Abstract
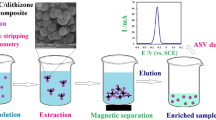
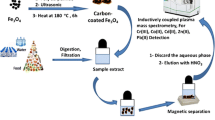
The authors describe double-shell magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) to give nanospheres of the type MBT-Fe3O4@SiO2@C). These are shown to be viable and acid-resistant adsorbents for magnetic separation of the heavy metal ions Ni(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II). MBT act as a binding reagent, and the carbon shell and the silica shell protect the magnetic core. Following 12 min incubation, the loaded nanospheres are magnetically separated, the ions are eluted with 2 M nitric acid and then determined by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy. The limits of detection of this method are 2, 82 and 103 ng L‾1 for Ni(II), Cu(II), and Pb(II) ions, respectively, and the relative standard deviations (for n = 7) are 6, 7.8, and 7.4 %. The protocol is successfully applied to the quantitation of these ions in tap water and food samples (mint, cabbage, potato, peas). Recoveries from spiked water samples ranged from 97 to 100 %.

Mercaptobenzothiazole-functionalized magnetic carbon nanospheres of type Fe3O4@SiO2@C were synthesized. Then applied for magnetic solid phase extraction of Ni(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II) from water and food samples with LOD of 0.002, 0.082 and 0.103 μg L−1 respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang H, Chen L, Zhang LP, Yu XJ (2010) Investigation of radionuclide 63Ni(II) sorption on ZSM-5 zeolite. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287:357–365
AlOthman ZA, Habila MA, Hashem A (2013) Removal of zinc(II) from aqueous solutions using modified agricultural wastes: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Arab J Geosci 6:4245–4255
Baig JA, Kazi TG, Kazi SAQ, Arain MB, Afridi HI, Kandhro GA, Khan S (2009) Ptimization of cloud point extraction and. Solid phase extraction methods for speciation of arsenic in natural water using multivariate technique. Anal Chim Acta 651:57–63
Kandhro GA, Soylak M, Kazi TG (2014) Solid phase extraction of thorium on multiwalled carbon nanotubes prior to UV-Vis spectrophotometric determination in ore samples. At Spectrosc 35:267–171
Li C, Zhang Z, Pan J, Gao J, Zhao G, Guan W, Yan Y (2010) Synthesis and characterisation of sodium trititanate whisker surface Cd(II) ion-imprinted polymer and selective solid-phase extraction of cadmium. Int J Mater Struct Integr 4:291–307
Taghizadeh M, Asgharinezhad AA, Samkhaniany N, Tadjarodi A, Abbaszadeh A, Pooladi M (2014) Solid phase extraction of heavy metal ions based on a novel functionalized magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube composite with the aid of experimental design methodology. MicrochimActa 181:597–605
Mahmoud ME, Soliman EM (1997) Silica-immobilized formylsalicylic acid as a selective phase for the extraction of iron(III). Talanta 44:15–22
Wang X, Zheng Y, Wang A (2009) Fast removal of copper ions from aqueous solution by chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite composites. J Hazard Mater 168:970–977
Habila M, Yilmaz E, ALOthman ZA, Soylak M (2014) Flame atomic adsorption spectrometric determination of Cd, Pb and Cu in food samples after preconcentration using 4-(2-thiazolylazo) resorcinol-modified activated carbon. J Ind Eng Chem 20:3989–3993
AlOthman ZA, Habila MA, Yilmaz E, Soylak M (2012) Solid phase extraction of Cd(II), Pb(II), Zn(II) and Ni(II) from food samples using multiwalled carbon nanotubes impregnated with 4-(2-thiazolylazo)resorcinol. Microchim Acta 177:397–403
El-Toni AM, Habila MA, Ibrahim MA, Labis JP, ALOthman ZA (2014) Simple and facile synthesis of amino functionalized hollow core-mesoporous shell silica spheres using anionic surfactant for Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) adsorption and recovery. Chem Eng J 251:441–450
Wang X, Guo Y, Yang L, Han M, Zhao J, Cheng X (2012) Nanomaterials as sorbents to remove heavy metal ions in wastewater treatment. J Environ Anal Toxicol 2(7):154–161
