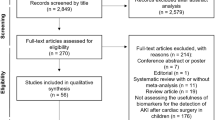
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by a sudden decrease in kidney function. Children with congenital heart disease are a special group at risk of develo** AKI. We performed a systematic review of the literature to search for studies reporting the usefulness of novel urine, serum, and plasma biomarkers in the diagnosis and progression of AKI and their association with clinical outcomes in children undergoing pediatric cardiac surgery. In thirty studies, we analyzed the capacity to predict AKI and poor outcomes of five biomarkers: Cystatin C, Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, Interleukin-18, Kidney injury molecule-1, and Liver fatty acid–binding protein. In conclusion, we suggest the need for further meta-analyses with the availability of additional studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li PK, Burdmann EA, Mehta RL (2013) Acute kidney injury: global health alert. Kidney Int 83:372–376
Filho LT, Grande AJ, Colonetti T, Della ESP, da Rosa MI (2017) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury diagnosis in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1979–1988
Basu RK, Devarajan P, Wong H, Wheeler DS (2011) An update and review of acute kidney injury in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med 12:339–347
Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R (2017) Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in children worldwide, including develo** countries. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1301–1314
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E et al (2005) Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294:813–818
Thakar CV, Worley S, Arrigain S, Yared JP, Paganini EP (2005) Influence of renal dysfunction on mortality after cardiac surgery: modifying effect of preoperative renal function. Kidney Int 67:1112–1119
Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW (2005) Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3365–3370
Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, Tchervenkov CI, Gottesman R, Dancea A, Hyder A, Alkandari O (2009) A small postoperative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 76:885–892
Singh SP (2016) Acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery. Ann Card Anaesth 19:306–313
Lex DJ, Toth R, Cserep Z, Alexander SI, Breuer T, Sapi E, Szatmari A, Szekely E, Gal J, Szekely A (2014) A comparison of the systems for the identification of postoperative acute kidney injury in pediatric cardiac patients. Ann Thorac Surg 97:202–210
Kwiatkowski DM, Krawczeski CD (2017) Acute kidney injury and fluid overload in infants and children after cardiac surgery. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1509–1517
Jefferies JL, Devarajan P (2016) Early detection of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery. Prog Pediatr Cardiol 41:9–16
Watkins SC, Williamson K, Davidson M, Donahue BS (2014) Long-term mortality associated with acute kidney injury in children following congenital cardiac surgery. Paediatr Anaesth 24:919–926
Li S, Krawczeski CD, Zappitelli M, Devarajan P, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Coca SG, Kim RW, Parikh CR (2011) Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med 39:1493–1499
Devarajan P (2006) Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1503–1520
Dupont M, Mullens W, Tang WH (2011) Impact of systemic venous congestion in heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep 8:233–241
de Melo Bezerra Cavalcante CT, Castelo Branco KM, Pinto Junior VC, Meneses GC, de Oliveira Neves FM, de Souza NM, Penaforte KL, Martins AM, Liborio AB (2016) Syndecan-1 improves severe acute kidney injury prediction after pediatric cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 152:178–186
Wang Y, Bellomo R (2017) Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: risk factors, pathophysiology and treatment. Nat Rev Nephrol 13:697–711
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P (2004) Acute renal failure - definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 8:24
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11:R31. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc5713
Blinder JJ, Goldstein SL, Lee VV, Baycroft A, Fraser CD, Nelson D, Jefferies JL (2012) Congenital heart surgery in infants: effects of acute kidney injury on outcomes. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 143:368–374
