilongjiang Touyan Innovation Team Program (Tree Genetics and Breeding Innovation Team), and the 111 Project, China (B20088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, F., Li, C., Qiao, B. et al. Computer-aided design of molecularly imprinted polymer reinforced by double hybrid monomers for selective purification of hydroxycamptothecin. Microchim Acta 190, 419 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05997-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05997-4