Abstract
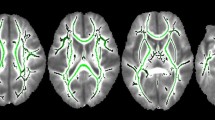
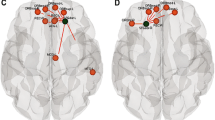
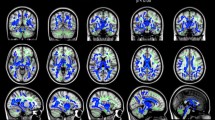
Children born very preterm (VPT) at less than 32 weeks’ gestational age (GA) are prone to disrupted white matter maturation and impaired cognitive development. The aims of the present study were to identify differences in white matter microstructure and connectivity of children born VPT compared to term-born children, as well as relations between white matter measures with cognitive outcomes and early brain injury. Diffusion images and T1-weighted anatomical MR images were acquired along with developmental assessments in 31 VPT children (mean GA: 28.76 weeks) and 28 term-born children at 4 years of age. FSL’s tract-based spatial statistics was used to create a cohort-specific template and mean fractional anisotropy (FA) skeleton that was applied to each child’s DTI data. Whole brain deterministic tractography was performed and graph theoretical measures of connectivity were calculated based on the number of streamlines between cortical and subcortical nodes derived from the Desikan-Killiany atlas. Between-group analyses included FSL Randomise for voxel-wise statistics and permutation testing for connectivity analyses. Within-group analyses between FA values and graph measures with IQ, language and visual-motor scores as well as history of white matter injury (WMI) and germinal matrix/intraventricular haemorrhage (GMH/IVH) were performed. In the children born VPT, FA values within major white matter tracts were reduced compared to term-born children. Reduced measures of local strength, clustering coefficient, local and global efficiency were present in the children born VPT within nodes in the lateral frontal, middle and superior temporal, cingulate, precuneus and lateral occipital regions. Within-group analyses revealed associations in term-born children between FA, Verbal IQ, Performance IQ and Full scale IQ within regions of the superior longitudinal fasciculus, inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, forceps minor and forceps major. No associations with outcome were found in the VPT group. Global efficiency was reduced in the children born VPT with a history of WMI and GMH/IVH. These findings are evidence for under-developed and less connected white matter in children born VPT, contributing to our understanding of white matter development within this population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard S, Bullmore E (2007) Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput Biol 3(2):0174–0183
Allin MPG, Kontis D, Walshe M, Wyatt J, Barker GJ, Kanaan RAA et al (2011) White matter and cognition in adults who were born preterm. PLoS One 6(10):1–9
Anderson PJ (2014) Neuropsychological outcomes of children born very preterm. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 19(2):90–96
Anderson MJ, Robinson J (2001) Permutation tests for linear models. Aust N Zeal J Stat 43(1):75–88
Anjari M, Srinivasan L, Allsop JM, Hajnal JV, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD, Counsell SJ (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging with tract-based spatial statistics reveals local white matter abnormalities in preterm infants. NeuroImage 35(3):1021–1027
Ball G, Boardman JP, Rueckert D, Aljabar P, Arichi T, Merchant N et al (2012) The effect of preterm birth on thalamic and cortical development. Cereb Cortex 22(5):1016–1024
Ball G, Srinivasan L, Aljabar P, Counsell SJ, Durighel G, Hajnal JV et al (2013) Development of cortical microstructure in the preterm human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(23):9541–9546
Batalle D, Hughes EJ, Zhang H, Tournier J-D, Tusor N, Aljabar P et al (2017) Early development of structural networks and the impact of prematurity on brain connectivity. NeuroImage 149(January):379–392
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):435–455
Beery K, Buktenica N, Beery N (2010) Beery–Buktenica test of visual motor integration. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 57(1):289–300
