Abstract
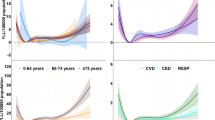
This study used the time series data of Ganzhou city to explore the individual and interaction effects of temperature and humidity on COPD death, and identify vulnerable subgroups of the population. We collected daily COPD mortality and meteorological data in Ganzhou from 2016 to 2019. The nonlinear distribution lag model was used to examine the associations and interaction between daily mean temperature and humidity and COPD mortality. For the total population, male and 65 years old or above, the relative risk (RR) for COPD mortality could be significant at extremely low temperature (3.3 ℃), reaching 1.799 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.216, 2.662), 1.894 (95% CI: 1.164, 3.084) and 1.779 (95% CI:1.185, 2.670). Also, at extremely low humidity (47.8%), the risk reached 1.888 (95% CI: 1.217, 2.930), 1.837 (95% CI: 1.066, 3.165) and 2.166 (95% CI: 1.375, 3.414). The cumulative COPD death risk for females was 3.524 (95% CI: 1.340, 9.267) at high temperature (30.7 ℃), 1.953(95% CI: 1.036, 3.683) at low humidity (47.8%) and 1.726 (95% CI: 1.048, 2.845) at high humidity (96.7%). For the total COPD deaths and subgroups, the interaction effects between daily temperature and humidity were not significant (p > 0.05). Both extremely low temperature and low humidity increased the risk of COPD death in Ganzhou city, especially for males and people over 65 years old. Females were more sensitive to extremely high temperature and humidity. Patients with COPD should pay attention to self-protection under extreme temperature and humidity weather conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets generated and/or analyzed in the course of the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Adeloye D, Song P, Zhu Y, Campbell H, Sheikh A, Rudan I (2022) Global, regional, and national prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2019: a systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir Med 10:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(21)00511-7
Bao HR, Liu XJ, Tan EL, Shu J, Dong JY, Li S (2020) Effects of temperature and relative humidity on the number of outpatients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their interaction effect in Lanzhou, China. Bei**g Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 52:308–316. https://doi.org/10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.02.019
Chen C, Liu X, Wang X, Li W, Qu W, Dong L, Li X, Rui Z, Yang X (2019) Risk of temperature, humidity and concentrations of air pollutants on the hospitalization of AECOPD. PLoS One 14:e0225307. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225307
Chen J, Yang J, Zhou M, Yin P, Wang B, Liu J, Chen Z, Song X, Ou CQ, Liu Q (2019) Cold spell and mortality in 31 Chinese capital cities: Definitions, vulnerability and implications. Environ Int 128:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.04.049
Davis RE, McGregor GR, Enfield KB (2016) Humidity: A review and primer on atmospheric moisture and human health. Environ Res 144:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.10.014
de’Donato F K, Leone M, Scortichini M, De Sario M, Katsouyanni K, Lanki T, Basagaña X, Ballester F, Åström C, Paldy A, Pascal M, Gasparrini A, Menne B, Michelozzi P (2015) Changes in the Effect of Heat on Mortality in the Last 20 Years in Nine European Cities. Results from the PHASE Project. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12: 15567–83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121215006
Fang W, Li Z, Gao J, Meng R, He G, Hou Z, Zhu S, Zhou M, Zhou C, **ao Y, Yu M, Huang B, Xu X, Lin L, **ao J, ** D, Qin M, Yin P, Xu Y, Hu J, Liu T, Huang C, Ma W (2023) The joint and interaction effect of high temperature and humidity on mortality in China. Environ Int 171:107669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2022.107669
Gu S, Wang X, Mao G, Huang X, Wang Y, Xu P, Wu L, Lou X, Chen Z, Mo Z (2022) The effects of temperature variability on mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a time-series analysis in Hangzhou. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, China. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20588-1
Guo H, Du P, Zhang H, Zhou Z, Zhao M, Wang J, Shi X, Lin J, Lan Y, **ao X, Zheng C, Ma X, Liu C, Zou J, Yang S, Luo J, Feng X (2022) Time series study on the effects of daily average temperature on the mortality from respiratory diseases and circulatory diseases: a case study in Mianyang City. BMC Public Health 22:1001. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-13384-6
Guo M, Zhou M, Li B, Du C, Yao R, Wang L, Yang X, Yu W (2022) Reducing indoor relative humidity can improve the circulation and cardiorespiratory health of older people in a cold environment: A field trial conducted in Chongqing. China. Sci Total Environ 817:152695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152695
Hajat S, Kosatky T (2010) Heat-related mortality: a review and exploration of heterogeneity. J Epidemiol Community Health 64:753–60. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2009.087999
