Abstract
Purpose
Therapeutic decisions in esophageal adenocarcinomas (EAC) restricted to mucosa (pT1a) or submucosa (pT1b) depend mainly on classic histomorphology-based criteria like tumor grading or lymphovascular invasion with limited success. There is a strong need for reliable pre-therapeutical biomarker-based evaluation also applicable on endoscopically obtained biopsies.
Methods
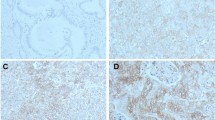
Patients who underwent esophagectomy due to EAC in a high volume center between 1999 and 2016 were included. Tissue microarrays (TMA) were retrospectively established from the formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded material of the resected specimens and immunohistochemically stained using a monoclonal primary antibody specific for IMP3. IMP3 staining intensity was scored manually according to a 3-tier-scoring system (negative, weak and strong).
Results
371 EACs were interpretable for analysis. 109 patients (29%) had early invasive (pT1a/pT1b) and 262 patients (71%) locally advanced EAC (> pT2). 259 EACs (70%) revealed positive immunostaining for IMP3 including 167 strongly and 92 weakly positive. Early EAC had significantly lower IMP3 expression compared to advanced tumor stages (p < 0.0001). IMP3 positive pT1 EAC revealed higher levels of lymph node metastases (LNM) (p = 0.0001) and pT1b tumors showed higher rates of IMP3 positivity compared to pT1a (p = 0.007). Subdividing the submucosa in thirds, there was a significant trend for higher IMP3 expression with deeper tumor infiltration from pT1a to pT1b (sm3) (p = 0.0001). There was an association between IMP3 expression and shortened survival in pT1 EAC (p = 0.038).
Conclusions
IMP3 expression correlates with depth of tumor infiltration, rate of LNM and is associated with worse outcome. Thus, IMP3 might be useful for therapeutic decisions in early-invasive EAC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D (2015) Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut 64:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308124
Arnold M, Laversanne M, Brown LM et al (2017) Predicting the future burden of esophageal cancer by histological subtype: international trends in incidence up to 2030. Am J Gastroenterol 112(8):1247–1255
Bollschweiler E, Baldus SE, Schröder W et al (2006) High rate of lymph-node metastasis in submucosal esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Endoscopy 38:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-924993
Boys JA, Worrell SG, Chandrasoma P et al (2016) Can the risk of lymph node metastases be gauged in endoscopically resected submucosal esophageal adenocarcinomas? A multi-center study. J Gastrointest Surg 20:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2950-9
Burdelski C, Jakani-Karimi N, Jacobsen F et al (2018) IMP3 overexpression occurs in various important cancer types and is linked to aggressive tumor features: a tissue microarray study on 8,877 human cancers and normal tissues. Oncol Rep 39:3–12. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.6072
Chen Z, Ren Y, Du XL et al (2017) Incidence and survival differences in esophageal cancer among ethnic groups in the United States. Oncotarget. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16694
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:2241–2252. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra035010
Feng W, Zhou Z, Peters JH et al (2011) Expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 in human esophageal adenocarcinoma and its precursor lesions. Arch Pathol Lab Med 135:1024–1031. https://doi.org/10.5858/2009-0617-OAR2
Helbig D, Ihle MA, Pütz K et al (2016) Oncogene and therapeutic target analyses in A typical fibroxanthomas and pleomorphic dermal sarcomas. Oncotarget 7:21763–21774. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7845
Hölscher AH, Schneider PM, Gutschow C, Schröder W (2007) Laparoscopic ischemic conditioning of the stomach for esophageal replacement. Ann Surg 245:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000245847.40779.10
Hölscher AH, Bollschweiler E, Schröder W et al (2011) Prognostic impact of upper, middle, and lower third mucosal or submucosal infiltration in early esophageal cancer. Ann Surg 254:802–808. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182369128
Kazeminezhad B, Mirafsharieh SA, Dinyari K et al (2014) Usefulness of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 (IMP3) as a new marker for the diagnosis of esophageal adenocarcinoma in challenging cases. Turk J Gastroenterol 25:253–256. https://doi.org/10.5152/tjg.2014.5454
Li C, Rock KL, Woda BA et al (2007) IMP3 is a novel biomarker for adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine cervix: an immunohistochemical study in comparison with p16(INK4a) expression. Mod Pathol 20:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800735
Li D, Yan D, Tang H et al (2009) IMP3 is a novel prognostic marker that correlates with colon cancer progression and pathogenesis. Ann Surg Oncol 16:3499–3506. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0648-5
Liao B, Hu Y, Herrick DJ, Brewer G (2005) The RNA-binding protein IMP-3 is a translational activator of insulin-like growth factor II leader-3 mRNA during proliferation of human K562 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 280:18517–18524. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M500270200
Lu D, Vohra P, Chu PG et al (2009) An oncofetal protein IMP3. Am J Surg Pathol 33:521–525. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181483ff8
Manner H, Pech O, Heldmann Y et al (2013) Efficacy, safety, and long-term results of endoscopic treatment for early stage adenocarcinoma of the esophagus with low-risk sm1 invasion. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:630–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2012.12.040
Mönig SP, Schröder W, Baldus SE, Hölscher AH (2002) Preoperative lymph-node staging in gastrointestinal cancer—correlation between size and tumor stage. Onkologie 25:342–344
