Abstract
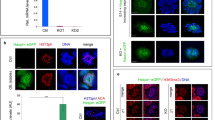
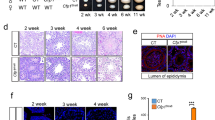
Heterochromatin protein 1β (HP1β), encoded by the Cbx1 gene, has been functionally linked to chromatin condensation, transcriptional regulation, and DNA damage repair. Here we report that testis-specific Cbx1 conditional knockout (Cbx1 cKO) impairs male germ cell development in mice. Depletion of HP1β negatively affected sperm maturation and increased seminiferous tubule degeneration in Cbx1 cKO mice. In addition, the spermatogonia have elevated γ-H2AX foci levels as do Cbx1 deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) as compared to wild-type (WT) control MEFs. The increase in γ-H2AX foci in proliferating Cbx1 cKO cells indicates defective replication-dependent DNA damage repair. Depletion or loss of HP1β from human cells and MEFs increased DNA replication fork stalling and firing of new origins of replication, indicating defective DNA synthesis. Taken together, these results suggest that loss of HP1β in proliferating cells leads to DNA replication defects with associated DNA damage that impact spermatogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed EA, Sfeir A, Takai H, Scherthan H (2013) Ku70 and non-homologous end joining protect testicular cells from DNA damage. J Cell Sci 126:3095–3104
Allers T, Lichten M (2001) Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell 106:47–57
Aston KI, Punj V, Liu L, Carrell DT (2012) Genome-wide sperm deoxyribonucleic acid methylation is altered in some men with abnormal chromatin packaging or poor in vitro fertilization embryogenesis. Fertil Steril 97:285–292
Aucott R, Bullwinkel J, Yu Y, Shi W, Billur M, Brown JP, Menzel U, Kioussis D, Wang G, Reisert I, Weimer J, Pandita RK, Sharma GG, Pandita TK, Fundele R, Singh PB (2008) HP1-beta is required for development of the cerebral neocortex and neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol 183:597–606
Ayoub N, Jeyasekharan AD, Bernal JA, Venkitaraman AR (2008) HP1-beta mobilization promotes chromatin changes that initiate the DNA damage response. Nature 453:682–686
Bartkova J, Falck J, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Skakkebaek NE, Lukas J, Bartek J (2001) Chk2 tumour suppressor protein in human spermatogenesis and testicular germ-cell tumours. Oncogene 20:5897–5902
Bosch-Presegue L, Raurell-Vila H, Thackray JK, Gonzalez J, Casal C, Kane-Goldsmith N, Vizoso M, Brown JP, Gomez A, Ausio J, Zimmermann T, Esteller M, Schotta G, Singh PB, Serrano L, Vaquero A (2017) Mammalian HP1 isoforms have specific roles in heterochromatin structure and organization. Cell Rep 21:2048–2057
Brunner AM, Nanni P, Mansuy IM (2014) Epigenetic marking of sperm by post-translational modification of histones and protamines. Epigenetics Chromatin 7(1):2
Chakraborty S, Pandita RK, Hambarde S, Mattoo AR, Charaka V, Ahmed KM, Iyer SP, Hunt CR, Pandita TK (2018) SMARCAD1 phosphorylation and ubiquitination are required for resection during DNA double-strand break repair. iScience 2:123–135
Cherry SM, Adelman CA, Theunissen JW, Hassold TJ, Hunt PA, Petrini JH (2007) The Mre11 complex influences DNA repair, synapsis, and crossing over in murine meiosis. Curr Biol 17:373–378
Chevillard C, Reik W, McDermott M, Fontes M, Mattei MG, Singh PB (1993) Chromosomal localization of human homologs of the Drosophila heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) gene. Mamm Genome 4:124–126