Sutherland SM, Kwiatkowski DM (2017) Acute Kidney Injury in Children. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 24:380–387
Greenberg JH, Zappitelli M, Devarajan P, Thiessen-Philbrook HR, Krawczeski C, Li S, Garg AX, Coca S, Parikh CR (2016) Kidney outcomes 5 years after pediatric cardiac surgery: the TRIBE-AKI study. JAMA Pediatr 170:1071–1078
McCaffrey J, Coupes B, Chaloner C, Webb NJ, Barber R, Lennon R (2015) Towards a biomarker panel for the assessment of AKI in children receiving intensive care. Pediatr Nephrol 30:1861–1871
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J et al (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365:1231–1238
Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V, Wei H, Hession CA, Cate RL, Sanicola M (1998) Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem 273:4135–4142
Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Bennett M, Mitsnefes MM, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2007) Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts acute kidney injury, morbidity and mortality after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective uncontrolled cohort study. Crit Care 11:R127
Hoffman SB, Massaro AN, Soler-Garcia AA, Perazzo S, Ray PE (2013) A novel urinary biomarker profile to identify acute kidney injury (AKI) in critically ill neonates: a pilot study. Pediatr Nephrol 28:2179–2188
Du Y, Zappitelli M, Mian A, Bennett M, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Mehta R, Goldstein SL (2011) Urinary biomarkers to detect acute kidney injury in the pediatric emergency center. Pediatr Nephrol 26:267–274
Hassinger AB, Backer CL, Lane JC, Haymond S, Wang D, Wald EL (2012) Predictive power of serum cystatin C to detect acute kidney injury and pediatric-modified RIFLE class in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Pediatr Crit Care Med 13:435–440
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Hundley HE, Montesanti A, Parwar P, Sonjara S, Ambalavanan N (2012) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury in newborns. J Pediatr 161:270–275
Alge JL, Arthur JM (2015) Biomarkers of AKI: a review of mechanistic relevance and potential therapeutic implications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:147–155
Kashani K, Cheungpasitporn W, Ronco C (2017) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury: the pathway from discovery to clinical adoption. Clin Chem Lab Med 55:1074–1089
Greenberg JH, Parikh CR (2017) Biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of AKI in children: one size does not fit all. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1551–1557
Krawczeski CD, Vandevoorde RG, Kathman T, Bennett MR, Woo JG, Wang Y, Griffiths RE, Devarajan P (2010) Serum cystatin C is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1552–1557
Zappitelli M, Krawczeski CD, Devarajan P, Wang Z, Sint K, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Li S, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Shlipak MG, Garg AX, Parikh CR, TRIBE-AKI consortium (2011) Early postoperative serum cystatin C predicts severe acute kidney injury following pediatric cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 80:655–662
Hazle MA, Gajarski RJ, Aiyagari R, Yu S, Abraham A, Donohue J, Blatt NB (2013) Urinary biomarkers and renal near-infrared spectroscopy predict intensive care unit outcomes after cardiac surgery in infants younger than 6 months of age. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 146:861–867
Koyner JL, Garg AX, Shlipak MG, Patel UD, Sint K, Hong K, Devarajan P, Edelstein CL, Zappitelli M, Thiessen-Philbrook H et al (2013) Urinary cystatin C and acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Am J Kidney Dis 61:730–738
Peco-Antic A, Ivanisevic I, Vulicevic I, Kotur-Stevuljevic J, Ilic S, Ivanisevic J, Miljkovic M, Kocev N (2013) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury in pediatric cardiac surgery. Clin Biochem 46:1244–1251
Zheng JY, **ao YY, Yao Y, Han L (2013) Is serum cystatin C an early predictor for acute kidney injury following cardiopulmonary bypass surgery in infants and young children? Kaohsiung J Med Sci 29:494–499
Seitz S, Rauh M, Gloeckler M, Cesnjevar R, Dittrich S, Koch AM (2013) Cystatin C and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: biomarkers for acute kidney injury after congenital heart surgery. Swiss Med Wkly 143:w13744