Zhao D, Jaroniec M, Hsiao BS (2010) Separation/preconcentration of trace amounts of Cr, Cu and Pb in environmental samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction with Bismuthiol-II immobilized magnetic nanoparticles and their determination by ICP-OES. J Mater Chem 20:4476–4477
Sadeghi S, Azhdari H, Arabi H, Moghaddam AZ (2012) Surface modified magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a selective sorbent for solid phase extraction of uranyl ions from water samples. J Hazard Mater 215:208–216
Wang J, Zheng S, Shao Y, Liu J, Xu Z, Zhu D (2010) Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 349:293–299
Shishehbore MR, Afkhami A, Bagheri H (2011) Salicylic acid functionalized silicacoated magnetite nanoparticles for solid phase extraction and preconcentration of some heavy metal ions from various real samples. CHEM CENT J 5(41):1–10
Wan SR, Huang JS, Yan HS, Liu KL (2006) Characterization and analytical application of surface modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 16:298–303
Deng Y, Qi D, Deng C, Zhang X, Zhao D (2008) Superparamagnetic high-magnetization microspheres with an Fe3O4@SiO2 core and perpendicularly aligned mesoporous SiO2 shell for removal of microcystins. J Am Chem Soc 130:28–29
Li Y, Leng TH, Lin HQ, Deng CH, Xu XQ, Yao N, et al. (2007) Preparation of Fe3O4@ZrO2 core-shell microspheres as affinity probes for selective enrichment and direct determination of phosphopeptides using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 6:4498–4510
Kong L, Lu X, Bian X, Zhang W, Wang C (2011) Constructing carbon-coated Fe3O4 microspheres as antiacid and magnetic support for palladium nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Appl Mater Interfaces 3:35–42
Shen HY, Zhu Y, Wen XE, Zhuang YM (2007) Preparation of Fe3O4-C18 nano-magnetic composite materials and their cleanup properties for organophosphorous pesticides. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:2227–2237
Wu X, Hu J, Zhu B, Lu L, Huang X, Pang D (2011) Aptamer-targeted magnetic spheres as a solid-phase extraction sorbent for determination of ochratoxin a in food samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:7341–7346
You LJ, Xu S, Ma WF, Li D, Zhang YT, Guo J, et al. (2012) Ultrafast hydrothermal synthesis of high quality magnetic Core phenol − formaldehyde Shell composite microspheres using the microwave method. Langmuir 28:10565–10572
Yoon T, Chae C, Sun YK, Zhao X, Kung HH, Lee JK (2011) Bottom-up in situ formation of Fe3O4 nanocrystals in a porous carbon foam for lithium-ion battery anodes. J Mater Chem 21:17325–17330
Zhang XB, Tong HW, Liu SM, Yong GP, Guan YF (2013) An improved Stöber method towards uniform and monodisperse Fe3O4@C spheres. J Mater Chem A 1:7488–7493
**ong Z, Qin H, Wan H, Huang G, Zhang Z, Dong J, et al. (2013) Layer-by-layer assembly of multilayer polysaccharide coated magnetic nanoparticles for the selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Chem Commun 49:9284–9286
**ao J, Qiu L, Jiang X, Zhu Y, Ye S, Jiang X (2013) Magnetic porous carbons with high adsorption capacity synthesized by a microwave-enhanced high temperature ionothermal method from a Fe-based metal-organic framework. Carbon 59:372–382
Aomoa N, Sarmah T, Deshpande UP, Sathe V, Banerjee A, Shripathi T, et al. (2015) Plasma-assisted synthesis of carbon encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles with controlled sizes correlated to smooth variation of magnetic properties. Carbon 84:24–37
Sevilla M, Valle-Vigo’n P, Fuertes AB (2011) N-doped Polypyrrole-based porous carbons for CO2 capture. Adv Funct Mater 21:2781–2787
Wang L, Yin J, Zhao L, Tian C, Yu P, Wang J, et al. (2013) Ion-exchanged route synthesis of Fe2N–N-doped graphitic nanocarbons composite as advanced oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. Chem Commun 49:3022–3024
Parham H, Zargar B, Shiralipour R (2012) Fast and efficient removal of mercury from water samples using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole. J Hazard Mater 94:205–206
Liu J, Sun Z, Deng Y, Zou Y, Li C, Guo X, et al. (2009) Highly water-dispersible biocompatible magnetite particles with low cytotoxicity stabilized by citrate groups. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:5875–5879
