Abstract
Purpose
To examine safety and efficacy of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for centrally located hepatocellular carcinoma (CL-HCC).
Methods
Fifty-three patients with CL-HCC were treated with SBRT from 2011 to 2017 in our institution. CL-HCC was defined as a tumor sited in segments 4, 5, or 8 adjacent to the hepatic hilum, or < 1.5 cm from main portal branches. Primary endpoints were treatment response, local control (LC), and hepatobiliary toxicity (HBT).
Results
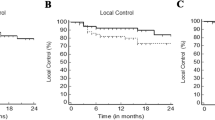
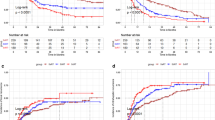
Thirty-three (62.3%) patients had Child–Turcotte–Pugh score A, 20 (37.77%)—score B. Albumin–bilirubin grade 1 constituted 6 (11.3%) cases, grade 2–32 (60.4%), grade 3–15 (28.3%). Median tumor diameter was 34 mm. Median BED10 was 72 Gy. Complete/partial response was observed in 40 (75.5%) lesions, stable disease—in 9 (17.0%). At a median follow-up of 12.2 months, there were 6 (11.3%) local failures. The actuarial 2-year LC rate was 87.9%. 2-year LC was better with higher BED10 (> 70 vs ≤ 70 Gy) 96.9 vs 72.5%, p = 0.01. The 2-year rates for disease-specific and overall survival were 53.2 and 39.1%, respectively. The incidence of any Grade ≥ 3 AE was 9 (17.0%). There were no grade 5 AEs. There was a trend toward an increased risk of grade ≥ 3 AE with mean liver dose > 10 Gy (p = 0.07).
Conclusions
In the present cohort, SBRT to the CL-HCC produced excellent treatment response with acceptable HBT and LC. Select HCC patients who are not candidates for surgery or other locoregional therapies can be considered for SBRT to the central liver.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M et al (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e447–e453
Bujold A, Massey CA, Kim JJ et al (2013) Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 31:1631–1639
Cárdenes HR, Price TR, Perkins SM et al (2010) Phase I feasibility trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 12:218–225
Eriguchi T, Takeda A, Sanuki N et al (2013) Acceptable toxicity after stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver tumors adjacent to the central biliary system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:1006–1011
Gkika E, Schultheiss M, Bettinger D et al (2017) Excellent local control and tolerance profile after stereotactic body radiotherapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol 12:116
Huertas A, Baumann AS, Saunier-Kubs F et al (2015) Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an ablative treatment for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 115:211–216
Jang WI, Kim MS, Bae SH et al (2013) High-dose stereotactic body radiotherapy correlates increased local control and overall survival in patients with inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol 8:250
Kwon JH, Bae SH, Kim JY et al (2010) Long-term effect of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma ineligible for local ablation therapy or surgical resection. Stereotactic radiotherapy for liver cancer. BMC Cancer 10:475
Lencioni R, Llovet JM (2010) Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 30:52–60
Mendez Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM et al (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: a single institution phase I-II study. Acta Oncol 45:831–837
Osmundson EC, Wu Y, Luxton G et al (2015) Predictors of toxicity associated with stereotactic body radiation therapy to the central hepatobiliary tract. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91:986–994
Takeda A, Sanuki N, Tsurugai Y et al (2016) Phase 2 study of stereotactic body radiotherapy and optional transarterial chemoembolization for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma not amenable to resection and radiofrequency ablation. Cancer 122(13):2041–2049
Toesca DA, Osmundson EC, Eyben RV et al (2017) Central liver toxicity after SBRT: an expanded analysis and predictive nomogram. Radiother Oncol 122:130–136
Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G et al (2008) Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:657–664
Wahl DR, Stenmark MH, Tao Y et al (2016) Outcomes after stereotactic body radiotherapy or radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 34:452–459
Weiner AA, Olsen J, Ma D et al (2016) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatic malignancies—report of a phase I/II institutional study. Radiother Oncol 121:79–85
Yamashita H, Onishi H, Murakami N et al (2015) Survival outcomes after stereotactic body radiotherapy for 79 Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Radiat Res 56:561–567
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of the study have no commercial interests, and no actual, or potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazarev, S., Hardy-Abeloos, C., Factor, O. et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally located hepatocellular carcinoma: outcomes and toxicities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 2077–2083 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2729-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2729-y