Boardman JP, Counsell SJ, Rueckert D, Kapellou O, Bhatia KK, Aljabar P et al (2006) Abnormal deep grey matter development following preterm birth detected using deformation-based morphometry. NeuroImage 32(1):70–78
Brown JA, Rudie JD, Bandrowski A, Van Horn JD, Bookheimer SY (2012) The UCLA multimodal connectivity database: a web-based platform for brain connectivity matrix sharing and analysis. Front Neuroinform 6(28):1–17
Brown CJ, Miller SP, Booth BG, Andrews S, Chau V, Poskitt KJ, Hamarneh G (2014) NeuroImage Structural network analysis of brain development in young preterm neonates. NeuroImage 101:667–680
Bullmore ET, Sporns O (2012) The economy of brain network organization. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(5):336–349
Cao M, Huang H, Peng Y, Dong Q, He Y (2016). Toward developmental connectomics of the human brain. Front Neuroanat. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2016.00025
Cao M, Huang H, He Y (2017a) Developmental connectomics from infancy through early childhood. Trends Neurosci 40(8):494–506
Cao M, He Y, Dai Z, Liao X, Jeon T, Ouyang M et al (2017b) Early development of functional network segregation revealed by connectomic analysis of the preterm human brain. Cereb Cortex 27(3):1949–1963
Chang L-C, Jones DK, Pierpaoli C (2005) RESTORE: Robust estimation of tensors by outlier rejection. Magn Reson Med 53(5):1088–1095
Constable RT, Ment LR, Vohr BR, Kesler SR, Fulbright RK, Lacadie C et al (2008) Prematurely born children demonstrate white matter microstructural differences at 12 years of age, relative to term control subjects: an investigation of group and gender effects. Pediatrics 121(2):306–316
Counsell SJ, Edwards AD, Chew ATM, Anjari M, Dyet LE, Srinivasan L et al (2008) Specific relations between neurodevelopmental abilities and white matter microstructure in children born preterm. Brain 131:3201–3208
Dean JM, Mcclendon E, Hansen K, Azimi-zonooz A, Chen K, Riddle A et al (2013) Prenatal cerebral ischemia disrupts MRI-defined cortical micrtostructure through disturbances in neuronal arborization. Sci Transl Med 5(168):1–22
Dean JM, Bennet L, Back S, McClendon E, Riddle A, Gunn AJ (2014) What brakes the preterm brain? An arresting story. Pediatr Res 75(1–2):227–233
Delobel-Ayoub M, Arnaud C, White-Koning M, Casper C, Pierrat V, Garel M et al (2009) Behavioral problems and cognitive performance at 5 years of age after very preterm birth: the EPIPAGE study. Pediatrics 123(6):1485–1492
Desikan RS, Se F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D et al (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 31:968–980
Doria V, Beckmann CF, Arichi T, Merchant N, Groppo M, Turkheimer FE et al (2010) Emergence of resting state networks in the preterm human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(46):20015–20020
Dubois J, Dehaene-Lambertz G, Kulikova S, Poupon C, Hüppi PS, Hertz-Pannier L (2014) The early development of brain white matter: a review of imaging studies in fetuses, newborns and infants. Neuroscience 276:48–71
Duerden EG, Card D, Lax ID, Donner EJ, Taylor MJ (2013) Alterations in frontostriatal pathways in children born very preterm. Dev Med Child Neurol 55(10):952–958
Duerden EG, Foong J, Chau V, Branson H, Poskitt KJ, Grunau RE et al (2015) Tract-based spatial statistics in preterm-born neonates predicts cognitive and motor outcomes at 18 months. Am J Neuroradiol 36(8):1565–1571
Feldman HM, Lee ES, Loe IM, Yeom KW, Grill-Spector K, Luna B (2012) White matter microstructure on diffusion tensor imaging is associated with conventional magnetic resonance imaging findings and cognitive function in adolescents born preterm. Dev Med Child Neurol 54(9):809–814
Feldman HM, Lee ES, Yeatman JD, Yeom KW (2013) Language and reading skills in school-aged children adolescents born preterm are associated with white matter properties on diffusion tensor imaging. Neuropsychologia 50(14):3348–3362