Cho C, Jung-Ha H, Willis WD, Goulding EH, Stein P, Xu Z, Schultz RM, Hecht NB, Eddy EM (2003) Protamine 2 deficiency leads to sperm DNA damage and embryo death in mice. Biol Reprod 69:211–217
Cohen PE, Pollard JW (2001) Regulation of meiotic recombination and prophase I progression in mammals. Bioessays 23:996–1009
Eissenberg JC, Elgin SC (2000) The HP1 protein family: getting a grip on chromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:204–210
Farley FW, Soriano P, Steffen LS, Dymecki SM (2000) Widespread recombinase expression using FLPeR (flipper) mice. Genesis 28:106–110
Gannon JR, Emery BR, Jenkins TG, Carrell DT (2014) The sperm epigenome: implications for the embryo. Adv Exp Med Biol 791:53–66
Garcia-Rodriguez A, Gosalvez J, Agarwal A, Roy R, Johnston S (2018) DNA damage and repair in human reproductive cells. Int J Mol Sci 20
Gunes S, Al-Sadaan M, Agarwal A (2015) Spermatogenesis, DNA damage and DNA repair mechanisms in male infertility. Reprod BioMed Online 31:309–319
Guo Y, Song Y, Guo Z, Hu M, Liu B, Duan H, Wang L, Yuan T, Wang D (2018) Function of RAD6B and RNF8 in spermatogenesis. Cell Cycle 17:162–173
Gupta A, Guerin-Peyrou TG, Sharma GG, Park C, Agarwal M, Ganju RK, Pandita S, Choi K, Sukumar S, Pandita RK, Ludwig T, Pandita TK (2008) The mammalian ortholog of Drosophila MOF that acetylates histone H4 lysine 16 is essential for embryogenesis and oncogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 28:397–409
Gupta A, Hunt CR, Pandita RK, Pae J, Komal K, Singh M, Shay JW, Kumar R, Ariizumi K, Horikoshi N, Hittelman WN, Guha C, Ludwig T, Pandita TK (2013) T-cell-specific deletion of Mof blocks their differentiation and results in genomic instability in mice. Mutagenesis 28:263–270
Horikoshi N, Pandita RK, Mujoo K, Hambarde S, Sharma D, Mattoo AR, Chakraborty S, Charaka V, Hunt CR, Pandita TK (2016) beta2-spectrin depletion impairs DNA damage repair. Oncotarget 7:33557–33570
Horikoshi N, Sharma D, Leonard F, Pandita RK, Charaka VK, Hambarde S, Horikoshi NT, Gaur Khaitan P, Chakraborty S, Cote J, Godin B, Hunt CR, Pandita TK (2019) Pre-existing H4K16ac levels in euchromatin drive DNA repair by homologous recombination in S-phase. Commun Biol 2:253
Jiang H, Gao Q, Zheng W, Yin S, Wang L, Zhong L, Ali A, Khan T, Hao Q, Fang H, Sun X, Xu P, Pandita TK, Jiang X, Shi Q (2018) MOF influences meiotic expansion of H2AX phosphorylation and spermatogenesis in mice. PLoS Genet 14:e1007300
Kalousi A, Hoffbeck AS, Selemenakis PN, Pinder J, Savage KI, Khanna KK, Brino L, Dellaire G, Gorgoulis VG, Soutoglou E (2015) The nuclear oncogene SET controls DNA repair by KAP1 and HP1 retention to chromatin. Cell Rep 11:149–163
Kumar R, Hunt CR, Gupta A, Nannepaga S, Pandita RK, Shay JW, Bachoo R, Ludwig T, Burns DK, Pandita TK (2011) Purkinje cell-specific males absent on the first (mMof) gene deletion results in an ataxia-telangiectasia-like neurological phenotype and backward walking in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:3636–3641
Kumar R, Horikoshi N, Singh M, Gupta A, Misra HS, Albuquerque K, Hunt CR, Pandita TK (2012) Chromatin modifications and the DNA damage response to ionizing radiation. Front Oncol 2:214
Lee YH, Kuo CY, Stark JM, Shih HM, Ann DK (2013) HP1 promotes tumor suppressor BRCA1 functions during the DNA damage response. Nucleic Acids Res 41:5784–5798
Legartova S, Lochmanova G, Zdrahal Z, Kozubek S, Sponer J, Krepl M, Pokorna P, Bartova E (2019) DNA damage changes distribution pattern and levels of HP1 protein isoforms in the nucleolus and increases phosphorylation of HP1beta-Ser88. Cells 8