Mamikonian LS, Mamo LB, Smith PB, Koo J, Lodge AJ, Turi JL (2014) Cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with hemolysis and acute kidney injury in neonates, Infants and Children. Pediatr Crit Care Med 15:e111–e119
Basu RK, Wong H, Krawczeski CD, Wheeler DS, Manning PB, Chawla LS, Devarajan P, Goldstein SL (2014) Combining functional and tubular damage biomarkers improves diagnostic precision for acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:2753–2762
Herbert C, Patel M, Nugent A, Dimas VV, Guleserian KJ, Quigley R, Modem V (2015) Serum cystatin C as an early marker of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-positive acute kidney injury resulting from cardiopulmonary bypass in infants with congenital heart disease. Congenit Heart Dis 10:E180–E188
Cantinotti M, Giordano R, Scalese M, Molinaro S, Storti S, Murzi B, Pak V, Poli V, Iervasi G, Clerico A (2017) Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic valued of plasmatic Cystatin-C in children undergoing pediatric cardiac surgery. Clin Chim Acta 471:113–118
Greenberg JH, Zappitelli M, Jia Y, Thiessen-Philbrook HR, de Fontnouvelle CA, Wilson FP, Coca S, Devarajan P, Parikh CR (2018) Biomarkers of AKI progression after pediatric cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol 29:1549–1556
Bennett M, Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Grenier F, Workman R, Syed H, Ali S, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2008) Urine NGAL predicts severity of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: a prospective study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:665–673
Fadel FI, Abdel Rahman AM, Mohamed MF, Habib SA, Ibrahim MH, Sleem ZS, Bazaraa HM, Soliman MM (2012) Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as an early biomarker for prediction of acute kidney injury after cardio-pulmonary bypass in pediatric cardiac surgery. Arch Med Sci 8:250–255
Krawczeski CD, Goldstein SL, Woo JG, Wang Y, Piyaphanee N, Ma Q, Bennett M, Devarajan P (2011) Temporal relationship and predictive value of urinary acute kidney injury biomarkers after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. J Am Coll Cardiol 58:2301–2309
Krawczeski CD, Woo J, Wang Y, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Pediatr 158:1009–1015.e1
Parikh CR, Devarajan P, Zappitelli M, Sint K, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Li S, Kim RW, Koyner JL, Coca SG, Edelstein CL et al (2011) Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after pediatric cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1737–1747
Cantinotti M, Storti S, Lorenzoni V, Arcieri L, Moschetti R, Murzi B, Spadoni I, Passino C, Clerico A (2012) The combined use of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and brain natriuretic peptide improves risk stratification in pediatric cardiac surgery. Clinical Trial Clin Chem Lab Med 50:2009–2017
Ricci Z, Netto R, Garisto C, Lacoella C, Favia I, Cogo P (2012) Whole blood assessment of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin versus pediatricRIFLE for acute kidney injury diagnosis and prognosis after pediatric cardiac surgery: cross-sectional study*. Pediatr Crit Care Med 13:667–670
Bojan M, Vicca S, Lopez-Lopez V, Mogenet A, Pouard P, Falissard B, Journois D (2014) Predictive performance of urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for dialysis requirement and death following cardiac surgery in neonates and infants. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:285–294
Alacarz AJ, Gil-Ruiz MA, Castillo A, López J, Romero C, Fernàndez SN, Carrilo A (2014) Postoperative neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery. Pediatr Crit Care Med 15:121–130
Dong L, Ma Q, Bennett M, Devarajan P (2017) Urinary biomarkers of cell cycle arrest are delayed predictors of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. Pediatr Nephrol 32:2351–2360
Parikh CR, Mishra J, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Dursun B, Ma Q, Kelly C, Dent C, Devarajan P, Edelstein CL (2006) Urinary IL-18 is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 70:199–203
Zheng J, **ao Y, Yao Y, Xu G, Li C, Zhang Q, Li H, Han L (2013) Comparison of urinary biomarkers for early detection of acute kidney injury after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery in infants and young children. Pediatr Cardiol 34:880–886
