Abstract
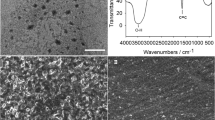
A disposable screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) modified with an ionic liquid/graphene composite (IL/G) exhibits a wider potential window, excellent conductivity, and specific surface area for the improvement in the voltammetric signal of rapamycin detection. The modified composite was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The electrochemical behavior of rapamycin at the modified SPCE was investigated by cyclic and square wave voltammetry in 60:40 EtOH: 0.1 M LiClO4 at pH 5.0. A high reproducible and well-defined peak with a high peak current were obtained for rapamycin detection at a position potential of + 0.98 V versus Ag/AgCl. Under the optimized conditions, the rapamycin concentration in the range 0.1 to 100 μM (R2 = 0.9986) had a good linear relation with the peak current. The detection limit of this method was 0.03 μM (3SD/slope). The proposed device can selectively detect rapamycin in the presence of commonly interfering compounds. Finally, the proposed method was successfully applied to determine rapamycin in urine and blood samples with excellent recoveries. These devices are disposable and cost-effective and might be used as an alternative tool for detecting rapamycin in biological samples and other biological compounds.

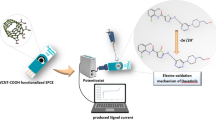
Schematic presentation of wide electrochemical window and disposable screen-printed sensor using ionic liquid/graphene composite for the determination of rapamycin. This composite can enhance the oxidation current and expand the potential for rapamycin detection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bielas J, Herbst A, Widjaja K, Hui J, Aiken JM, McKenzie D, Miller RA, Brooks SV, Wanagat J (2018) Long term rapamycin treatment improves mitochondrial DNA quality in aging mice. Exp Gerontol 106:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2018.02.021
Bäckman L, Kreis H, Morales JM, Wilczek H, Taylor R, Burke JT (2002) Sirolimus steady-state trough concentrations are not affected by bolus methylprednisolone therapy in renal allograft recipients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 54(1):65–68. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01594.x
Rao RN, Maurya PK, Ramesh M, Srinivas R, Agwane SB (2010) Development of a validated high-throughput LC-ESI-MS method for determination of sirolimus on dried blood spots. Biomed Chromatogr 24(12):1356–1364. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.1450
Cattaneo D, Perico N, Gaspari F (2002) Assessment of sirolimus concentrations in whole blood by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr B 774(2):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1570-0232(02)00204-0
Mochizuki N, Suka E, Matsumoto K, Akimoto O, Ohno K, Shimamura T, Furukawa H, Todo S, Kishino S (2009) Liquid chromatographic method for the determination of sirolimus in blood using electrochemical detection. Biomed Chromatogr 23(3):267–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.1109
Pieri M, Capone D, Gentile A, Miraglia N, Leo E, Federico S, Basile V, Acampora A (2007) Immunoassay determination of rapamycin: reliability of the method with respect to liquid chromatography mass spectrometric quantification. Clin Transpl 21(5):633–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2007.00701.x
Zhou Y, Yang Y, Deng X, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Shuang S, He Y, Sun W (2018) Electrochemical sensor for determination of ractopamine based on aptamer/octadecanethiol Janus particles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 276:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.08.110
Khorshed AA, Khairy M, Banks CE (2018) Voltammetric determination of meclizine antihistamine drug utilizing graphite screen-printed electrodes in physiological medium. J Electroanal Chem 824:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.07.029
Gupta VK, Jain R, Radhapyari K, Jadon N, Agarwal S (2011) Voltammetric techniques for the assay of pharmaceuticals—a review. Anal Biochem 408(2):179–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2010.09.027
Stanković DM, Kalcher K (2015) The immunosuppressive drug – rapamycin – electroanalytical sensing using boron- doped diamond electrode. Electrochim Acta 168:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.200
Mohamed HM (2016) Screen-printed disposable electrodes: pharmaceutical applications and recent developments. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 82:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.02.010
Biswas S, Drzal LT (2010) Multilayered nano-architecture of variable sized graphene nanosheets for enhanced supercapacitor electrode performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2(8):2293–2300. https://doi.org/10.1021/am100343a
Dong X, Wang X, Wang L, Song H, Zhang H, Huang W, Chen P (2012) 3D graphene foam as a monolithic and macroporous carbon electrode for electrochemical sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(6):3129–3133. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300459m
Ji D, Liu Z, Liu L, Low SS, Lu Y, Yu X, Zhu L, Li C, Liu Q (2018) Smartphone-based integrated voltammetry system for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid with graphene and gold nanoparticles modified screen-printed electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 119:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.07.074
Zhang S, Zhuang X, Chen D, Luan F, He T, Tian C, Chen L (2019) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of guanine and adenine using MnO2 nanosheets and ionic liquid-functionalized graphene combined with a permeation-selective polydopamine membrane. Microchim Acta 186(7):450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3577-4
Li X, Liu Y, Zheng L, Dong M, Xue Z, Lu X, Liu X (2013) A novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on silver nanoparticles and ionic liquid functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube composite modified electrode. Electrochim Acta 113:170–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.09.049
