Abstract
Electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)-(PVA)-poly(acrylic acid) (PAA)/carbon nanotubes(CNTs)-cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) (PVA-PAA/CNT-CNC) composite nanofibers were prepared and characterized using Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy. The resultant composite was used as an effective and novel sorbent for pipette-tip micro-solid phase extraction (PT-μSPE) of seven opioid analgesics (OAs) in biological samples followed by HPLC-UV analysis. Addition of CNT-CNC with the high specific surface area and plenty of OH-functional groups endows the nanofibers with considerable extraction efficiency. Under the optimum conditions, the linearity was obtained in the range 1.5 to 700.0 ng mL−1 for morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and tramadol, and 0.5 to 1000.0 ng mL−1 for nalbuphine, thebaine, and noscapine with coefficient of determination (r2) ≥ 0.9990. Detection limits (LODs) based on S/N = 3 were in the range of 0.15–0.50 ng mL−1. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) of 4.1–5.4% (intra-day, n = 5) and 5.2–6.4% (inter-day, n = 3) for three consecutive days were achieved. Finally, the efficiency of the PT-μSPE-HPLC-UV method was evaluated for the determination of OAs in human plasma and urine samples with good recoveries (87.3 to 97.8%).
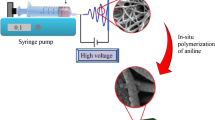
Graphical abstract

A: Schematic illustration for the preparation of PVA-PAA/CNT-CNC composite nanofibers.
B: Schematic presentation of applying PVA-PAA/CNT-CNC composite nanofibers as the sorbent in pipette-tip micro solid-phase extraction (PT–μSPE) for the preconcentration of seven opioid analgesic drugs in biological samples before HPLC–UV analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khosropour H, Rezaei B, Alinajafi HA, Ensafi AA (2021) Electrochemical sensor based on glassy carbon electrode modified by polymelamine formaldehyde/graphene oxide nanocomposite for ultrasensitive detection of oxycodone. Microchim Acta 188(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04655-3
Krizman-Matasic I, Kostanjevecki P, Ahel M, Terzic S (2018) Simultaneous analysis of opioid analgesics and their metabolites in municipal wastewaters and river water by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1533:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.12.025
Feliu C, Konecki C, Binet L, Vautier D, Haudecoeur C, Oget O, Fouley A, Marty H, Gozalo C, Cazaubon Y, Djerada Z (2020) Quantification of methadone, buprenorphine, naloxone, opioids, and their derivates in whole blood by liquid chromatographyhigh-resolution mass spectrometry: analysis of their involvement in fatal forensic cases. J Chromatogr B 1152:122226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122226
Amini S, Ebrahimzadeh H, Seidi S, Jalilian N (2020) Polyacrylonitrile/MIL-53(Fe) electrospun nanofiber for pipette-tip micro solid phase extraction of nitrazepam and oxazepam followed by HPLC analysis. Microchim Acta 187(2):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4112-3
Rohanifar A, Alipourasiabi N, Shyam Sunder GS, Lawrence JG, Kirchhoff JR (2020) Reversible chelating polymer for determination of heavy metals by dispersive micro solid-phase extraction with ICP-MS. Microchim Acta 187:339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04308-5
Ansari S, Masoum S (2021) A hybrid imprinted polymer based on magnetic graphene oxide and carbon dots for ultrasonic assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction of oxycodone. Microchem 164:105988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.105988
Amini S, Ebrahimzadeh H, Seidi S, Jalilian N (2020) Preparation of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/Ni-MOF-74 nanofibers for extraction of atenolol and captopril prior to HPLC-DAD. Microchim Acta 187(9):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04483-5
Sun T, Mujahid AM, Wang D, Du Z (2020) On-site rapid screening of benzodiazepines in dietary supplements using pipette-tip micro-solid phase extraction coupled to ion mobility spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1610:460547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460547
Wang R, Li C, Li Q, Zhang S, Lv F, Yan Z (2020) Electrospinning fabrication of covalent organic framework composite nanofibers for pipette tip solid phase extraction of tetracycline antibiotics in grass carp and duck. J Chromatogr A 1622:461098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461098
Uhlschmied C, Krieg C, Abel G, Popp M, Huck CW, Bonn GK (2013) Evaluation of commercial solid-phase extraction (SPE) carrier materials for the selective automated enrichment of monoterpenoides and their analysis in cough drops, mouthwashes and Bath additives by gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Anal.Chem. 7:12–21. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874065001307010012