Zappitelli M, Greenberg JH, Coca SG, Krawczeski CD, Li S, Thiessen-Philbrook HR, Bennett MR, Devarajan P, Parikh CR (2015) Association of definition of acute kidney injury by cystatin C rise with biomarkers and clinical outcomes in children undergoing cardiac surgery. JAMA Pediatr 169:583–591
Han WK, Waikar SS, Johnson A, Betensky RA, Dent CL, Devarajan P, Bonventre JV (2008) Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 73:863–869
Portilla D, Dent C, Sugaya T, Nagothu KK, Kundi I, Moore P, Noiri E, Devarajan P (2008) Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 73:465–472
Zhang Z, Lu B, Sheng X, ** N (2011) Cystatin C in prediction of acute kidney injury: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 58:356–365
Dharnidharka VR, Kwon C, Stevens G (2002) Serum cystatin C is superior to serum creatinine as a marker of kidney function: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 40:221–226
Roos JF, Doust J, Tett SE, Kirkpatrick CM (2007) Diagnostic accuracy of cystatin C compared to serum creatinine for the estimation of renal dysfunction in adults and children--a meta-analysis. Clin Biochem 40:383–391
Koyner JL, Bennett MR, Worcester EM, Ma Q, Raman J, Jeevanandam V, Kasza KE, O'Connor MF, Konczal DJ, Trevino S et al (2008) Urinary cystatin C as an early biomarker of acute kidney injury following adult cardiothoracic surgery. Kidney Int 74:1059–1069
Westhuyzen J (2006) Cystatin C: a promising marker and predictor of impaired renal function. Ann Clin Lab Sci 36:387–394
Ataei N, Bazargani B, Ameli S, Madani A, Javadilarijani F, Moghtaderi M, Abbasi A, Shams S, Ataei F (2014) Early detection of acute kidney injury by serum cystatin C in critically ill children. Pediatr Nephrol 29:133–138
Laterza OF, Price CP, Scott MG (2002) Cystatin C: an improved estimator of glomerular filtration rate? Clin Chem 48:699–707
Herget-Rosenthal S, Feldkamp T, Volbracht L, Kribben A (2004) Measurement of urinary cystatin C by particle-enhanced nephelometric immunoassay: precision, interferences, stability and reference range. Ann Clin Biochem 41:111–118
Filler G, Lepage N (2003) Should the Schwartz formula for estimation of GFR be replaced by cystatin C formula? Pediatr Nephrol 18:981–985
Zappitelli M, Parvex P, Joseph L, Paradis G, Grey V, Lau S, Bell L (2006) Derivation and validation of cystatin C-based prediction equations for GFR in children. Am J Kidney Dis 48:221–230
Schwartz GJ, Schneider MF, Maier PS, Moxey-Mims M, Dharnidharka VR, Warady BA, Furth SL, Munoz A (2012) Improved equations estimating GFR in children with chronic kidney disease using an immunonephelometric determination of cystatin C. Kidney Int 82:445–453
Toda Y, Sugimoto K (2017) AKI after pediatric cardiac surgery for congenital heart diseases-recent developments in diagnostic criteria and early diagnosis by biomarkers. J Intensive Care 5:49
Ristikankare A, Poyhia R, Kuitunen A, Skrifvars M, Hammainen P, Salmenpera M, Suojaranta-Ylinen R (2010) Serum cystatin C in elderly cardiac surgery patients. Ann Thorac Surg 89:689–694
Wald R, Liangos O, Perianayagam MC, Kolyada A, Herget-Rosenthal S, Mazer CD, Jaber BL (2010) Plasma cystatin C and acute kidney injury after cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1373–1379
Ho J, Tangri N, Komenda P, Kaushal A, Sood M, Brar R, Gill K, Walker S, MacDonald K, Hiebert BM et al (2015) Urinary, plasma, and serum biomarkers' utility for predicting acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery in adults: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 66:993–1005
Zwiers AJ, de Wildt SN, van Rosmalen J, de Rijke YB, Buijs EA, Tibboel D, Cransberg K (2015) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin identifies critically ill young children with acute kidney injury following intensive care admission: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 19:181
Devarajan P (2010) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Biomark Med 4:265–280
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2534–2543
Reiter K, Balling G, Bonelli V, Pabst von Ohain J, Braun SL, Ewert P, Ruf B (2018) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin reflects inflammation and is not a reliable renal biomarker in neonates and infants after cardiopulmonary bypass: a prospective case-control study. Cardiol Young 28:243–251