Hu X, Tao J, Zheng H, Ding Z, Cheng J, Shen T (2022) Impact of cold spells on COPD mortality in Jiangsu Province. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, China. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22387-0
Huang C, Chu C, Wang X, Barnett AG (2015) Unusually cold and dry winters increase mortality in Australia. Environ Res 136:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.08.046
Ivey MA, Simeon DT, Monteil MA (2003) Climatic variables are associated with seasonal acute asthma admissions to accident and emergency room facilities in Trinidad, West Indies. Clin Exp Allergy 33:1526–30. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01801.x
Liener K, Leiacker R, Lindemann J, Rettinger G, Keck T (2003) Nasal mucosal temperature after exposure to cold, dry air and hot, humid air. Acta Otolaryngol 123:851–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480310000601a
Luan G, Yin P, Wang L, Zhou M (2019) Association between ambient temperature and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a population-based study of the years of life lost. Int J Environ Health Res 29:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2018.1533533
Ma Y, Zhou L, Chen K (2020) Burden of cause-specific mortality attributable to heat and cold: A multicity time-series study in Jiangsu Province. China. Environ Int 144:105994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105994
MC McCormack LM Paulin CE Gummerson RD Peng GB Diette NN Hansel 2017 Colder temperature is associated with increased COPD morbidity Eur Respir J 49https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01501-2016
Mei Y, Li A, Zhao M, Xu J, Li R, Zhao J, Zhou Q, Ge X, Xu Q (2023) Associations and burdens of relative humidity with cause-specific mortality in three Chinese cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30:3512–3526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22350-z
Mu Z, Chen PL, Geng FH, Ren L, Gu WC, Ma JY, Peng L, Li QY (2017) Synergistic effects of temperature and humidity on the symptoms of COPD patients. Int J Biometeorol 61:1919–1925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-017-1379-0
Rocklöv J, Forsberg B, Ebi K, Bellander T (2014) Susceptibility to mortality related to temperature and heat and cold wave duration in the population of Stockholm County. Sweden. Glob Health Action 7:22737. https://doi.org/10.3402/gha.v7.22737
Shen Y, Zhang X, Chen C, Lin Q, Li X, Qu W, Liu X, Zhao L, Chang S (2021) The relationship between ambient temperature and acute respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in Shenyang, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:20058–20071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11934-2
Tseng CM, Chen YT, Ou SM, Hsiao YH, Li SY, Wang SJ, Yang AC, Chen TJ, Perng DW (2013) The effect of cold temperature on increased exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a nationwide study. PLoS One 8:e57066. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057066
Vanos JK, Cakmak S, Kalkstein LS, Yagouti A (2015) Association of weather and air pollution interactions on daily mortality in 12 Canadian cities. Air Qual Atmos Health 8:307–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-014-0266-7
Wang C, Xu J, Yang L, Xu Y, Zhang X, Bai C, Kang J, Ran P, Shen H, Wen F, Huang K, Yao W, Sun T, Shan G, Yang T, Lin Y, Wu S, Zhu J, Wang R, Shi Z, Zhao J, Ye X, Song Y, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Ding L, Yang T, Chen Y, Guo Y, **ao F, Lu Y, Peng X, Zhang B, **ao D, Chen C-S, Wang Z, Zhang H, Bu X, Zhang X, An L, Zhang S, Cao Z, Zhan Q, Yang Y, Cao B, Dai H, Liang L, He J (2018) Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): a national cross-sectional study. The Lancet 391:1706–1717. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30841-9
Zhang Y, Liu X, Kong D, Fu J, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Lian H, Zhao X, Yang J, Fan Z (2020) Effects of Ambient Temperature on Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Results from a Time-Series Analysis of 143318 Hospitalizations. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 15:213–223. https://doi.org/10.2147/copd.S224198
Zhao Q, Li S, Coelho M, Saldiva PHN, Xu R, Huxley RR, Abramson MJ, Guo Y (2019) Ambient heat and hospitalisation for COPD in Brazil: a nationwide case-crossover study. Thorax 74:1031–1036. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-213486
Funding
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42165012) and Ph.D. Start-up Fund of Gannan Medical University (QD202013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chenyang Shi performed software code, performed formal analysis, and wrote the original draft of the manuscript. **yun Zhu, Qingfeng Wu and Yanhong Liu assisted in data collection, gave guidance and constructive suggestions. Yanbin Hao contributed to conceptualization, wrote, reviewed, edited the manuscript, and was responsible for fund acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, C., Zhu, J., Wu, Q. et al. Effects of ambient temperature and humidity on COPD mortality in Ganzhou city, China. Int J Biometeorol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-024-02705-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-024-02705-6