Mueller-Pillasch F, Pohl B, Wilda M et al (1999) Expression of the highly conserved RNA binding protein KOC in embryogenesis. Mech Dev 88:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(99)00160-4
Müeller-Pillasch F, Lacher U, Wallrapp C et al (1997) Cloning of a gene highly overexpressed in cancer coding for a novel KH-domain containing protein. Oncogene 14:2729–2733. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201110
Nielsen J, Christiansen J, Lykke-Andersen J et al (1999) A family of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding proteins represses translation in late development. Mol Cell Biol 19:1262–1270. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.19.2.1262
Okada K, Fujiwara Y, Nakamura Y et al (2012) Oncofetal protein, IMP-3, a potential marker for prediction of postoperative peritoneal dissemination in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol 105:780–785. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.22108
Pech O, Bollschweiler E, Manner H et al (2011) Comparison between endoscopic and surgical resection of mucosal esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus at two high-volume centers. Ann Surg 254:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e31821d4bf6
Plum PS, Bollschweiler E, Hölscher AH, Warnecke-Eberz U (2013) Novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Expert Opin Med Diagn 7:557–571. https://doi.org/10.1517/17530059.2013.843526
Plum PS, Warnecke-Eberz U, Dhaouadi O et al (2015) Molecular markers predicting lymph node metastasis in early esophageal cancer. Histol Histopathol 30:1193–1202. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-11-618
Porschen R, Buck A, Fischbach W et al (2015) S3-Guideline of diagnostic and therapy of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (Long Version 1.0-September 2015, AWMF-registry number: 021/023OL). Z Gastroenterol 53:1288–1347
Prasad GA, Wu TT, Wigle DA et al (2009) Endoscopic and surgical treatment of mucosal (T1a) esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 137:815–823. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.05.059
Simon R, Mirlacher M, Sauter G (2005) Tissue microarrays. Methods Mol Med 114:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-923-0:257
Takata A, Takiguchi S, Okada K et al (2014) Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA-binding protein-3 as a marker for predicting clinical outcome in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett 8:2027–2031. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2014.2465
Trivedi A, Cartun RW, Ligato S (2014) Role of lymphovascular invasion and immunohistochemical expression of IMP3 in the risk stratification of superficially invasive pT1 esophageal adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 210:402–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2014.01.018
Vikesaa J, Hansen TVO, Jønson L et al (2006) RNA-binding IMPs promote cell adhesion and invadopodia formation. EMBO J 25:1456–1468. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601039
Wang T, Fan L, Watanabe Y et al (2003) L523S, an RNA-binding protein as a potential therapeutic target for lung cancer. Br J Cancer 88:887–894. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6600806
**e SH, Mattsson F, Lagergren J (2017) Incidence trends in oesophageal cancer by histological type: an updated analysis in Sweden. Cancer Epidemiol 47:114–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2017.02.004
Yaniv K, Yisraeli JK (2002) The involvement of a conserved family of RNA binding proteins in embryonic development and carcinogenesis. Gene 287(1–2):49–54
Yantiss RK, Woda BA, Fanger GR et al (2005) KOC (K homology domain containing protein overexpressed in cancer): a novel molecular marker that distinguishes between benign and malignant lesions of the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol 29(2):188–195
Yoshino K, Motoyama S, Koyota S et al (2014) Identification of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 as a radioresistance factor in squamous esophageal cancer cells. Dis Esophagus 27:479–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01415.x
Zehetner J, DeMeester SR, Hagen JA et al (2011) Endoscopic resection and ablation versus esophagectomy for high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 141:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.08.058
Zhang Y (2013) Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 19:5598–5606. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5598
Zheng W, Yi X, Fadare O et al (2008) The oncofetal protein IMP3: a novel biomarker for endometrial serous carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 32:304–315. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181483ff8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Zander reports grants from NRW Government during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Roche, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Lilly, personal fees from MSD, personal fees from BMS, personal fees from AstraZeneca, personal fees from Sanofi, outside the submitted work. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the current study involving human tumor specimens were in accordance with ethical standards of the local research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University Hospital of Cologne.
Informed consent
The single protein immunohistochemical staining was performed during the regular pathological diagnostics and therefore no additional informed consent was obtained.
Additional information
The authors Patrick Sven Plum, Thomas Zander, Hakan Alakus, Alexander Quaas and Heike Loeser are members of the “Gastrointestinal Cancer Group Cologne (GCGC)”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plum, P.S., Ulase, D., Bollschweiler, E. et al. Upregulation of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 (IMP3) has negative prognostic impact on early invasive (pT1) adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 1731–1739 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2698-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2698-1