Devarajan P (2008) Emerging urinary biomarkers in the diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Expert Opin Med Diagn 2:387–398
Zhou F, Luo Q, Wang L, Han L (2016) Diagnostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for early diagnosis of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 49:746–755
Haase-Fielitz A, Haase M, Devarajan P (2014) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury: a critical evaluation of current status. Ann Clin Biochem 51:335–351
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54:1012–1024
Palermo J, Dart AB, De Mello A, Devarajan P, Gottesman R, Garcia Guerra G, Hansen G, Joffe AR, Mammen C, Majesic N et al (2017) Biomarkers for early acute kidney injury diagnosis and severity prediction: a pilot multicenter Canadian study of children admitted to the ICU. Pediatr Crit Care Med 18:e235–e244
Gist KM, Kwiatkowski DM, Cooper DS (2018) Acute kidney injury in congenital heart disease. Curr Opin Cardiol 33:101–107
Schrezenmeier EV, Barasch J, Budde K, Westhoff T, Schmidt-Ott KM (2017) Biomarkers in acute kidney injury—pathophysiological basis and clinical performance. Acta Physiol 219:554–572
Beker BM, Corleto MG, Fieiras C, Musso CG (2018) Novel acute kidney injury biomarkers: their characteristics, utility and concerns. Int Urol Nephrol 50:705–713
Slocum JL, Heung M, Pennathur S (2012) Marking renal injury: can we move beyond serum creatinine? Transl Res 159:277–289
Parikh CR, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Garg AX, Kadiyala D, Shlipak MG, Koyner JL, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P, Patel UD, Zappitelli M et al (2013) Performance of kidney injury molecule-1 and liver fatty acid-binding protein and combined biomarkers of AKI after cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1079–1088
Maatman RG, Van Kuppevelt TH, Veerkamp JH (1991) Two types of fatty acid-binding protein in human kidney. Isolation, characterization and localization. Biochem J 273:759–766
Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Kimura K (2006) Urinary fatty acid binding protein in renal disease. Clin Chim Acta 374:1–7
Yokoyama T, Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Hoshino S, Yasuda T, Kimura K (2009) Urinary excretion of liver type fatty acid binding protein accurately reflects the degree of tubulointerstitial damage. Am J Pathol 174:2096–2106
Doi K, Noiri E, Sugaya T (2010) Urinary L-type fatty acid-binding protein as a new renal biomarker in critical care. Curr Opin Crit Care 16:545–549
Reitsma S, Slaaf DW, Vink H, van Zandvoort MA, oude Egbrink MG (2007) The endothelial glycocalyx: composition, functions, and visualization. Pflugers Arch 454:345-359
Gouverneur M, Spaan JA, Pannekoek H, Fontijn RD, Vink H (2006) Fluid shear stress stimulates incorporation of hyaluronan into endothelial cell glycocalyx. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:26
Pries AR, Secomb TW, Gaehtgens P (2000) The endothelial surface layer. Pflugers Arch 440:653–666
Weinbaum S, Tarbell JM, Damiano ER (2007) The structure and function of the endothelial glycocalyx layer. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 9:121–167
Nieuwdorp M, Meuwese MC, Mooij HL, Ince C, Broekhuizen LN, Kastelein JJ, Stroes ES, Vink H (1985) Measuring endothelial glycocalyx dimensions in humans: a potential novel tool to monitor vascular vulnerability. J Appl Physiol 104:845–852
Myers GJ, Wegner J (2017) Endothelial glycocalyx and cardiopulmonary bypass. J Extra Corpor Technol 49:174–181
Perrin RM, Harper SJ, Bates DO (2007) A role for the endothelial glycocalyx in regulating microvascular permeability in diabetes mellitus. Cell Biochem Biophys 49:65–72
Rehm M, Haller M, Orth V, Kreimeier U, Jacob M, Dressel H, Mayer S, Brechtelsbauer H, Finsterer U (2001) Changes in blood volume and hematocrit during acute preoperative volume loading with 5% albumin or 6% hetastarch solutions in patients before radical hysterectomy. Anesthesiology 95:849–856
Pillinger NL, Kam P (2017) Endothelial glycocalyx: basic science and clinical implications. Anaesth Intensive Care 45:295–307
Bruegger D, Brettner F, Rossberg I, Nussbaum C, Kowalski C, Januszewska K, Becker BF, Chappell D (2015) Acute degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx in infants undergoing cardiac surgical procedures. Ann Thorac Surg 99:926–931
