Abstract
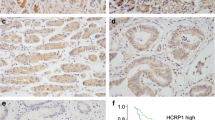
The tripartite motif protein tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) is involved in human cancer progression. However, the expression pattern and biological roles of TRIM24 in human gastric cancer have not been studied. Here, we report that expression of TRIM24 protein was upregulated in 65 of 133 gastric cancer specimens. TRIM24 upregulation positively correlated with clinical stage, local invasion, and poor patient prognosis. We overexpressed TRIM24 by transfection in SGC-7901 cells and used an siRNA strategy to knock down TRIM24 in MKN-1 cells. MTT and colony formation assays showed that transfection of TRIM24 plasmid accelerated, while its depletion inhibited cell proliferation rate. TRIM24 overxpression also induced chemoresistance to 5-FU in gastric cancer cells. Further analysis showed that TRIM24 overexpression upregulated cyclin D1 and Akt phosphorylation. Akt inhibitor LY294002 reversed the role of TRIM24 on chemoresistance. In conclusion, our study shows that TRIM24 is overexpressed in human gastric cancer and accelerates cell growth as well as induce chemoresistance, possibly through the Akt pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90
Brenner H, Rothenbacher D, Arndt V (2009) Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Methods Mol Biol 472:467–477
Jia B, Liu H, Kong Q, Li B (2012) RKIP expression associated with gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Tumour Biol 33(4):919–925
Jia Y, Dong B, Tang L, Liu Y, Du H, Yuan P, Wu A, Ji J (2012) Apoptosis index correlates with chemotherapy efficacy and predicts the survival of patients with gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 33(4):1151–1158
Oishi Y, Watanabe Y, Yoshida Y, Sato Y, Hiraishi T, Oikawa R, Maehata T, Suzuki H, Toyota M, Niwa H, Suzuki M, Itoh F (2012) Hypermethylation of Sox17 gene is useful as a molecular diagnostic application in early gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 33(2):383–393
Le Douarin B, Nielsen AL, Garnier JM, Ichinose H, Jeanmougin F, Losson R, Chambon P (1996) A possible involvement of TIF1 alpha and TIF1 beta in the epigenetic control of transcription by nuclear receptors. EMBO J 15(23):6701–6715
Le Douarin B, Nielsen AL, You J, Chambon P, Losson R (1997) TIF1 alpha: a chromatin-specific mediator for the ligand-dependent activation function AF-2 of nuclear receptors? Biochem Soc Trans 25(2):605–612
Le Douarin B, Zechel C, Garnier JM, Lutz Y, Tora L, Pierrat P, Heery D, Gronemeyer H, Chambon P, Losson R (1995) The N-terminal part of TIF1, a putative mediator of the ligand-dependent activation function (AF-2) of nuclear receptors, is fused to B-raf in the oncogenic protein T18. EMBO J 14(9):2020–2033
Klugbauer S, Rabes HM (1999) The transcription coactivator HTIF1 and a related protein are fused to the RET receptor tyrosine kinase in childhood papillary thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene 18(30):4388–4393
Zhong S, Delva L, Rachez C, Cenciarelli C, Gandini D, Zhang H, Kalantry S, Freedman LP, Pandolfi PP (1999) A RA-dependent, tumour-growth suppressive transcription complex is the target of the PML-RARalpha and T18 oncoproteins. Nat Genet 23(3):287–295
Belloni E, Trubia M, Gasparini P, Micucci C, Tapinassi C, Confalonieri S, Nuciforo P, Martino B, Lo-Coco F, Pelicci PG, Di Fiore PP (2005) 8p11 myeloproliferative syndrome with a novel t(7;8) translocation leading to fusion of the FGFR1 and TIF1 genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 42(3):320–325
Katzenellenbogen BS (1996) Estrogen receptors: bioactivities and interactions with cell signaling pathways. Biol Reprod 54(2):287–293
Tsai WW, Wang Z, Yiu TT, Akdemir KC, **a W, Winter S, Tsai CY, Shi X, Schwarzer D, Plunkett W, Aronow B, Gozani O, Fischle W, Hung MC, Patel DJ, Barton MC (2010) TRIM24 links a non-canonical histone signature to breast cancer. Nature 468(7326):927–932
Chambon M, Orsetti B, Berthe ML, Bascoul-Mollevi C, Rodriguez C, Duong V, Gleizes M, Thenot S, Bibeau F, Theillet C, Cavailles V (2011) Prognostic significance of TRIM24/TIF-1alpha gene expression in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 178(4):1461–1469
Li H, Sun L, Tang Z, Fu L, Xu Y, Li Z, Luo W, Qiu X, Wang E (2012) Overexpression of TRIM24 correlates with tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 7(5):e37657
Zhang LH, Yin AA, Cheng JX, Huang HY, Li XM, Zhang YQ, Han N, and Zhang X (2015) TRIM24 promotes glioma progression and enhances chemoresistance through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncogene 34:600–610
Jeong SH, Ko GH, Cho YH, Lee YJ, Cho BI, Ha WS, Choi SK, Kim JW, Lee CW, Heo YS, Shin SH, Yoo J, Hong SC (2012) Pyrophosphatase overexpression is associated with cell migration, invasion, and poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 33(6):1889–1898
Yu HF, Zhao G, Ge ZJ, Wang DR, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zha TZ, Zhang K, Zhang M, Tan YF, Zhou SJ, Jiang C (2012) High RIN1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol 33(5):1557–1563
**e C, Fu L, Han Y, Li Q, Wang E (2014) Decreased ARID1A expression facilitates cell proliferation and inhibits 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma. Tumour Biol 35:7921–7792
Yothaisong S, Dokduang H, Techasen A, Namwat N, Yongvanit P, Bhudhisawasdi V, Puapairoj A, Riggins GJ, Loilome W (2013) Increased activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is associated with cholangiocarcinoma metastasis and PI3K/mTOR inhibition presents a possible therapeutic strategy. Tumour Biol 34(6):3637–3648
Shin JY, Kim JO, Lee SK, Chae HS, Kang JH (2010) LY294002 may overcome 5-FU resistance via down-regulation of activated p-AKT in Epstein–Barr virus-positive gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 10:425
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, ZF., Wang, ZN., Zhao, TT. et al. TRIM24 is upregulated in human gastric cancer and promotes gastric cancer cell growth and chemoresistance. Virchows Arch 466, 525–532 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1737-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1737-4