El-Toni AM, Ibrahim MA, Labis JP, Khan A, Alhoshan M (2013) Optimization of synthesis parameters for mesoporous shell formation on magnetic nanocores and their application as nanocarriers for docetaxel cancer drug. In J Mol Sci 14:11496–11509
Yang TY, Liu J, Zheng Y, Monteiro M, Qiao SZ (2013) Facile frabrication of core-shell structured ag@carborn and mesoporous yolk-shell structured Ag@carbon@silica by an extended stober method. Chemistry - A Europe J 19:6942–6945
Yamamoto Y, Nishimura T, Suzuki T, Tamon H (2001) Control of mesoporosity of carbon gels prepared by sol–gel polycondensation and freeze drying. J Non-Cryst Solids 288(1–3):46–55
Gong JY, Li SZ, Zhang DG, Zhang XB, Liu C, Tong ZW (2010) High quality self-assembly magnetite (Fe3O4) chain-like core-shell nanowires with luminescence synthesized by a facile one-pot hydrothermal process. Chem Commun 46:3514–3516
Mouaziz H, Veyret R, Theretz A, Ginot F, Elaissari A (2009) Aminodextran containing magnetite nanoparticles for molecular biology applications: preparation and evaluation. J Biomed Nanotechnol 5:172–182
Li CH, Qi SH, Zhang DN (2010) Thermal degradation of environmentally friendly phenolic resin/Al2O3 hybrid composite. J Appl Polym Sci 115:3675–3679
Huang X, Wang G, Yang M, Guo W, Gao H (2011) Synthesis of polyanilinemodified Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 composite microsphere and photocatalytic application. Mater Lett 65:2887–2890
Soliman EM, Mahmoud ME, Ahmed SA (2001) Synthesis, characterization and structure effects on selectivity properties of silica gel covalently bonded diethylenetriamine mono- and bis-salicyaldehyde and naphthaldehyde Schiff,s bases towards some heavy metal ions. Talanta 54(2):243–248 250-253
Pearson RG (1963) Hard and soft acids and bases. Am Chem Soc 85:3533–3539
**e F, Lin X, Wu X, **e Z (2008) Solid phase extraction of lead (II), copper (II), cadmium (II) and nickel (II) using gallic acid-modified silica gel prior to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 74:836–843
AlOthman ZA, Unsal YE, Habila M, Tuzen M, Soylak M (2015) A membrane filtration procedure for the enrichment, separation, and flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations of some metals in water, hair, urine, and fish samples. Desalin Water Treat 53(13):3457–3465
Habila MA, ALOthman ZA, El-Toni AM, Labis JP, Soylak M (2016) Synthesis and application of Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 for photocatalytic decomposition of organic matrix simultaneously with magnetic solid phase extraction of heavy metals prior to ICP-MS analysis. Talanta 154:539–547
Shahamirifarda SAR, Ghaedia M, Rahimi MR, Hajati S, Montazerozohori S, Soylak M (2016) Simultaneous extraction and preconcentration of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ ions using Ag nanoparticle-loaded activated carbon: response surface methodology. Adv Powder Technol 27:426–435
Yilmaz E, Alosmanov RM, Soylak M (2015) Magnetic solid phase extraction of lead (II) and cadmium (II) on a magnetic phosphorus-containing polymer (M-PhCP) for their microsampling flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. RSC Adv 5:33801–33808
Kandhro GA, Soylak M, Kazi TG, Yilmaz E, Afridi HI (2012) Room temperature ionic liquid based Microextraction for pre-concentration of cadmium and copper from biological samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. At Spectrosc 33:166–172
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding this work through Research Group No. RG–1435–002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 573 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habila, M.A., ALOthman, Z.A., El-Toni, A.M. et al. Mercaptobenzothiazole-functionalized magnetic carbon nanospheres of type Fe3O4@SiO2@C for the preconcentration of nickel, copper and lead prior to their determination by ICP-MS. Microchim Acta 183, 2377–2384 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1880-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1880-x