Amini S, Ebrahimzadeh H, Seidi S, Jalilian N (2021) Preparation of Polyacrylonitrile/Ni-MOF electrospun nanofiber as an efficient fiber coating material for headspace solid-phase microextraction of diazinon and chlorpyrifos followed by CD-IMS analysis. Food Chem 350:129242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129242
Chen D, Xu H (2020) Electrospun core-shell nanofibers as an adsorbent for on-line micro-solid phase extraction of monohydroxy derivatives of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from human urine, and their quantitation by LC-MS. Microchim Acta 187:57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4007-3
Mehrani Z, Karimpour Z, Ebrahimzadeh H (2020) Using PVA/CA/au NPs electrospun nanofibers as a green nanosorbent to preconcentrate and determine Pb2+ and Cu2+ in rice samples, water sources and cosmetics. New J Chem 44:15000–15009. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ03352A
Cui J, Lu T, Li F, Wang Y, Lei J, Ma W, Zou Y, Huang C (2021) Flexible and transparent composite nanofibre membrane that was fabricated via a “green” electrospinning method for efficient particulate matter 2.5 capture. J Colloid Interface Sci 582:506–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.075
Pramanik C, Gissinger JR, Kumar S, Heinz H (2017) Carbon nanotube dispersion in solvents and polymer solutions: mechanisms, assembly, and preferences. ACS Nano 11:12805–12816. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b07684
Zhang S, Shi Q, Christodoulatos C, Meng X (2019) Lead and cadmium adsorption by electrospun PVA/PAA nanofibers: batch, spectroscopic, and modeling study. Chemosphere 233:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.190
Ates B, Koytepe S, Ulu A, Gurses C, Thakur VK (2020) Chemistry, structures, and advanced applications of nanocomposites from biorenewable resources. Chem Rev 120:9304–9362. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00553
Kulkarni PV, Roney CA, Antich P, Bonte FJ, Raghu AV, Aminabhavi TM (2010) Quinoline-n-butylcyanoacrylate-based nanoparticles for brain targeting for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, vol 2. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan
Suhas DP, Aminabhavi TM, Raghu AV (2014) Mixed matrix membranes of H-ZSM5-loaded poly(vinyl alcohol) used in pervaporation dehydration of alcohols: influence of silica/alumina ratio. R Eng Sci 54:1774–1782. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.23717
Atta NF, Galal A, Hassan SH (2019) Ultrasensitive determination of nalbuphine and tramadol narcotic analgesic drugs for postoperative pain relief using nano-cobalt oxide/ionic liquid crystal/carbon nanotubes-based electrochemical sensor. J Electroanal Chem 839:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.03.002
Sajid M, Khaled Nazal M, Ihsanullah I (2021) Novel materials for dispersive (micro) solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples: a review. Anal Chim Acta 1141:246–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.07.064
Wang X, Cheng WL, Wang D, Ni XH, Han GP (2019) Electrospun Polyvinylidene fluoride-based fibrous nanocomposite membranes reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals for efficient separation of water-in-oil emulsions. J Membr Sci 575:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.12.057
Huan SQ, Bai L, Cheng WL, Han GP (2016) Manufacture of electrospun all-aqueous poly(vinyl alcohol)/cellulose nanocrystal composite Nanofibrous Mats with enhanced properties through controlling fibers arrangement and microstructure. Polymer 92:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.03.082
Han J, Wang S, Zhu S, Huang C, Yue Y, Mei C, Xu X, **a C (2019) Electrospun core−shell nanofibrous membranes with nanocellulose-stabilized carbon nanotubes for use as high-performance flexible supercapacitor electrodes with enhanced water resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical toughness. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:44624–44635. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b16458
**e L, Huang J, Han Q, Song Y, Liuc P, Kang X (2019) Solid phase extraction with Polypyrrole nanofibers for simultaneously determination of three water-soluble vitamins in urine. J Chromatogr A 1589:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.12.062
Pourbahman F, Zeeb M, Monzavi A, Homami SS (2019) Simultaneous trace monitoring of prokinetic drugs in human plasma using magnetic dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on a new graphene oxide/metal–organic framework-74/Fe3O4/polytyramine nanoporous composite in combination with HPLC. Chem. 73:3135–3150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00855-1
Srivastava P K, Singh V P, Singh A, Tripathi D K, Singh S, Prasad S M, Chauhan D K (2020) Pesticides in Crop Production: Physiological and Biochemical Action, Wiley, New York, pp 221-231.
