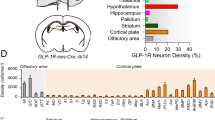
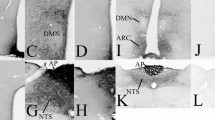
Abstract
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and its agonists exert anorexigenic effect at least partly via acting on GLP-1 receptors (GLP-1R) in the arcuate nucleus (ARC). While the anorexigenic, proopiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons of the ARC were shown previously to express GLP-1R, the putative GLP-1R-content of the orexigenic, neuropeptide Y (NPY) neurons remained so far undetected. As GLP-1R is abundant in the ventromedial ARC, where NPY neurons are located; here, we address the possibility that GLP-1 can act directly on the orexigenic NPY system via GLP-1R. Double-labeling immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization were performed on tissues of adult male mice to detect GLP-1R in NPY neurons. In double-immunolabeled preparations, GLP-1R-immunoreactivity was observed in NPY neurons and in axons ensheathing the majority of NPY neurons. Ultrastructural studies confirmed that GLP-1R-immunoreactivity is associated with the outer membrane of NPY perikarya as well as with axons forming symmetric type, inhibitory synapses on NPY-containing neurons. Double-labeling in situ hybridization experiments demonstrated the expression of GLP-1R mRNA in approximately 20% of NPY mRNA-containing neurons of the ARC. In summary, our data demonstrate the presence of GLP-1R protein and mRNA in NPY neurons of ARC and also reveal the innervation of NPY neurons by GLP-1R-containing inhibitory neurons. These observations suggest that GLP-1 signaling can influence NPY neurons both directly and indirectly. Furthermore, GLP-1 signaling on energy homeostasis appears to involve both direct and indirect effects of GLP-1 on the orexigenic NPY neurons, in addition to the previously known effects via the anorexigenic POMC neuronal system.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alvarez E, Roncero I, Chowen JA, Thorens B, Blazquez E (1996) Expression of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene in rat brain. J Neurochem 66(3):920–927. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66030920.x
Astrup A, Rossner S, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, Niskanen L, Al Hakim M, Madsen J, Rasmussen MF, Lean ME, Group NNS (2009) Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 374(9701):1606–1616. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61375-1
Baggio LL, Drucker DJ (2007) Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 132(6):2131–2157. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.054
Candeias EM, Sebastiao IC, Cardoso SM, Correia SC, Carvalho CI, Placido AI, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Moreira PI, Duarte AI (2015) Gut-brain connection: the neuroprotective effects of the anti-diabetic drug liraglutide. World J Diabetes 6(6):807–827. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i6.807
Cork SC, Richards JE, Holt MK, Gribble FM, Reimann F, Trapp S (2015) Distribution and characterisation of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expressing cells in the mouse brain. Mol Metab 4(10):718–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2015.07.008
Drucker DJ (2005) Biologic actions and therapeutic potential of the proglucagon-derived peptides. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 1(1):22–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpendmet0017
Farkas E, Szilvasy-Szabo A, Ruska Y, Sinko R, Rasch MG, Egebjerg T, Pyke C, Gereben B, Knudsen LB, Fekete C (2021) Distribution and ultrastructural localization of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) in the rat brain. Brain Struct Funct 226(1):225–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-020-02189-1
Flint A, Raben A, Ersboll AK, Holst JJ, Astrup A (2001) The effect of physiological levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 on appetite, gastric emptying, energy and substrate metabolism in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25(6):781–792. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801627
Gabery S, Salinas CG, Paulsen SJ, Ahnfelt-Ronne J, Alanentalo T, Baquero AF, Buckley ST, Farkas E, Fekete C, Frederiksen KS, Helms HCC, Jeppesen JF, John LM, Pyke C, Nohr J, Lu TT, Polex-Wolf J, Prevot V, Raun K, Simonsen L, Sun G, Szilvasy-Szabo A, Willenbrock H, Secher A, Knudsen LB (2020) Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.133429
Graham DL, Durai HH, Trammell TS, Noble BL, Mortlock DP, Galli A, Stanwood GD (2020) A novel mouse model of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expression: a look at the brain. J Comp Neurol 528(14):2445–2470. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.24905
Guo XH (2016) The value of short- and long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: experience with exenatide. Curr Med Res Opin 32(1):61–76. https://doi.org/10.1185/03007995.2015.1103214
Harris KM, Weinberg RJ (2012) Ultrastructure of synapses in the mammalian brain. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a005587
He Z, Gao Y, Lieu L, Afrin S, Cao J, Michael NJ, Dong Y, Sun J, Guo H, Williams KW (2019) Direct and indirect effects of liraglutide on hypothalamic POMC and NPY/AgRP neurons—implications for energy balance and glucose control. Mol Metab 28:120–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2019.07.008
Heppner KM, Kirigiti M, Secher A, Paulsen SJ, Buckingham R, Pyke C, Knudsen LB, Vrang N, Grove KL (2015) Expression and distribution of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor mRNA, protein and binding in the male nonhuman primate (Macaca mulatta) brain. Endocrinology 156(1):255–267. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2014-1675
Holst JJ (2004) Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with agonists of the GLP-1 receptor or DPP-IV inhibitors. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 9(1):155–166. https://doi.org/10.1517/eoed.9.1.155.32952
Hrabovszky E, Csapó AK, Kalló I, Wilheim T, Túri GF, Liposits Z (2006) Localization and osmotic regulation of vesicular glutamate transporter-2 in magnocellular neurons of the rat hypothalamus. Neurochem Int 48(8):753–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2005.12.013
Jensen CB, Pyke C, Rasch MG, Dahl AB, Knudsen LB, Secher A (2018) Characterization of the glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor in male mouse brain using a novel antibody and in situ hybridization. Endocrinology 159(2):665–675. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2017-00812
