Abstract
This study reports on a simple approach for the fabrication of an electrode modified with biocompatible C-dot wrapped ZnO nanoparticles for selective photoelectrochemical monitoring of H2O2 released from living cells. The biocompatibility of the ZnO nanoparticles was confirmed through in-vitro cellular testing using the MTT assay on Huh7 cell lines. The ZnO nanoparticles wrapped with dopamine-derived C-dots possess numerous catalytically active sites, excessive surface defects, good electrical conductivity, and efficient separation ability of photo-induced electrons and holes. These properties offer highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic photo-electrochemical monitoring of H2O2 released from HeLa cells after stimulation with N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. The sensor has a wide linear range (20–800 nM), low detection limit (2.4 nM), and reliable reproducibility, this implying its suitability for biological and biomedical applications.

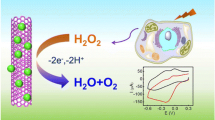
Schematic of the fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles by using a plant extract as a reducing agent. Wrap** of ZnO with C-dots enhances the photoelectrocatalytic efficacy. Sensitive and selective photoelectrochemical monitoring of H2O2 released from cancer cells is demonstrated.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
López ML, Uribe-Cruz C, Osvaldt A, Kieling CO, Simon L, Tobar S, Andrades M, Matte U (2016) Encapsulated platelets modulate kupffer cell activation and reduce oxidative stress in a model of acute liver failure. Liver Transpl 22(11):1562–1572
Córdova A, Sureda A, Albina ML, Linares V, Bellés M, Sánchez DJ (2015) Oxidative stress markers after a race in professional cyclists. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 25(2):171–178
Grisham MB (2013) Methods to detect hydrogen peroxide in living cells: possibilities and pitfalls. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 165(4):429–438
Nogueira RFP, Oliveira MC, Paterlini WC (2005) Simple and fast spectrophotometric determination of H2O2 in photo-Fenton reactions using metavanadate. Talanta 66(1):86–91
Reichert J, McNeight S, Rudel H (1939) Determination of hydrogen peroxide and some related peroxygen compounds. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 11(4):194–197
Gomes A, Fernandes E, Lima JL (2005) Fluorescence probes used for detection of reactive oxygen species. J Biochem Biophys Methods 65(2–3):45–80
Lyu Y-P, Wu Y-S, Wang T-P, Lee C-L, Chung M-Y, Lo C-T (2018) Hydrothermal and plasma nitrided electrospun carbon nanofibers for amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185(8):371
Zhao S, Zhang J, Li Z, Zhang P, Li Y, Liu G, Wang Y, Yue Z (2017) Photoelectrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide using a gold electrode modified with fluorescent gold nanoclusters and graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 184(3):677–686
Su Y, Zhou X, Long Y, Li W (2018) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on amino-functionalized carbon dots for the sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185(2):114
Liu J, Yang C, Shang Y, Zhang P, Liu J, Zheng J (2018) Preparation of a nanocomposite material consisting of cuprous oxide, polyaniline and reduced graphene oxide, and its application to the electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185(3):172
Zhang Y, Huang B, Yu F, Yuan Q, Gu M, Ji J, Zhang Y, Li Y (2018) 3D nitrogen-doped graphite foam@ Prussian blue: an electrochemical sensing platform for highly sensitive determination of H2O2 and glucose. Microchim Acta 185(2):86
Akhtar N, El-Safty SA, Khairy M, El-Said WA (2015) Fabrication of a highly selective nonenzymatic amperometric sensor for hydrogen peroxide based on nickel foam/cytochrome c modified electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 207:158–166
Li H, Hao W, Hu J, Wu H (2013) A photoelectrochemical sensor based on nickel hydroxyl-oxide modified n-silicon electrode for hydrogen peroxide detection in an alkaline solution. Biosens Bioelectron 47:225–230
Amanulla B, Palanisamy S, Chen S-M, Velusamy V, Chiu T-W, Chen T-W, Ramaraj SK (2017) A non-enzymatic amperometric hydrogen peroxide sensor based on iron nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. J Colloid Interface Sci 487:370–377