Sun W, Wang Y, Gong S, Cheng Y, Shi F, Sun Z (2013) Application of poly(acridine orange) and graphene modified carbon/ionic liquid paste electrode for the sensitive electrochemical detection of rutin. Electrochim Acta 109:298–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.124
Chaiyo S, Mehmeti E, Siangproh W, Hoang TL, Nguyen HP, Chailapakul O, Kalcher K (2018) Non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose with a disposable paper-based sensor using a cobalt phthalocyanine–ionic liquid–graphene composite. Biosens Bioelectron 102:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.11.015
Chaiyo S, Mehmeti E, Žagar K, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O, Kalcher K (2016) Electrochemical sensors for the simultaneous determination of zinc, cadmium and lead using a Nafion/ionic liquid/graphene composite modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Anal Chim Acta 918:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.03.026
Atta NF, Galal A, Ahmed YM (2019) New strategy for determination of anti-viral drugs based on highly conductive layered composite of MnO2/graphene/ionic liquid crystal/carbon nanotubes. J Electroanal Chem 838:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.02.056
Boobphahom S, Ruecha N, Rodthongkum N, Chailapakul O, Remcho VT (2019) A copper oxide-ionic liquid/reduced graphene oxide composite sensor enabled by digital dispensing: non-enzymatic paper-based microfluidic determination of creatinine in human blood serum. Anal Chim Acta 1083:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.07.029
Butmee P, Tumcharern G, Saejueng P, Stankovic D, Ortner A, Jitcharoen J, Kalcher K, Samphao A (2019) A direct and sensitive electrochemical sensing platform based on ionic liquid functionalized graphene nanoplatelets for the detection of bisphenol a. J Electroanal Chem 833:370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.12.014
Dosi M, Lau I, Zhuang Y, Simakov DSA, Fowler MW, Pope MA (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemical methane sensors based on solid polymer electrolyte-infused laser-induced graphene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(6):6166–6173. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b22310
Li Y, Liu R, Wang Q, Tang Q, Liu F, Jia J (2019) Poly(ionic liquids)/reduced graphene oxide miniemulsion polymers as effective support for immobilization of Ag nanoparticles and its amperometric sensing of l-cysteine. J Iran Chem Soc 16(1):201–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-018-1497-6
Govindhan M, Chen A (2016) Enhanced electrochemical sensing of nitric oxide using a nanocomposite consisting of platinum-tungsten nanoparticles, reduced graphene oxide and an ionic liquid. Microchim Acta 183(11):2879–2887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1936-y
Mahyari M (2016) Electrochemical sensing of thiodiglycol, the main hydrolysis product of sulfur mustard, by using an electrode composed of an ionic liquid, graphene nanosheets and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183(8):2395–2401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1881-9
Niu X, Chen W, Wang X, Men Y, Wang Q, Sun W, Li G (2018) A graphene modified carbon ionic liquid electrode for voltammetric analysis of the sequence of the Staphylococcus aureus nuc gene. Microchim Acta 185(3):167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2719-4
Islambulchilar Z, Ghanbarzadeh S, Emami S, Valizadeh H, Zakeri-Milani P (2012) Development and validation of an HPLC method for the analysis of sirolimus in drug products. Adv Pharm Bull 2(2):135–139. https://doi.org/10.5681/apb.2012.021
Berton N, Brachet M, Thissandier F, Le Bideau J, Gentile P, Bidan G, Brousse T, Sadki S (2014) Wide-voltage-window silicon nanowire electrodes for micro-supercapacitors via electrochemical surface oxidation in ionic liquid electrolyte. Electrochem Commun 41:31–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.01.010
Electrochemical Sensors. Idn: Analytical Electrochemistry. pp 201–243. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/0471790303.ch6
Gan T, Sun J, Cao S, Gao F, Zhang Y, Yang Y (2012) One-step electrochemical approach for the preparation of graphene wrapped-phosphotungstic acid hybrid and its application for simultaneous determination of sunset yellow and tartrazine. Electrochim Acta 74:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.039
Cincotto FH, Canevari TC, Machado SAS (2014) Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for determination of vitamin D in mixtures of water-ethanol. Electroanalysis 26(12):2783–2788. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201400451
Lee EJ, Kim H-K, Ahn S, Lee W, Kim HS, Chun S, Min W-K (2019) Accuracy evaluation of automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for everolimus and sirolimus compared to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Clin Lab Anal 33(7):e22941. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.22941
Jeong H-J, Itayama S, Ueda H (2015) A signal-on fluorosensor based on quench-release principle for sensitive detection of antibiotic rapamycin. Biosensors 5(2):131–140
Mastanamma SK, Reehana SK, Prudhvi L, Kiran R (2019) UV spectrophotometric method for the determination of sirolimus in bulk and its dosage form. Res J Pharm Technol 12(4):1655–1658. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00277.4
Gaumann A, Schlitt HJ, Geissler EK (2008) Immunosuppression and tumor development in organ transplant recipients: the emerging dualistic role of rapamycin. Transpl Int 21(3):207–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2007.00610.x
Funding
Financial support for this research was obtained from the Chulalongkorn University for the development of new faculty staff (DNS_62_032_61_001_1), the Ratchadaphiseksomphot Endowment Fund for a Postdoctoral Fellowship, the Thailand Research Fund via the Research Team Promotion Grant (RTA6080002), and the ASEA UNINET funding (Graz, Austria).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3613 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaiyo, S., Jampasa, S., Thongchue, N. et al. Wide electrochemical window of screen-printed electrode for determination of rapamycin using ionic liquid/graphene composites. Microchim Acta 187, 245 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4190-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4190-2