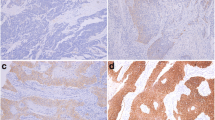
Abstract
Background
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a heterogeneous disease in the sense that the biological behavior is regulated by the activation of various signaling pathways. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationships between the expressions of various targetable proteins and the clinicopathological characteristics of ESCC patients.
Methods
A total of 286 patients with ESCC who had undergone curative surgical resection without neoadjuvant therapy were enrolled in this study. The protein expressions of EGFR, HER2, MET, IGF1R, FGFR2, p53, and PD-L1 were immunohistochemically evaluated in a tissue microarray analysis. The relationships between the expression statuses of each of the above molecules, and the PD-L1 expression status as well as the clinicopathological characteristics, including the survival outcome were assessed.
Results
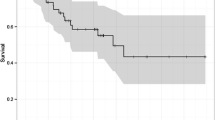
The expression frequencies of EGFR, HER2, MET, IGF1R, FGFR2, p53, and PD-L1 were as follows: 90.9, 1.0, 2.4, 71.0, 16.1, 62.9 and 23.4%. The overlap** expressions of two or more receptor tyrosine kinases were observed in 72.0%. MET expression was the only poor prognostic factor of recurrence-free survival [hazard ratio (HR) 1.89, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.15–3.11]; in contrast, PD-L1 was the only favorable prognostic factor for both recurrence-free survival (HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.38–0.87) and overall survival (HR 0.56, 95% CI 0.35–0.89). No correlation was observed between the expressions of PD-L1 and the other molecules.
Conclusions
This large cohort study demonstrated that multiple molecules were co-expressed in most of the ESCC cases, suggesting that combining molecular targeted agents for these co-expressed molecules should be considered.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi-Ardekani B, Dar NA, Mir MM, Zargar SA, Lone MM, Martel-Planche G, Villar S, Mounawar M, Saidi F, Malekzadeh R et al (2012) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations and expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus in central Asia. BMC Cancer 12:602
Chen K, Cheng G, Zhang F, Zhang N, Li D, ** J, Wu J, Ying L, Mao W, Su D (2016) Prognostic significance of programmed death-1 and programmed death-ligand 1 expression in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 7:30772–30780
Comoglio PM, Giordano S, Trusolino L (2008) Drug development of MET inhibitors: targeting oncogene addiction and expedience. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:504–516
Crosby T, Hurt CN, Falk S, Gollins S, Mukherjee S, Staffurth J, Ray R, Bashir N, Bridgewater JA, Geh JI et al (2013) Chemoradiotherapy with or without cetuximab in patients with oesophageal cancer (SCOPE1): a multicentre, phase 2/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 14:627–637
Doi T, Piha-Paul SA, Jalal SI, Mai-Dang H, Yuan S, Koshiji M, Csiki I, Bennouna J (2015) Pembrolizumab (MK-3475) for patients (pts) with advanced esophageal carcinoma: preliminary results from KEYNOTE-028. In: ASCO annual meeting, p. Abstract 4010, Chicago
Dutton SJ, Ferry DR, Blazeby JM, Abbas H, Dahle-Smith A, Mansoor W, Thompson J, Harrison M, Chatterjee A, Falk S et al (2014) Gefitinib for oesophageal cancer progressing after chemotherapy (COG): a phase 3, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 15:894–904
Gao YB, Chen ZL, Li JG, Hu XD, Shi XJ, Sun ZM, Zhang F, Zhao ZR, Li ZT, Liu ZY et al (2014) Genetic landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet 46:1097–1102
Hatogai K, Kitano S, Fujii S, Kojima T, Daiko H, Nomura S, Yoshino T, Ohtsu A, Takiguchi Y, Doi T et al (2016) Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of tumor microenvironment immune status in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 7:47252–47264
Huang Z, Wu Y, Zhou X, Qian J, Zhu W, Shu Y, Liu P (2015) Clinical efficacy of mTOR inhibitors in solid tumors: a systematic review. Future Oncol 11:1687–1699
Ilson DH, Moughan J, Suntharalingam M, Dicker A, Kachnic LA, Konski AA, Chakravarthy B (2014) RTOG 0436: a phase III trial evaluating the addition of cetuximab to paclitaxel, cisplatin, and radiation for patients with esophageal cancer treated without surgery. J Clin Oncol 32:abstr4007
Imsumran A, Adachi Y, Yamamoto H, Li R, Wang Y, Min Y, Piao W, Nosho K, Arimura Y, Shinomura Y et al (2007) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a marker for prognosis and a therapeutic target in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 28:947–956
Janku F, Hong DS, Fu S, Piha-Paul SA, Naing A, Falchook GS, Tsimberidou AM, Stepanek VM, Moulder SL, Lee JJ et al (2014) Assessing PIK3CA and PTEN in early-phase trials with PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors. Cell Rep 6:377–387
