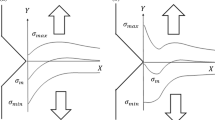
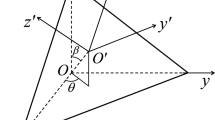
Abstract
Accurately assessing the fatigue performance of components is the key to ensuring structural integrity and reliability, but there is a lack of fatigue life prediction methods that effectively couple the stress gradient effect, the non-proportional additional strengthening effect, and the size effect. Accordingly, a fatigue life prediction model for notched specimens under multiaxial loading is established by analyzing the influence of tension–torsion proportional load and tension–torsion non-proportional load on the fatigue strength of notched specimens. Firstly, based on the energy critical plane method, the location of the critical plane is determined with the help of the coordinate transformation principle. Secondly, the material constant is used to quantify the level of cyclic strengthening, and a non-proportional additional strengthening function is proposed by considering the influence of phase difference. Thirdly, the influence of the non-uniform stress field at the notch root on the fatigue life is considered, and the distribution of equivalent stress on the specific paths is extracted and normalized to give an equivalent stress gradient factor. Then, a fatigue strength reduction factor is constructed by considering the influence of different notch geometrical parameters. Finally, a fatigue life assessment method for notched specimens is proposed based on the Manson–Coffin equation. With the help of the test data of three materials, En8, Al7050-T7451, and GH4169, the method is validated and compared with the calculation results of the Manson–Coffin equation, SWT model, and FS model. The results show that the prediction accuracy of the method in this study is high, which is located in the two-fold error dispersion band, and the prediction results are better than that of the other three models.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Branco, R., Prates, P.A., Costa, J.D., et al.: Rapid assessment of multiaxial fatigue lifetime in notched components using an averaged strain energy density approach. Int. J. Fatigue 124, 89–98 (2019)
Infante, G.D., Qian, G.A., Miguelez, H., et al.: Analysis of the effect of out-of-phase biaxial fatigue loads on crack paths in cruciform specimens using XFEM. Int. J. Fatigue 123, 87–95 (2019)
Liao, D., Zhu, S.P.: Energy field intensity approach for notch fatigue analysis. Int. J. Fatigue 127, 190–202 (2019)
Sun, L., Zhang, X.C., Wang, R.Z., et al.: Evaluation of fatigue and creep-fatigue damage levels on the basis of engineering damage mechanics approach. Int. J. Fatigue 166, 107277 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107277
Wang, R.Z., Zhu, S.P., Zhang, X.C., et al.: High temperature fatigue and creep-fatigue behaviors in a Ni-based superalloy: damage mechanisms and life assessment. Int. J. Fatigue 118, 08–21 (2019)
Gu, H.H., Wang, R.Z., Zhu, S.P., et al.: Machine learning assisted probabilistic creep-fatigue damage assessment. Int. J. Fatigue 156, 106677 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106677
Gu, H.H., Wang, R.Z., Zhang, X.C., et al.: Creep-fatigue reliability assessment for high-temperature components fusing on-line monitoring data and physics-of-failure by engineering damage mechanics approach. Int. J. Fatigue 169, 107481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107481
Luo, P., Yao, W.X., Wang, Y.Y., et al.: A survey on fatigue life analysis approaches for metallic notched components under multi-axial loading. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 233(10), 3870–3890 (2019)
Li, H.R., Peng, Y., Liu, Y., et al.: Corrected stress field intensity approach based on averaging superior limit of intrinsic damage dissipation work. J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 25(10), 1094–1103 (2018)
Groza, M., Nadot, Y., Varadi, K.: Defect size map for nodular cast iron components with ellipsoidal surface defects based on the defect stress gradient approach. Int. J. Fatigue 112, 206–215 (2018)
Branco, R., Costa, J.D., Borrego, L.P., et al.: Notch fatigue analysis and life assessment using an energy field intensity approach in 7050–T6 aluminium alloy under bending-torsion loading. Int. J. Fatigue 162, 106947 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.106947
He, J.C., Zhu, S.P., Liao, D., et al.: Probabilistic fatigue assessment of notched components under size effect using critical distance theory. Eng. Fract. Mech. 235, 107150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107150
Luo, P., Yu, M., Wen, C.L.: A strain energy density field method to predict the life of metallic notched components under multiaxial fatigue loading. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2686/1/012011
Liao, D., Zhu, S.P., Qian, G.A.: A strain energy density field method to predict the life of metallic notched components under multiaxial fatigue loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 163, 38–50 (2019)
