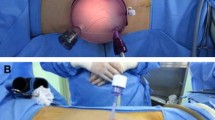
Abstract
Background
Donor safety and cosmetic outcome are the main concerns raised by most living-donors. Pure laparoscopic living-donor hepatectomy (PLLDH) can provide the balance between those concerns. No studies evaluated the donors’ satisfaction after PLLDH. The aim of this study is to evaluate the donors’ satisfaction after PLLDH compared with donors who underwent open approach.
Methods
We randomly assigned a questionnaire (Donor satisfaction questionnaire) to the donors, operated between 2011 and 2017, during their follow-up visits in the outpatient clinic. Donors who responded to the questionnaire were included in our study. Donors were divided into 3 groups: L group (conventional inverted L incision), M group (midline incision), and PL group (laparoscopic approach).
Results
149 donors were included in our study. L group included 60 donors (40.3%), M group included 39 patients (26.2%), and PL group included 50 patients (33.5%). There were no significant differences between the groups regarding preoperative and perioperative outcomes apart from shorter operation time in PL group and higher wound infection in M group. Body image scale was significantly better in PL group (p = 0.001). Cosmetic scale was significantly higher in PL group (p = 0.001). Regarding self-confidence scale, it was significantly higher in PL group (p = 0.001). There was no significant difference between the groups regarding the sense of dullness or numbness on the scar (p = 0.113).
Conclusion
PLLDH is safe and feasible for living-donor hepatectomy. Donors operated by pure laparoscopic approach have better satisfaction scores compared to conventional open approach.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecassis MM, Fisher RA, Olthoff KM et al (2012) Complications of living donor hepatic lobectomy—a comprehensive report. Am J Transpl 12:1208–1217
Brige P, Hery G, Chopinet S et al (2018) Morbidity and mortality of hepatic right lobe living donors: systematic review and perspectives. J Gastrointest Liver Dis 27(2):169
Samstein B, Griesemer A, Halazun K et al (2018) Pure laparoscopic donor hepatectomies: ready for widespread adoption? Ann Surg 268(4):602–609
Au KP, Chok KS (2018) Minimally invasive donor hepatectomy, are we ready for prime time? World J Gastroenterol 24(25):2698–2709
Lee KW, Hong SK, Suh KS et al (2018) One hundred fifteen cases of pure laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy at a single center. Transplantation 102(11):1878–1884
Suh KS, Hong SK, Lee KW et al (2018) Pure laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy: focus on 55 donors undergoing right hepatectomy. Am J Transpl 18(2):434–443
Soubrane O, Kwon CH (2017) Tips for pure laparoscopic right hepatectomy in the live donor. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 24(2):E1–E5
Han HS, Cho JY, Yoon YS et al (2015) Total laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy. Surg Endosc 29(1):184
Kim KH, Kang SH, Jung DH et al (2017) Initial outcomes of pure laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy in an experienced adult living donor liver transplant center. Transplantation 101(5):1106–1110
Takahara T, Wakabayashi G, Hasegawa Y et al (2015) Minimally invasive donor hepatectomy: evolution from hybrid to pure laparoscopic techniques. Ann Surg 261:e3–e4
Park J, Kwon CH, Choi GS et al (2019) One-year recipient morbidity of liver transplantation using pure laparoscopic versus open living donor right hepatectomy: propensity score analysis. Liver Transpl 25(11):1642–1650
Rhu J, Choi GS, Kim JM et al (2020) Feasibility of total laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy compared with open surgery: comprehensive review of 100 cases of the initial stage. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 27:16–25
Lind MY, Hop WC, Weimar W et al (2004) Body image after laparoscopic or open donor nephrectomy. Surg Endosc 18:1276–1279
Suh SW, Lee KW, Lee JM et al (2015) Clinical outcomes of and patient satisfaction with different incision methods for donor hepatectomy in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 21(1):72–78
Lee KW, Kim SH, Han SS et al (2011) Use of an upper midline incision for living donor partial hepatectomy: a series of 143 consecutive cases. Liver Transpl 17(8):969–975
Dunker MS, Stiggelbout AM, van Hogezand RA et al (1998) Cosmesis and body image after laparoscopic-assisted and open ileocolic resection for Crohn’s disease. Surg Endosc 12:1334–1340
Yi NJ, Suh KS, Cho JY et al (2007) Three-quarters of right liver donors experienced postoperative complications. Liver Transpl 13:797–806
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213
Takahara T, Wakabayashi G, Beppu T et al (2015) Long-term and perioperative outcomes of laparoscopic versus open liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with propensity score matching: a multi institutional Japanese study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 22(10):721–727
Han HS, Shehta A, Ahn S et al (2015) Laparoscopic versus open liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: case-matched study with propensity score matching. J Hepatol 63:643–650
Cipriani F, Rawashdeh M, Stanton L et al (2016) Propensity score-based analysis of outcomes of laparoscopic versus open liver resection for colorectal metastases. Br J Surg 103(11):1504–1512
Chen KH, Siow TF, Chio UC et al (2018) Laparoscopic donor hepatectomy. Asian J Endosc Surg 11(2):112–117
Sotiropoulos GC, Radtke A, Molmenti EP et al (2011) Long-term follow-up after right hepatectomy for adult living donation and attitudes toward the procedure. Ann Surg 254(5):694–701
Ishizaki M, Kaibori M, Matsui K et al (2012) Change in donor quality of life after living donor liver transplantation surgery: a single-institution experience. Transpl Proc 44:344–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Lee JM, Shehta A, Lee KW, Hong SK, Cho JH, Yi NJ, and Suh KS have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JM., Shehta, A., Lee, KW. et al. Donor wound satisfaction after living-donor liver transplantation in the era of pure laparoscopic donor hepatectomy. Surg Endosc 35, 2265–2272 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07640-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07640-2