Yan Z, Wu M, Hu B, Yao M, Zhang L, Lu Q, Pang J (2018) Electrospun UiO-66/polyacrylonitrile nanofibers as efficient sorbent for pipette tip solid phase extraction of phytohormones in vegetable samples. J Chromatogr A 1542:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.02.030
Raghu AV, Jeong MH (2008) Synthesis, characterization of novel dihydrazide containing polyurethanes based onN1,N2-bis[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylene]ethanedihydrazide and various diisocyanates. J Appl Polym Sci 107:3401–3407. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.27447
Ishak WH, Ahmad I, Ramli S, Iqbal Mohd Ami MC (2018) Gamma irradiation-assisted synthesis of cellulose nanocrystal-reinforced gelatin hydrogels. Nanomaterials 8:749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100749
NozohourYazdi M, Yamini Y, Asiabi H (2018) Multiwall carbon nanotube- zirconium oxide nanocomposite hollow fiber solid phase microextraction for determination of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in water, coffee and tea samples. J Chromatogr A 1554:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.040
Fontanals N, Borrull F, Marcé RM (2013) On-line weak cationic mixed-mode solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry to determine illicit drugs at low concentration levels from environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1286:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.069
Boojaria A, Masrournia M, Ghorbani H, Ebrahimitalab A, Miandarhoie M (2015) Silane modified magnetic nanoparticles as a novel adsorbent for determination of morphine at trace levels in human hai samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 11:497–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-015-9702-8
Ahmar H, Nejati-Yazdinejad M, Najafi M, Hasheminasab K (2018) Switchable hydrophilicity solvent-based homogenous liquid–liquid microextraction (SHS-HLLME) combined with GC-FID for the quantification of methadone and tramadol. Chromatographia 81:1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3528-y
Song A, Wang J, Lu G, Jia Z, Yang J, Shi E (2018) Oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes coated fibers for headspace solid-phase microextraction of amphetamine-type stimulants in human urine. Forensic Sci Int 290:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.06.031
Hamid Y, Fat’Hi MR (2018) A simple vortex-assisted graphene oxide nanosheets dispersive micro-solid phase extraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for UV-Vis detection of tramadol in biological samples. Sep Purif Methods 53:1689–1697. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1439960
Seidi S, Yamini Y, Heydaria A, Moradi M, Esrafili A, Rezazadeh M (2011) Determination of thebaine in water samples, biological fluids, poppy capsule, and narcotic drugs, using electromembrane extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography analysis. Anal Chim Acta 701:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.05.042
Habibi B, Rostamkhani S, Hamidi M (2018) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for dispersive micro solid-phase extraction and determination of buprenorphine in human urine samples by HPLC-FL. J Iran Chem Soc 15:1569–1580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-018-1355-6
Moradi E, Mehrani Z, Ebrahimzadeh H (2020) Gelatin/sodium triphosphate hydrogel electrospun nanofiber mat as a novel nanosorbent for microextraction in packed syringe of La3+ and Tb3+ ions prior to their determination by ICP-OES. React Funct Polym 153:104627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104627
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
In this work, all scientific ethical practices have been considered and respected.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not applicable for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 645 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hejabri Kandeh, S., Amini, S. & Ebrahimzadeh, H. Simultaneous trace-level monitoring of seven opioid analgesic drugs in biological samples by pipette-tip micro solid phase extraction based on PVA-PAA/CNT-CNC composite nanofibers followed by HPLC-UV analysis. Microchim Acta 188, 275 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04931-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04931-w