Zhou, J., Tan, Z.C., Cao, L.W., et al.: An improved critical plane-energy multiaxial fatigue life prediction model considering shear mean stress. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 37(05), 2333–2341 (2023)
Zhang, X.L., Huang, H.Z., Zhang, X.L., et al.: A multiaxial probabilistic fatigue life prediction method for nickel-based single crystal turbine blade considering mean stress correction. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 39(05), 1735–1755 (2023)
Sun, J.Y., Qian, G.A., Li, J.H., et al.: A framework to simulate the crack initiation and propagation in very-high-cycle fatigue of an additively manufactured AlSi10Mg alloy. J. Mech. Phys. Solids (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2023.105293
Zhang, Z.B., Zhan, M., Fu, M.W.: Microstructural and geometrical size effects on the fatigue of metallic materials. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 218, 107058 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.107058
He, J.C., Zhun, S.P., Gao, J.W., et al.: Microstructural size effect on the notch fatigue behavior of a Ni-based superalloy using crystal plasticity modelling approach. Int. J. Plast. 172, 103857 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPLAS.2023.103857
Li, K.S., Wang, R.Z., Wang, J., et al.: Investigation of creep-fatigue crack initiation by using an optimal dual-scale modelling approach. Int. J. Fatigue 172, 107621 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107621
Hua, F.L., Liu, J.H., Pan, X.M., et al.: Research on multiaxial fatigue life of notched specimens based on Weibull distribution and Bayes estimation. Int. J. Fatigue 166, 107271 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107271
Liu, J.H., Zi, R., Wei, Y.B., et al.: A stress gradient-based fatigue life prediction method for multiaxial notched specimen considering additional hardening effect. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 195, 104597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPVP.2021.104597
Tang, Y.H., Song, Y.X., Yin, G.F., et al.: Notch fatigue life prediction model considering stress gradient influence depth and weight function. Metals 13(03), 539 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030539
Zhao, H., Liu, J.H., Hua, F.H., et al.: Multiaxial fatigue life prediction model considering stress gradient and size effect. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 199, 104703 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPVP.2022.104703
Zhong, B., Wang, Y.R., Wei, D.S., et al.: Multiaxial fatigue life prediction for powder metallurgy superalloy FGH96 based on stress gradient effect. Int. J. Fatigue 109, 26–36 (2018)
Lamba, H.S., Sidebottom, O.M.: Cyclic plasticity for nonproportional paths: part 1—cyclic hardening, erasure of memory, and subsequent strain hardening experiments. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 100(01), 96–103 (1978)
Xu, L., Wang, R.Z., Wang, J., et al.: On multiaxial creep–fatigue considering the non-proportional loading effect: Constitutive modeling, deformation mechanism, and life prediction. Int. J. Plast. 155, 103337 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2022.103337
Ye, W.L., Zhu, S.P., Niu, X.P., et al.: Fatigue life prediction of notched components under size effect using critical distance theory. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 121, 103519 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TAFMEC.2022.103519
Zhu, S.P., Wu, Y.L., Yi, X.J., et al.: Probabilistic fatigue assessment of notched components under size effect using generalized weakest-link model. Int. J. Fatigue 162, 107005 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107005
Brown, M.W., Miller, K.J.: A theory for fatigue failure under multiaxial stress-strain conditions. Arch Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 20, 745–755 (1973)
Kandil, F.A., Brown, M.W., Miller, K.J.: Biaxial low-cycle fatigue fracture of 316 stainless steel at elevated temperature. Microcomput. Des. Appl. 280, 205–210 (1982)
Wang, C.H., Brown, M.W.: A path-independent parameter for fatigue under proportional and non-proportional loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 16(12), 1285–1297 (1993)
Smith, K.N., Watson, P., Topper, T.H.: Stress-strain function for the fatigue of metals. J. Mater. Sci. 5(04), 767–778 (1970)
Fatemi, A., Socie, D., et al.: A critical plane approach to multiaxial fatigue damage including out-of-phase loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 11(03), 149–165 (1988)
Liu, J.H., Lu, J.M., Zhou, F., et al.: Multiaxial fatigue life prediction model for notched specimen based on modified energy gradient and critical plane method. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 125, 103880 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2023.103880
Liu, J.H., Hua, F.L., Lang, S.S., et al.: Evaluation of fatigue strength on multiaxial notched specimenss considering failure probability. Int. J. Fatigue 156, 106649 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106649