Lin DC, Hao JJ, Nagata Y, Xu L, Shang L, Meng X, Sato Y, Okuno Y, Varela AM, Ding LW et al (2014) Genomic and molecular characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet 46:467–473
Maeng CH, Lee J, van Hummelen P, Park SH, Palescandolo E, Jang J, Park HY, Kang SY, MacConaill L, Kim KM et al (2012) High-throughput genoty** in metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma identifies phosphoinositide-3-kinase and BRAF mutations. PLoS One 7:e41655
Mesteri I, Schoppmann SF, Preusser M, Birner P (2014) Overexpression of CMET is associated with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and diminished prognosis in oesophageal adenocarcinoma but not in squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 50:1354–1360
Modjtahedi H, Essapen S (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in cancer treatment: advances, challenges and opportunities. Anticancer Drugs 20:851–855
Murata A, Baba Y, Watanabe M, Shigaki H, Miyake K, Karashima R, Imamura Y, Ida S, Ishimoto T, Iwagami S et al (2013) p53 immunohistochemical expression and patient prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol 30:728
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Horn LA, Haile ST (2014) The programmed death-1 immune-suppressive pathway: barrier to antitumor immunity. J Immunol 193:3835–3841
Ozawa Y, Nakamura Y, Fujishima F, Felizola SJ, Takeda K, Okamoto H, Ito K, Ishida H, Konno T, Kamei T et al (2015) c-Met in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: an independent prognostic factor and potential therapeutic target. BMC Cancer 15:451
Ren Y, Cao B, Law S, **e Y, Lee PY, Cheung L, Chen Y, Huang X, Chan HM, Zhao P et al (2005) Hepatocyte growth factor promotes cancer cell migration and angiogenic factors expression: a prognostic marker of human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 11:6190–6197
Saeki H, Ohno S, Araki K, Egashira A, Kawaguchi H, Ikeda Y, Morita M, Kitamura K, Sugimachi K (2000) Alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking in relation to high frequency of p53 protein accumulation in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma in the Japanese. Br J Cancer 82:1892–1894
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz M, Wittekind C (2009) TNM classification of malignant tumors, 7th edn. Wiley, New York
Song Y, Li L, Ou Y, Gao Z, Li E, Li X, Zhang W, Wang J, Xu L, Zhou Y et al (2014) Identification of genomic alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature 509:91–95
Stern HM (2012) Improving treatment of HER2-positive cancers: opportunities and challenges. Sci Transl Med 4:127rv2
Sunshine J, Taube JM (2015) PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 23:32–38
Takada N, Yano Y, Matsuda T, Otani S, Osugi H, Higashino M, Kinoshita H, Fukushima S (1995) Expression of immunoreactive human hepatocyte growth factor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Lett 97:145–148
Ura T, Muro K, Hara H, Yamaguchi K, Hironaka S, Iwasa S, Kato K, Kojima T, Tsushima T, Yasui H et al (2015) Phase 2 study of nivolumab (anti-PD-1; ONO-4538) in patients with esophageal cancer: preliminary report. In: The European esophageal cancer congress 2015, p. #2301, Vienna
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M, Fitzgibbons P et al (2013) Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 31:3997–4013
Xu Y, Peng Z, Li Z, Lu M, Gao J, Li Y, Li Y, Shen L (2015) Expression and clinical significance of c-Met in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 15:6
Xu YP, Lin G, Sun XJ, Yan MH, Zhang G, Hu JL, Sun WY, Yu JM (2016) C-Met as a molecular marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its association with clinical outcome. J Cancer 7:587–594
Yoshino M, Ishiwata T, Watanabe M, Matsunobu T, Komine O, Ono Y, Yamamoto T, Fujii T, Matsumoto K, Tokunaga A et al (2007) Expression and roles of keratinocyte growth factor and its receptor in esophageal cancer cells. Int J Oncol 31:721–728
Zhang T, Shen H, Dong W, Qu X, Liu Q, Du J (2014) Antitumor effects and molecular mechanisms of figitumumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody to IGF-1 receptor, in esophageal carcinoma. Sci Rep 4:6855
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Ms. Yuka Nakamura for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of the National Cancer Center (Registration No. 2014-135).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatogai, K., Fujii, S., Kojima, T. et al. Large-scale comprehensive immunohistochemical biomarker analyses in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 2351–2361 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2482-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2482-7