Ferrer NMB, de Melo Bezerra Cavalcante CT, Branco KMC, Junior VCP, Meneses GC, de Oliveira Neves FM, de Souza NMG, LourencoPenaforte K, Martins AMC, Liborio AB (2018) Urinary Syndecan-1 and acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery. Clin Chim Acta 485:205–209
Emlet DR, Pastor-Soler N, Marciszyn A, Wen X, Gomez H, Humphries WH, Morrisroe S, Volpe JK, Kellum JA (2017) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2: differential expression and secretion in human kidney tubule cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 312(2):F284–F296
Stetler-Stevenson WG (2008) Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in cell signaling: metalloproteinase-independent biological activities. Sci Signal 1:re6
Ortega LM, Heung M (2018) The use of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in the early detection of acute kidney injury. Is this the new renal troponin? Nefrologia 38:361–367
Jia HM, Huang LF, Zheng Y, Li WX (2017) Prognostic value of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in patients at high risk for acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrology 22:831–837
Meersch M, Schmidt C, Van Aken H, Martens S, Rossaint J, Singbartl K, Gorlich D, Kellum JA, Zarbock A (2014) Urinary TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 as early biomarkers of acute kidney injury and renal recovery following cardiac surgery. PLoS One 9:e93460
Pilarczyk K, Edayadiyil-Dudasova M, Wendt D, Demircioglu E, Benedik J, Dohle DS, Jakob H, Dusse F (2015) Urinary [TIMP-2] *[IGFBP7] for early prediction of acute kidney injury after coronary artery bypass surgery. Ann Intensive Care 5:50
Dusse F, Edayadiyil-Dudasova M, Thielmann M, Wendt D, Kahlert P, Demircioglu E, Jakob H, Schaefer ST, Pilarczyk K (2016) Early prediction of acute kidney injury after transapical and transaortic aortic valve implantation with urinary G1 cell cycle arrest biomarkers. BMC Anesthesiol 16:76
Wang Y, Zou Z, ** J, Teng J, Xu J, Shen B, Jiang W, Zhuang Y, Liu L, Luo Z et al (2017) Urinary TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 for the prediction of acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery. BMC Nephrol 18:177
Oezkur M, Magyar A, Thomas P, Stork T, Schneider R, Bening C, Stork S, Heuschmann PU, Leyh RG, Wagner M (2017) TIMP-2*IGFBP7 (Nephrocheck(R)) Measurements at intensive care unit admission after cardiac surgery are predictive for acute kidney injury within 48 hours. Kidney Blood Press Res 42:456–467
Levante C, Ferrari F, Manenti C, Husain-Syed F, Scarpa M, Hinna Danesi T, De Cal M, Corradi V, Virzi GM, Brendolan A et al (2017) Routine adoption of TIMP2 and IGFBP7 biomarkers in cardiac surgery for early identification of acute kidney injury. Int J Artif Organs 40:714–718
Mayer T, Bolliger D, Scholz M, Reuthebuch O, Gregor M, Meier P, Grapow M, Seeberger MD, Fassl J (2017) Urine Biomarkers of Tubular Renal Cell Damage for the Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Surgery-A Pilot Study. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 31:2072–2079
Gist KM, Goldstein SL, Wrona J, Alten JA, Basu RK, Cooper DS, Soranno DE, Duplantis J, Altmann C, Gao Z et al (2017) Kinetics of the cell cycle arrest biomarkers (TIMP-2*IGFBP-7) for prediction of acute kidney injury in infants after cardiac surgery. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1611–1619
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Cavalcante—global concept of the study, data collection, and critical review of the manuscript. B. Cavalcante—global concept of the study, manuscript writing, interpretation and discussion of data, and critical review of the manuscript. C. Branco—manuscript writing, interpretation and discussion of data. D. Chang—interpretation and discussion of data and critical review of the manuscript. E. Libório—data collection and interpretation and critical review of the manuscript. F. Maia; Pompeu; Brito and Telles—critical review of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by regional independent ethics committees and national regulatory health authorities and conducted in accordance with Good Clinical Practices and the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavalcante, C.T.d.M.B., Cavalcante, M.B., Castello Branco, K.M.P. et al. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury in pediatric cardiac surgery. Pediatr Nephrol 37, 61–78 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-05094-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-05094-9