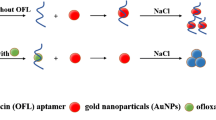
Abstract
A fluorometric method is described for the determination of ofloxacin (OFL). It is based on the use of the fluorescent intercalator SYBR Green I (SG-I). The OFL-aptamer has G-quadruplex structures and can be recognized by SG-I. It results in strong fluorescence of SG-I. If OFL is present, OFL will bind to its aptamer to form stable complexes. This induces the despiralization of partial dsDNA regions, leads to changes in the structure of the aptamer. Thus, SG-I is released from the OFL-aptamer into solution. Hence, the fluorescence of SG-I drops. Fluorescence decreases linearly in the 1.1 to 200 nM OFL concentration range, and the limit of detection is 0.34 nM. The method shows good selectivity to much interference including analogues, hormones, pesticides. It is also effortless and fast with the times of measurement of <40 min. In addition, good recoveries of 91.3–119.0% were found for tap water, river water and artificial urine spiked with OFL with relative standard deviation (RSD) of ≤11.6%.

A sensitive fluorometric method is developed for ofloxacin (OFL) detection in aqueous samples based on the fluorescence intensity change of SYBR Green I (SG-I) with or without OFL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitani K, Kataoka H (2006) Determination of fluoroquinolones in environmental waters by in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 562(1):16–22
Hooper DC, Wolfson JS (1985) The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicities in humans. Antimicrob Agents Ch 28(5):716–721
Chen T, Huang K, Chen J (2012) An electrochemical approach to simultaneous determination of acetaminophen and Ofloxacin. B Environ Contam Tox 89(6):1284–1288
Wong A, Silva TA, Vicentini FC, Fatibello-Filho O (2016) Electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide and ionic liquid for ofloxacin determination at nanomolar levels. Talanta 161(1):333–341
Timofeeva I, Timofeev S, Moskvin L, Bulatov A (2017) A dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using a switchable polarity dispersive solvent. Automated HPLC-FLD determination of ofloxacin in chicken meat. Anal Chim Acta 949(1):35–42
Chan KP, Chu KO, Lai WW, Choy KW, Wang CC, Lam DS, Pang CP (2006) Determination of ofloxacin and moxifloxacin and their penetration in human aqueous and vitreous humor by using high-performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection. Anal Biochem 353(1):30–36
Sun H, He P, Lv Y, Liang S (2007) Effective separation and simultaneous determination of seven fluoroquinolones by capillary electrophoresis with diode-array detector. J Chromatogr B 852(1–2):145–151
Wu F, Xu F, Chen L, Jiang B, Sun W, Wei X (2016) Cuprous oxide/nitrogen-doped graphene nanocomposites as electrochemical sensors for ofloxacin determination. CHEM Res Chinese U 32(3):468–473
Pagani AP, Ibañez GA (2019) Analytical approach for the simultaneous determination of quinolones in edible animal products. Modeling pH–modulated fluorescence excitation–emission matrices four–way arrays. Talanta 192(15):52–60
Wang X, Li Y, Li R, Yang H, Zhou B, Wang X, **e Y (2019) Comparison of chlorination behaviors between norfloxacin and ofloxacin: reaction kinetics, oxidation products and reaction pathways. Chemosphere 215:124–132
Vakh C, Pochivalov A, Koronkiewicz S, Kalinowski S, Postnov V, Bulatov A (2019) A chemiluminescence method for screening of fluoroquinolones in milk samples based on a multi-pum** flow system. Food Chem 270(1):10–16
Yan Z, Yi H, Wang L, Zhou X, Yan R, Zhang D, Wang S, Su L, Zhou S (2019) Fluorescent aptasensor for ofloxacin detection based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles and its effect on quenching the fluorescence of rhodamine B. Spectrochim Acta A 221(5):117203
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346(6287):818–822
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science (New York, NY) 249(4968):505–510
Abraham KM, Roueinfar M, Ponce AT, Lussier ME, Benson DB, Hong KL (2018) In vitro selection and characterization of a single-stranded DNA aptamer against the herbicide atrazine. Acs Omega 3(10):13576–13583
**ao S, Hu P, Li Y, Huang C, Huang T, **ao G (2009) Aptamer-mediated turn-on fluorescence assay for prion protein based on guanine quenched fluophor. Talanta 79(5):1283–1286
Yu F, Li H, Sun W, Zhao Y, Xu D, He F (2019) Selection of aptamers against Lactoferrin based on silver enhanced and fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Talanta 193(1):110–117
