Abstract
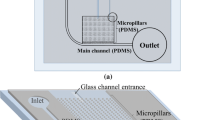
Blood separation is an essential first step when performing blood tests for clinical diagnosis purposes. Such tests are increasingly performed using microfluidic systems due to their rapid response time, low cost and potential for automated operation. This study proposes a simple microfluidic chip comprising a straight microchannel and a grating-type plasma filtration microchannel for the automatic separation of plasma from whole human blood for further biochemical detection. In the proposed device, the whole blood sample is introduced into the microfluidic chip by means of capillary forces and the plasma is then extracted from the whole blood via a size exclusion effect induced in the plasma filtration channel. The experimental results show that the plasma is extracted with an average flow rate of 0.01 μL/s. Moreover, the plasma collected in the outlet reservoirs has a residual cell concentration of less than 0.1%. The feasibility of the proposed device for clinical applications is demonstrated by means of creatinine detection tests with sample concentrations ranging from 0.11 to 1.78 mg/dL (10–160 μM) and prothrombin time (PT) tests with blood samples drawn from 20 healthy individuals. The experimental results show that the device has a detection sensitivity and degree of linearity of 12.68 count/μM and 95.38%, respectively. Moreover, the mean coagulation time in the PT tests is equal to approximately 13.3 s.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X, Cui DF, Liu CC, Li H (2007) Microfluidic chip for blood cell separation and collection based on crossflow filtration. Sens Actuator B 130:216–221
Crowley TA, Pizziconi V (2005) Isolation of plasma from whole blood using planar microfilters for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 5:922–929
Dimov IK, Basabe-Desmonts L, Garcia-Cordero JL, Ross BM, Ricco AJ, Lee LP (2011) Stand-alone self-powered integrated microfluidic blood analysis system (SIMBAS). Lab Chip 11:845–850
Fan R, Vermesh O, Srivastava A, Yen BKH, Qin L, Ahmad H, Kwong GA, Liu CC, Gould J, Hood L, Heath JR (2008) Integrated barcode chips for rapid, multiplexed analysis of proteins in microliter quantities of blood. Nat Biotechnol 26:1373–1378
Haeberle S, Brenner T, Zengerle R, Ducŕee J (2006) Centrifugal extraction of plasma from whole blood on a rotating disk. Lab Chip 6:776–781
Huang Y, Joo S, Duhon M, Heller M, Wallace B, Xu X (2002) Dielectrophoretic cell separation and gene expression profiling on microelectronic chip arrays. Anal Chem 74:3362–3371
Huang LR, Cox EC, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2004) Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304:987–990
Inglis DW, Riehn R, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2004) Continuous microfluidic immunomagnetic cell separation. Appl Phys Lett 85:5093–5095
Jäggi RD, Sandoz R, Effenhauser CS (2007) Microfluidic depletion of red blood cells from whole blood in high-aspect-ratio microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:47–53
Jung J, Han KH (2008) Lateral-driven continuous magnetophoretic separation of blood cells. Appl Phys Lett 93:223902
Kim JH, Woenker T, Adamec J, Regnier FE (2013) Simple, miniaturized blood plasma extraction method. Anal Chem 85:11501–11508
Kuo JN, Li BS (2014) Lab-on-CD microfluidic platform for rapid separation and mixing of plasma from whole blood. Biomed Microdevices 16:549–558
Kuo JN, Zhan YH (2015) Microfluidic chip for rapid and automatic extraction of plasma from whole human blood. Microsyst Technol 21:255–261
Lenshof A, Ahmad-Tajudin A, Jaras K, Sward-Nilsson AM, Aberg L, Gr Marko-Varga, Malm J, Lilja H, Laurell T (2009) Acoustic whole blood plasmapheresis chip for prostate specific antigen microarray diagnostics. Anal Chem 81(15):6030–6037
Lin CH, Lee GB, Lin YH, Chang GL (2001) A fast prototy** process for fabrication of microfluidic systems on soda-lime glass. J Micromech Microeng 11:726–732
Mach AJ, Carlo DD (2010) Continuous scalable blood filtration device using inertial microfluidics. Biotechnol Bioeng 107:302–311
Moorthy J, Beebe DJ (2003) In situ fabricated porous filters for microsystems. Lab Chip 3:62–66
Nakashima Y, Hata S, Yasuda T (2010) Blood plasma separation and extraction from a minute amount of blood using dielectrophoretic and capillary forces. Sens Actuators B 145:561–569
Petersson F, Aberg L, Sward-Nilsson AM, Laurell T (2007) Free flow acoustophoresis: microfluidic-based mode of particle and cell separation. Anal Chem 79:5117–5123
Smistrup K, Hansen O, Bruus H, Hansen MF (2005) Magnetic separation in microfluidic systems using microfabricated electromagnets-experiments and simulations. J Magn Magn Mater 293:597–604
Songjaroen T, Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS, Laiwattanapaisal W (2012) Blood separation on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Lab Chip 12:3392–3398
Szydzik C, Khoshmanesh K, Mitchell A, Karnutsch C (2015) Microfluidic platform for separation and extraction of plasma from whole blood using dielectrophoresis. Biomicrofluidics 9(6):064120
Tachi T, Kaji N, Tokeshi M, Baba Y (2009) Simultaneous separation, metering, and dilution of plasma from human whole blood in a microfluidic system. Anal Chem 81:3194–3198
Thorslund S, Klett O, Nikolajeff F, Markides K, Bergquist J (2006) A hybrid poly(dimethylsiloxane) microsystem for on-chip whole blood filtration optimized for steroid screening. Biomed Microdevices 8:73–79
Toner M, Irimia D (2005) Blood-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7:77–103
Tripathi S, Kumar YVBV, Prabhakar A, Joshi SS, Agrawal A (2015) Passive blood plasma separation at the microscale: a review of design principles and microdevices. J Micromech Microeng 25:083001
VanDelinder V, Groisman A (2006) Separation of plasma from whole human blood in a continuous cross-flow in a molded microfluidic device. Anal Chem 78:3765–3771
Voldman J, Gray ML, Toner M, Schmidt MA (2002) A microfabrication-based dynamic array cytometer. Anal Chem 74:3984–3990
Yang S, Undar A, Zahn JD (2006) A microfluidic device for continuous, real time blood plasma separation. Lab Chip 6:871–880
Yang X, Forouzan O, Brown TP, Shevkoplyas SS (2012) Integrated separation of blood plasma from whole blood for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Lab Chip 12:274–280
Zhang J, Guo Q, Liu M, Yang J (2008) A lab-on-CD prototype for high-speed blood separation. J Micromech Microeng 18:125025
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided to this study by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grant no. NSC 104-2221-E-150-056. In addition, the access provided to fabrication equipment by the Common Lab for Micro/Nano Science and Technology of National Formosa University is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, JN., Lin, BY. Microfluidic blood-plasma separation chip using channel size filtration effect. Microsyst Technol 24, 2063–2070 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3607-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3607-2