Lomberk G, Mathison AJ, Grzenda A, Seo S, DeMars CJ, Rizvi S, Bonilla-Velez J, Calvo E, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Iovanna J, Buttar NS, Urrutia R (2012) Sequence-specific recruitment of heterochromatin protein 1 via interaction with Kruppel-like factor 11, a human transcription factor involved in tumor suppression and metabolic diseases. J Biol Chem 287:13026–13039
Lorentz A, Ostermann K, Fleck O, Schmidt H (1994) Switching gene swi6, involved in repression of silent mating-type loci in fission yeast, encodes a homologue of chromatin-associated proteins from Drosophila and mammals. Gene 143:139–143
Luo M, Yang F, Leu NA, Landaiche J, Handel MA, Benavente R, La Salle S, Wang PJ (2013) MEIOB exhibits single-stranded DNA-binding and exonuclease activities and is essential for meiotic recombination. Nat Commun 4:2788
Ma J, Hwang KK, Worman HJ, Courvalin JC, Eissenberg JC (2001) Expression and functional analysis of three isoforms of human heterochromatin-associated protein HP1 in Drosophila. Chromosoma 109:536–544
Marcet-Ortega M, Pacheco S, Martinez-Marchal A, Castillo H, Flores E, Jasin M, Keeney S, Roig I (2017) p53 and TAp63 participate in the recombination-dependent pachytene arrest in mouse spermatocytes. PLoS Genet 13:e1006845
Mattoo AR, Pandita RK, Chakraborty S, Charaka V, Mujoo K, Hunt CR, Pandita TK (2017) MCL-1 depletion impairs DNA double-strand break repair and reinitiation of stalled DNA replication forks. Mol Cell Biol 37(3):e00535-16
Pandita TK, Richardson C (2009) Chromatin remodeling finds its place in the DNA double-strand break response. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1363–1377
Pandita TK, Westphal CH, Anger M, Sawant SG, Geard CR, Pandita RK, Scherthan H (1999) Atm inactivation results in aberrant telomere clustering during meiotic prophase. Mol Cell Biol 19:5096–5105
Pawlowska E, Szczepanska J, Blasiak J (2017) DNA2-an important player in DNA damage response or just another DNA maintenance protein? Int J Mol Sci 18
Roeder GS (1997) Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango. Genes Dev 11:2600–2621
Rossi SE, Foiani M, Giannattasio M (2018) Dna2 processes behind the fork long ssDNA flaps generated by Pif1 and replication-dependent strand displacement. Nat Commun 9:4830
Scherthan H, Jerratsch M, Dhar S, Wang YA, Goff SP, Pandita TK (2000) Meiotic telomere distribution and Sertoli cell nuclear architecture are altered in Atm- and Atm-p53-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 20:7773–7783
Schlacher K, Wu H, Jasin M (2012) A distinct replication fork protection pathway connects Fanconi anemia tumor suppressors to RAD51-BRCA1/2. Cancer Cell 22:106–116
Schwab KR, Smith GD, Dressler GR (2013) Arrested spermatogenesis and evidence for DNA damage in PTIP mutant testes. Dev Biol 373:64–71
Sharma GG, Hwang KK, Pandita RK, Gupta A, Dhar S, Parenteau J, Agarwal M, Worman HJ, Wellinger RJ, Pandita TK (2003) Human heterochromatin protein 1 isoforms HP1(Hsalpha) and HP1(Hsbeta) interfere with hTERT-telomere interactions and correlate with changes in cell growth and response to ionizing radiation. Mol Cell Biol 23:8363–8376
Simhadri S, Peterson S, Patel DS, Huo Y, Cai H, Bowman-Colin C, Miller S, Ludwig T, Ganesan S, Bhaumik M, Bunting SF, Jasin M, **a B (2014) Male fertility defect associated with disrupted BRCA1-PALB2 interaction in mice. J Biol Chem 289:24617–24629