Itoh, T., Nakata, T., Sakane, M., et al.: Nonproportional low cycle fatigue of 6061 aluminum alloy under 14 strain paths. Eur. Struct. Integr. Soc. 25, 41–54 (1999)
Borodii, M.V., Shukaev, S.M.: Additional cyclic strain hardening and its relation to material structure, mechanical characteristics, and lifetime. Int. J. Fatigue 29(06), 1184–1191 (2007)
Shamsaei, N., Fatemi, A.: Effect of microstructure and hardness on non-proportional cyclic hardening coefficient and predictions. Mater. Sci. Eng. 527(12), 3015–3024 (2010)
Itoh, T., Yang, T.: Material dependence of multiaxial low cycle fatigue lives under non-proportional loading. Int. J. Fatigue 33(08), 1025–1031 (2011)
Kida, S., Itoh, T., Sakane, M., et al.: Dislocation structure and non-proportional hardening of type 304 stainless steel. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 20, 1375–1386 (1997)
Gates, N., Fatemi, A.: Notch deformation and stress gradient effects in multiaxial fatigue. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 84, 03–25 (2016)
Wu, Y.L., Zhu, S.P., He, J.C., et al.: Assessment of notch fatigue and size effect using stress field intensity approach. Int. J. Fatigue 149, 106279 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106279
Amjad, M., Fatemi, A.: Multiaxial fatigue behavior of thermoplastics including mean stress and notch effects: experiments and modeling. Int. J. Fatigue 136, 105571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105571
Wang, R.Q., Li, D., Hu, D.Y., et al.: A combined critical distance and highly-stressed-volume model to evaluate the statistical size effect of the stress concentrator on low cycle fatigue of TA19 plate. Int. J. Fatigue 95, 08–17 (2017)
Qylafku, G., Azari, N., Kadi, N.: Application of a new model proposal for fatigue life prediction on notches and key-seats. Int. J. Fatigue 21(08), 753–760 (1999)
Made, L., Schmitz, S., Gottschalk, H., et al.: Combined notch and size effect modeling in a local probabilistic approach for LCF. Comput. Mater. Sci. 142, 377–388 (2018)
Peterson, R.E., Plunkett, R.: Stress concentration factors. Nav. Eng. J. 67(03), 697–708 (2010)
Faruq, N.Z., Susmel, L.: Proportional/nonproportional constant/variable amplitude multiaxial notch fatigue: cyclic plasticity, non-zero mean stresses, and critical distance/plane. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 42(09), 1849–1873 (2019)
Sun, G.Q., Shang, D.G.: Prediction of fatigue lifetime under multiaxial cyclic loading using finite element analysis. Mater. Des. 31(01), 126–133 (2010)
Tao, Z.Q., Shang, D.G., Sun, Y.J., et al.: Multiaxial notch fatigue life prediction based on pseudo stress correction and finite element analysis under variable amplitude loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 41(08), 1674–1690 (2018)
Manson, S.S.: Fatigue: a complex subject—some simple approximations. Exp. Mech. 05(04), 193–226 (1965)
Coffin, L.F.: A study of the effects of cyclic thermal stresses on a ductile metal. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 76(08), 931–950 (1954)
Manson, S.S., Halford, G.R.: Multiaxial low-cycle fatigue of type 304 stainless steel. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 99(03), 283–285 (1977)
Bonacuse, P.J., Kalluri, S.: Elevated temperature axial and torsional fatigue behavior of Haynes 188. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 117(02), 191–199 (1995)
Deng, Q.Y., Zhu, S.P., Niu, X.P.: Load path sensitivity and multiaxial fatigue life prediction of metals under non-proportional loadings. Int. J. Fatigue 166, 107281 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107281
He, Y.B., Liu, J.H., Hua, F.L.: Low-cycle multiaxial random fatigue life prediction model based on equivalent stress transformation. Int. J. Struct. Integr. 13(05), 870–882 (2022)
Tao, Z.Q., Qian, G.A., Sun, J.Y.: Multiaxial fatigue life prediction by equivalent energy-based critical plane damage parameter under variable amplitude loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 45(12), 3640–3657 (2022)
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: 52365016; Gansu Province Young Doctor Fund Project, Grant/Award Number: 2023QB-030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shenglei Wu was contributed to writing—original draft, methodology, software, investigation. Jianhui Liu was contributed to writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, resources, supervision. Jumei Lu was contributed to visualization, investigation. Yazhou Wang was contributed to data curation, formal analysis. Wenjun Kou was contributed to visualization, software, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Liu, J., Lu, J. et al. Fatigue life evaluation of notched components affected by multiple factors. Arch Appl Mech 94, 1871–1889 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-024-02607-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-024-02607-4