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C et al (2002) Whole brain segmentation: Neurotechnique automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 33(3):341–355
Gozzo Y, Vohr B, Lacadie C, Hampson M, Katz KH, Maller-Kesselman J et al (2009) Alterations in neural connectivity in preterm children at school age. NeuroImage 48(2):458–463
Hagmann P, Sporns O, Madan N, Cammoun L, Pienaar R, Wedeen VJ et al (2010) White matter maturation reshapes structural connectivity in the late develo** human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(44):19067–19072
Huang H, Shu N, Mishra V, Jeon T, Chalak L, Wang ZJ et al (2015) Development of human brain structural networks through infancy and childhood. Cereb Cortex 25(5):1389–1404
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TEJ, Woolrich MW, Smith SM (2012) FSL. NeuroImage 62(2):782–790
Jones DK, Knösche TR, Turner R (2013) White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: the do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. NeuroImage 73:239–254
Kapellou O, Counsell SJ, Kennea N, Dyet L, Saeed N, Stark J et al (2006) Abnormal cortical development after premature birth shown by altered allometric scaling of brain growth. PLoS Med 3(8):1382–1390
Keunen K, Benders MJ, Leemans A, Fieret-Van Stam PC, Scholtens LH, Viergever MA et al (2017). White matter maturation in the neonatal brain is predictive of school age cognitive capacities in children born very preterm. Dev Med Child Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13487
Krsnik Ž, Majić V, Vasung L, Huang H, Kostović I (2017) Growth of thalamocortical fibers to the somatosensory cortex in the human fetal brain. Front Neurosci 11(233):1–17
Loe IM, Lee ES, Feldman HM (2013) Attention and internalizing behaviors in relation to white matter in children born preterm. JDBP 34(3):156–164
Mangin KS, Horwood LJ, Woodward LJ (2017) Cognitive development trajectories of very preterm and typically develo** children. Child Dev 88(1):282–298
Mcclendon E, Ph D, Chen K, Gong X, Sharifnia E, Hagen M et al (2014) Prenatal cerebral ischemia triggers dysmaturation of caudate projection neurons. Ann Neurol 75(4):508–524
Miller SP, Cozzio CC, Goldstein RB, Ferriero DM, Partridge JC, Vigneron DB, Barkovich AJ (2003) Comparing the diagnosis of white matter injury in premature newborns with serial MR imaging and transfontanel ultrasonography findings. Am J Neuroradiol 24(8):1661–1669
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, Van Zijl PCM (1999) Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 45(2):265–269
Mori S, Wakana S, Van Zijl PCM, Nagai-Poetscher LM (2005) MRI atlas of human white matter. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mullen KM, Vohr BR, Katz KH, Schneider KC, Lacadie C, Hampson M et al (2012) Preterm birth results in alterations in neural connectivity at age 16 years. NeuroImage 54(4):2563–2570
Pandit AS, Robinson E, Aljabar P, Ball G, Gousias IS, Wang Z et al (2014) Whole-brain map** of structural connectivity in infants reveals altered connection strength associated with growth and preterm birth. Cereb Cortex 29(9):2324–2333
Pannek K, Scheck SM, Colditz PB, Boyd RN, Rose SE (2014) Magnetic resonance diffusion tractography of the preterm infant brain: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol 56(2):113–124
Papile L, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H (1978) Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr 92(4):529–534
Paus T, Collins DL, Evans AC, Leonard G, Pike B, Zijdenbos A (2001) Maturation of white matter in the human brain: a review of magnetic resonance studies. Brain Res Bull 54(3):255–266
Raybaud C, Ahmad T, Rastegar N, Shroff M, Al Nassar M (2013) The premature brain: developmental and lesional anatomy. Neuroradiology 55(Suppl 2):S23–S40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1231-0
Rubinov M, Sporns O (2010) Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 52(3):1059–1069
Salvan P, Tournier JD, Batalle D, Falconer S, Chew A, Kennea N et al (2017) Language ability in preterm children is associated with arcuate fasciculi microstructure at term. Hum Brain Mapp 38(8):3836–3847