Singh M, Hunt CR, Pandita RK, Kumar R, Yang CR, Horikoshi N, Bachoo R, Serag S, Story MD, Shay JW, Powell SN, Gupta A, Jeffery J, Pandita S, Chen BP, Deckbar D, Löbrich M, Yang Q, Khanna KK, Worman HJ, Pandita TK (2013) Lamin A/C depletion enhances DNA damage-induced stalled replication fork arrest. Mol Cell Biol 33(6):1210–1222
Singh DK, Pandita RK, Singh M, Chakraborty S, Hambarde S, Ramnarain D, Charaka V, Ahmed KM, Hunt CR, Pandita TK (2018) MOF suppresses replication stress and contributes to resolution of stalled replication forks. Mol Cell Biol:38
Sun X, Brieno-Enriquez MA, Cornelius A, Modzelewski AJ, Maley TT, Campbell-Peterson KM, Holloway JK, Cohen PE (2016) FancJ (Brip1) loss-of-function allele results in spermatogonial cell depletion during embryogenesis and altered processing of crossover sites during meiotic prophase I in mice. Chromosoma 125:237–252
Thangavel S, Berti M, Levikova M, Pinto C, Gomathinayagam S, Vujanovic M, Zellweger R, Moore H, Lee EH, Hendrickson EA, Cejka P, Stewart S, Lopes M, Vindigni A (2015) DNA2 drives processing and restart of reversed replication forks in human cells. J Cell Biol 208:545–562
Vyas R, Kumar R, Clermont F, Helfricht A, Kalev P, Sotiropoulou P, Hendriks IA, Radaelli E, Hochepied T, Blanpain C, Sablina A, van Attikum H, Olsen JV, Jochemsen AG, Vertegaal AC, Marine JC (2013) RNF4 is required for DNA double-strand break repair in vivo. Cell Death Differ 20:490–502
Wang G, Ma A, Chow CM, Horsley D, Brown NR, Cowell IG, Singh PB (2000) Conservation of heterochromatin protein 1 function. Mol Cell Biol 20:6970–6983
Ward IM, Minn K, van Deursen J, Chen J (2003) p53 binding protein 53BP1 is required for DNA damage responses and tumor suppression in mice. Mol Cell Biol 23:2556–2563
Xu Y, Ashley T, Brainerd EE, Bronson RT, Meyn MS, Baltimore D (1996) Targeted disruption of ATM leads to growth retardation, chromosomal fragmentation during meiosis, immune defects, and thymic lymphoma. Genes Dev 10:2411–2422
Xu X, Aprelikova O, Moens P, Deng CX, Furth PA (2003) Impaired meiotic DNA-damage repair and lack of crossing-over during spermatogenesis in BRCA1 full-length isoform deficient mice. Development 130:2001–2012
Zelazowski MJ, Sandoval M, Paniker L, Hamilton HM, Han J, Gribbell MA, Kang R, Cole F (2017) Age-dependent alterations in meiotic recombination cause chromosome segregation errors in spermatocytes. Cell 171(601–614):e613
Zhang Q, Ji SY, Busayavalasa K, Shao J, Yu C (2019) Meiosis I progression in spermatogenesis requires a type of testis-specific 20S core proteasome. Nat Commun 10:3387
Zheng L, Meng Y, Campbell JL, Shen B (2019) Multiple roles of DNA2 nuclease/helicase in DNA metabolism, genome stability and human diseases. Nucleic Acids Res
Zhu J, Su F, Mukherjee S, Mori E, Hu B, Asaithamby A (2015) FANCD2 influences replication fork processes and genome stability in response to clustered DSBs. Cell Cycle 14:1809–1822
Funding
This study received support from the NIH grants CA129537 and GM109768.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.C., C.R.H, and T.K.P. directed the study. V.C., C.R.H., and T.K.P. contributed to the design. V.C., A.T., R.K.P., and T.K.P. performed the experiments. V.C., C.H., and T.K.P wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 80.3 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charaka, V., Tiwari, A., Pandita, R.K. et al. Role of HP1β during spermatogenesis and DNA replication. Chromosoma 129, 215–226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-020-00739-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-020-00739-4