Liu K, Yan X, Mao B, Wang S, Deng L (2016) Aptamer-based detection of Salmonella enteritidis using double signal amplification by Klenow fragment and dual fluorescence. Microchim Acta 183(2):643–649
Reinemann C, von Fritsch UF, Rudolph S, Strehlitz B (2016) Generation and characterization of quinolone-specific DNA aptamers suitable for water monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 77:1039–1047
Pilehvar S, Reinemann C, Bottari F, Vanderleyden E, Van Vlierberghe S, Blust R, Strehlitz B, De Wael K (2017) A joint action of aptamers and gold nanoparticles chemically trapped on a glassy carbon support for the electrochemical sensing of ofloxacin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:1024–1035
Zhou X, Wang L, Shen G, Zhang D, **e J, Mamut A, Huang W, Zhou S (2018) Colorimetric determination of ofloxacin using unmodified aptamers and the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(7):355
Pu W, Zhao H, Huang C, Wu L, Xua D (2012) Fluorescent detection of silver(I) and cysteine using SYBR Green I and a silver(I)-specific oligonucleotide. Microchim Acta 177(1):137–144
Lv L, Li D, Liu R, Cui C, Guo Z (2017) Label-free aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection using SYBR Gold as a probe. Sensors Actuators B Chem 246:647–652
Yang C, Bie J, Zhang X, Yan C, Li H, Zhang M, Su R, Zhang X, Sun C (2018) A label-free aptasensor for the detection of tetracycline based on the luminescence of SYBR Green I. Spectrochim Acta A 202(5):382–388
Cai Y, Cai Y, Mou S, Lu Y (2006) High performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet photometric detection for the simultaneous determination of cephalosporins in human urine and bovine milk. Chin J Anal Chem 34(6):745–748
Zipper H, Brunner H, Bernhagen J, Vitzthum F (2004) Investigations on DNA intercalation and surface binding by SYBR Green I, its structure determination and methodological implications. Nucleic Acids Res 32(12):e103
Vitzthum F, Geiger G, Bisswanger H, Brunner H, Bernhagen J (1999) A quantitative fluorescence-based microplate assay for the determination of double-stranded DNA using SYBR Green I and a standard ultraviolet transilluminator gel imaging system. Anal Biochem 276(1):59–64
Yang Q, Li F, Huang Y, Xu H, Tang L, Wang L, Fan C (2013) Highly sensitive and selective detection of silver(I) in aqueous solution with silver(I)-specific DNA and Sybr green I. Analyst 138(7):2057–2060
Masiero S, Trotta R, Pieraccini S, De Tito S, Perone R, Randazzo A, Spada GP (2010) A non-empirical chromophoric interpretation of CD spectra of DNA G-quadruplex structures. Org Biomol Chem 8(12):2683–2692
Burge S, Parkinson GN, Hazel P, Todd AK, Neidle S (2006) Quadruplex DNA: sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res 34(19):5402–5415
Lan L, Wang R, Liu L, Cheng L (2019) A label-free colorimetric detection of microRNA via G-quadruplex-based signal quenching strategy. Anal Chim Acta 15(7):6260–6265
Xu H, Zhan S, Zhang D, **a B, Zhan X, Wang L, Zhou P (2015) A label-free fluorescent sensor for the detection of Pb2+ and Hg2+. Anal Methods-UK 7(15):6260–6265
Kypr J, Kejnovska I, Renciuk D, Vorlickova M (2009) Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 37(6):1713–1725
Zhan S, Xu H, Zhang W, Zhan X, Wu Y, Wang L, Zhou P (2015) Sensitive fluorescent assay for copper (II) determination in aqueous solution using copper-specific ssDNA and Sybr Green I. Talanta 142(1):176–182
Zhan S, Wu Y, Liu L, **ng H, He L, Zhan X, Luo Y, Zhou P (2013) A simple fluorescent assay for lead(ii) detection based on lead(ii)-stabilized G-quadruplex formation. RSC Adv 3(38):16962
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0800704), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21876109 & 41877494), and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY18B070029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 607 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, H., Yan, Z., Wang, L. et al. Fluorometric determination for ofloxacin by using an aptamer and SYBR Green I. Microchim Acta 186, 668 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3788-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3788-8