Hussain I, Singh N, Singh A, Singh H, Singh S (2016) Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol Lett 38(4):545–560
Liu R, Mahurin SM, Li C, Unocic RR, Idrobo JC, Gao H, Pennycook SJ, Dai S (2011) Dopamine as a carbon source: the controlled synthesis of hollow carbon spheres and yolk-structured carbon nanocomposites. Angew Chem 50(30):6799–6802
Khan F, Hashmi MU, Khalid N, Hayat MQ, Ikram A, Janjua HA (2016) Controlled assembly of silver nano-fluid in Heliotropium crispum extract: a potent anti-biofilm and bactericidal formulation. Appl Surf Sci 387:317–331
Akhtar N, El-Safty SA, Abdelsalam ME, Kawarada H (2015) One-pot fabrication of dendritic NiO@ carbon–nitrogen dot electrodes for screening blood glucose level in diabetes. Adv Healthc Mater 4(14):2110–2119
Sundrarajan M, Ambika S, Bharathi K (2015) Plant-extract mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pongamia pinnata and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Adv Powder Technol 26(5):1294–1299
Fu L, Fu Z (2015) Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract–assisted biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int 41(2):2492–2496
Barman MK, Mitra P, Bera R, Das S, Pramanik A, Parta A (2017) An efficient charge separation and photocurrent generation in the carbon dot–zinc oxide nanoparticle composite. Nanoscale 9(20):6791–6799
Bauermann LP, Bill J, Aldinger F (2006) Bio-friendly synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles in aqueous solution at near-neutral pH and low temperature. J Phys Chem B 110(11):5182–5185
Warkocki W, El-Safty SA, Shenashen MA, Elshehy E, Yamaguchi H, Akhtar N (2015) Photo-induced recovery, optical detection, and separation of noxious SeO 3 2− using a mesoporous nanotube hybrid membrane. J Mater Chem A 3(34):17578–17589
Chi P-W, Su C-W, Wei D-H (2017) Internal stress induced natural self-chemisorption of ZnO nanostructured films. Sci Rep 7:43281
Wang C, Hu X, Gao Y, Ji Y (2015) ZnO nanoparticles treatment induces apoptosis by increasing intracellular ROS levels in LTEP-a-2 cells. Biomed Res Int 2015
Akhtar MJ, Alhadlaq HA, Alshamsan A, Khan MM, Ahamed M (2015) Aluminum do** tunes band gap energy level as well as oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in MCF-7 cells. Sci Rep 5:13876
Yin H, Casey PS, McCall MJ, Fenech M (2010) Effects of surface chemistry on cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and the generation of reactive oxygen species induced by ZnO nanoparticles. Langmuir 26(19):15399–15408
Batra N, Tomar M, Gupta V (2012) Realization of an efficient cholesterol biosensor using ZnO nanostructured thin film. Analyst 137(24):5854–5859
Kim W, Son Y, Pawar A, Kang M, Zheng J, Sharma V, Mohanty P, Kang Y (2015) Facile fabrication and photoelectrochemical properties of a one axis-oriented NiO thin film with a (111) dominant facet. J Mater Chem A 3:447–447
Yue Z, Lisdat F, Parak WJ, Hickey SG, Tu L, Sabir N, Dorfs D, Bigall NC (2013) Quantum-dot-based photoelectrochemical sensors for chemical and biological detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(8):2800–2814
Zhang J, Tu L, Zhao S, Liu G, Wang Y, Wang Y, Yue Z (2015) Fluorescent gold nanoclusters based photoelectrochemical sensors for detection of H2O2 and glucose. Biosens Bioelectron 67:296–302
Zhang R, Jiang C, Fan X, Yang R, Sun Y, Zhang C (2018) A gold electrode modified with a nanoparticulate film composed of a conducting copolymer for ultrasensitive voltammetric sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185(1):58
Li Z, **n Y, Zhang Z (2015) New photocathodic analysis platform with quasi-core/shell-structured TiO2@Cu2O for sensitive detection of H2O2 release from living cells. Anal Chem 87(20):10491–10497
Li Z, **n Y, Wu W, Fu B, Zhang Z (2016) Topotactic conversion of copper (I) phosphide nanowires for sensitive electrochemical detection of H2O2 release from living cells. Anal Chem 88(15):7724–7729
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 965 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F., Akhtar, N., Jalal, N. et al. Carbon-dot wrapped ZnO nanoparticle-based photoelectrochemical sensor for selective monitoring of H2O2 released from cancer cells. Microchim Acta 186, 127 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3227-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3227-x