Schafer RJ, Lacadie C, Vohr B, Kesler SR, Katz KH, Schneider KC et al (2009) Alterations in functional connectivity for language in prematurely born adolescents. Brain 132:661–670
Semel E, Wiig E, Secord W (2004) Clinical evaluation of language fundamentals—preschool, 2nd edn. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage 44(1):83–98
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage 31:1487–1505
Song SK, Yoshino J, Le TQ, Lin SJ, Sun SW, Cross AH, Armstrong RC (2005) Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. NeuroImage 26(1):132–140
Tamnes CK, Ostby Y, Walhovd KB, Westlye LT, Due-Tonnessen P, Fjell AM (2010) Intellectual abilities and white matter microstructure in development: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Hum Brain Mapp 31(10):1609–1625
Thompson DK, Chen J, Beare R, Adamson CL, Ellis R, Ahmadzai ZM et al (2016) Structural connectivity relates to perinatal factors and functional impairment at 7 years in children born very preterm. NeuroImage 134:328–337
Travis KE, Adams JN, Ben-Shachar M, Feldman HM (2015) Decreased and increased anisotropy along major cerebral white matter tracts in preterm children and adolescents. Plos One 10(11):e0142860. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142860
Ullman H, Spencer-smith M, Thompson DK, Doyle LW, Inder TE, Anderson PJ, Klingberg T (2015) Neonatal MRI is associated with future cognition and academic achievement in preterm children. Brain 138(11):13251–13262
Vangberg TR, Skranes J, Dale AM, Martinussen M, Brubakk AM, Haraldseth O (2006) Changes in white matter diffusion anisotropy in adolescents born prematurely. NeuroImage 32:1538–1548
van Kooij BJM, de Vries LS, Ball G, van Haastert IC, Benders MJNL., Groenendaal F, Counsell SJ (2012) Neonatal tract-based spatial statistics findings and outcome in preterm infants. AJNR 33(1):188–194
Volpe JJ (2008) Intracranial hemorrhage: germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage of the premature infant. In: Neurology of the newborn, 5th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 517–588
Wang R, Benner T, Sorensen AG, Wedeen VJ (2007) Diffusion toolkit: a software package for diffusion imaging data processing and tractography. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 15:3720
Wechsler D (2002) Wechsler preschool and primary scales of intelligence, 3rd edn. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Woodward LJ, Moor S, Hood KM, Champion PR, Foster-Cohen S, Inder TE, Austin NC (2009) Very preterm children show impairments across multiple neurodevelopmental domains by age 4 years. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 94(5):F339–F344
**a M, Wang J, He Y (2013) BrainNet viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS One 8(7):e68910. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068910
Yap PT, Fan Y, Chen Y, Gilmore JH, Lin W, Shen D (2011). Development trends of white matter connectivity in the first years of life. PLoS One 6(9):e24678
Young JM, Morgan BR, Whyte HEA, Lee W, Smith ML, Raybaud C et al (2017) Longitudinal study of white matter development and outcomes in children born very preterm. Cereb Cortex 27(8):4094–4105. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw221
Acknowledgements
We thank all of the families who participated in the study. We also thank Tammy Rayner, Ruth Weiss, Dr. Steven Miller, Dr. Manohar Shroff, Dr. Charles Raybaud, Dr. Aideen Moore, Dr. Hilary Whyte, Dr. Bratislav Misic, Tamara Powell and Wayne Lee for their valuable support and contributions.
Funding
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-84399 and MOP-137115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, J.M., Vandewouw, M.M., Morgan, B.R. et al. Altered white matter development in children born very preterm. Brain Struct Funct 223, 2129–2141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-1614-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-018-1614-4