** SL, Han VK, Simmons JG, Towle AC, Lauder JM, Lund PK (1988) Distribution of glucagonlike peptide I (GLP-I), glucagon, and glicentin in the rat brain: an immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 271(4):519–532. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902710405
Knudsen LB, Secher A, Hecksher-Sorensen J, Pyke C (2016) Long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists have direct access to and effects on pro-opiomelanocortin/cocaine- and amphetamine-stimulated transcript neurons in the mouse hypothalamus. J Diabetes Investig 7(Suppl 1):56–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12463
Larsen PJ, Tang-Christensen M, Holst JJ, Orskov C (1997) Distribution of glucagon-like peptide-1 and other preproglucagon-derived peptides in the rat hypothalamus and brainstem. Neuroscience 77(1):257–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00434-4
Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Reimann F, Gribble FM, Trapp S (2011) Preproglucagon neurons project widely to autonomic control areas in the mouse brain. Neuroscience 180:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.02.023
Merchenthaler I, Lane M, Shughrue P (1999) Distribution of pre-pro-glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor messenger RNAs in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 403(2):261–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19990111)403:2%3c261::aid-cne8%3e3.0.co;2-5
O’Neil PM, Birkenfeld AL, McGowan B, Mosenzon O, Pedersen SD, Wharton S, Carson CG, Jepsen CH, Kabisch M, Wilding JPH (2018) Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet 392(10148):637–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31773-2
Pelletier G, Desy L, Kerkerian L, Cote J (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the human hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res 238(1):203–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215163
Peterfi Z, Farkas E, Nagyunyomi-Senyi K, Kadar A, Otto S, Horvath A, Fuzesi T, Lechan RM, Fekete C (2018) Role of TRH/UCN3 neurons of the perifornical area/bed nucleus of stria terminalis region in the regulation of the anorexigenic POMC neurons of the arcuate nucleus in male mice and rats. Brain Struct Funct 223(3):1329–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1553-5
Peterfi Z, Szilvasy-Szabo A, Farkas E, Ruska Y, Pyke C, Knudsen LB, Fekete C (2020) GLP-1 regulates the POMC neurons of the arcuate nucleus both directly and indirectly via presynaptic action. Neuroendocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1159/000512806
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG (2000) Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404(6778):661–671. https://doi.org/10.1038/35007534
Secher A, Jelsing J, Baquero AF, Hecksher-Sorensen J, Cowley MA, Dalboge LS, Hansen G, Grove KL, Pyke C, Raun K, Schaffer L, Tang-Christensen M, Verma S, Witgen BM, Vrang N, Bjerre Knudsen L (2014) The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J Clin Invest 124(10):4473–4488. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI75276
Shah M, Vella A (2014) Effects of GLP-1 on appetite and weight. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 15(3):181–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-014-9289-5
Sisley S, Gutierrez-Aguilar R, Scott M, D’Alessio DA, Sandoval DA, Seeley RJ (2014) Neuronal GLP1R mediates liraglutide’s anorectic but not glucose-lowering effect. J Clin Invest 124(6):2456–2463. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI72434
Valassi E, Scacchi M, Cavagnini F (2008) Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 18(2):158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2007.06.004
Vivas O, Kruse M, Hille B (2014) Nerve growth factor sensitizes adult sympathetic neurons to the proinflammatory peptide bradykinin. J Neurosci 34(36):11959–11971. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1536-14.2014
Wittmann G, Liposits Z, Lechan RM, Fekete C (2002) Medullary adrenergic neurons contribute to the neuropeptide Y-ergic innervation of hypophysiotropic thyrotropin-releasing hormone-synthesizing neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett 324(1):69–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(02)00165-9
Yang Y, Moghadam AA, Cordner ZA, Liang NC, Moran TH (2014) Long term exendin-4 treatment reduces food intake and body weight and alters expression of brain homeostatic and reward markers. Endocrinology 155(9):3473–3483. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2014-1052
Zhang L, Hernandez-Sanchez D, Herzog H (2019) Regulation of feeding-related behaviors by arcuate neuropeptide Y neurons. Endocrinology 160(6):1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2019-00056
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their appreciation to Andrea Juhász and Veronika Penksza for their great technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the Hungarian Science Foundation (OTKA K124767 and K128317), Hungarian National Brain Research Program (2017–1.2.1-NKP-2017–00002), EU H2020 THYRAGE no. 666869.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YR performed immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and in situ hybridization studies, contributed to data analysis. AS-S performed ultrastructural studies, analyzed data and was involved in the preparation of manuscript. DK was involved in the in situ hybridization studies. AK was involved in the ultrastructural studies. LM, RS, EH and BG generated the probes for in situ hybridization. CF planned and oversaw the experiments, interpreted data and was involved in the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
C.F. received funding from Novo Nordisk A/S. Y.R., A.Sz-Sz., D.K., A.K., L.M., R.S., E.H., and B.G. declare no competing interest.
Ethics approval
All experimental protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Welfare Committee at the Institute of Experimental Medicine. The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruska, Y., Szilvásy-Szabó, A., Kővári, D. et al. Expression of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in neuropeptide Y neurons of the arcuate nucleus in mice. Brain Struct Funct 227, 77–87 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-021-02380-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-021-02380-y