Abstract
Purpose
The recurrence rate of parotid gland cancer is high, but research on the prognosis of recurrent parotid gland cancer (RPC) is relatively limited. We aim to determine the potential prognosis factors of RPC.
Study design
Retrospective cohort analysis.
Setting
Tertiary cancer center.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective review from 2012 to 2021 on RPC patients treated at the China National Cancer Center (CNCC). To analyze the impact of various variables on overall survival (OS) after recurrence, a univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard model was employed.
Results
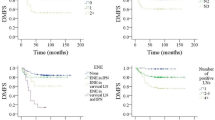
A total of 50/218 (23.0%) patients diagnosed with RPC and underwent surgery. The 5-year OS of all RPC patients in this cohort was 61.9%. 5 of 50 patients (10%) exhibited intraparotid node (IPN) metastasis. By univariate and multivariate analyses, we found that IPN metastasis was one of the prognostic factors of OS (p = 0.039) in RPC patients. The presence of IPN metastasis was also related to poor survival in individuals with negative cervical lymph nodes (CN0) (p = 0.011). In terms of the influence of surgical margins on prognosis, our findings revealed that RPC patients with negative margins exhibited a higher survival result than those with positive margins (p = 0.002).
Conclusion
According to this study, IPN metastasis indicate a high incidence of mortality in recurrent parotid cancer patients. Particularly, in CN0 patients, the presence of IPN metastasis was associated with poor survival in CN0 patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable. The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
Carlson ER, Schlieve T (2019) Salivary gland malignancies. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin N Am 31(1):125–144
Speight PM, Barrett AW (2002) Salivary gland tumours. Oral Dis 8(5):229–240
Żurek M, Rzepakowska A, Jasak K et al (2021) The epidemiology of salivary glands pathologies in adult population over 10 years in Poland-cohort study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(1):179
Guzzo M, Locati LD, Prott FJ et al (2010) Major and minor salivary gland tumors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 74(2):134–148
Feinstein TM, Lai SY, Lenzner D et al (2011) Prognostic factors in patients with high-risk locally advanced salivary gland cancers treated with surgery and postoperative radiotherapy. Head Neck 33(3):318–323
Terhaard CH, Lubsen H, Van der Tweel I et al (2004) Salivary gland carcinoma: independent prognostic factors for locoregional control, distant metastases, and overall survival: results of the Dutch head and neck oncology cooperative group. Head Neck 26(8):681–692 (discussion 692-3)
Lima RA, Tavares MR, Dias FL et al (2005) Clinical prognostic factors in malignant parotid gland tumors. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133(5):702–708
Spiro RH (1986) Salivary neoplasms: overview of a 35-year experience with 2,807 patients. Head Neck Surg 8(3):177–184
Gillespie MB, Albergotti WG, Eisele DW (2012) Recurrent salivary gland cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol 13(1):58–70
Carrillo JF, Vázquez R, Ramírez-Ortega MC et al (2007) Multivariate prediction of the probability of recurrence in patients with carcinoma of the parotid gland. Cancer 109(10):2043–2051
Nisa L, Borner U, Dür C et al (2018) Recurrent parotid gland carcinoma: how effective is salvage surgery? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275(2):507–513
Mannelli G, Comini LV, Sacchetto A et al (2022) Estimating survival after salvage surgery for recurrent salivary gland cancers: systematic review. Head Neck 44(8):1961–1975
Lassche G, van Boxtel W, Ligtenberg MJL et al (2019) Advances and challenges in precision medicine in salivary gland cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 80:101906
Chakrabarti S, Nair D, Malik A et al (2018) Prognostic factors in parotid cancers: Clinicopathological and treatment factors influencing outcomes. Indian J Cancer 55(1):98–104
Hu Y, **a L, Zhang C et al (2020) Clinicopathologic features and prognostic factors of widely invasive carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland: a clinicopathologic analysis of 126 cases in a Chinese population. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 78(12):2247–2257
Liu Y, Su M, Yang Y et al (2017) Prognostic factors associated with decreased survival in patients with acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 75(2):416–422
Fang Q, Wu J, Liu F (2019) Oncologic outcome and potential prognostic factors in primary squamous cell carcinoma of the parotid gland. BMC Cancer 19(1):752
Lee DY, Park MW, Oh KH et al (2016) Clinicopathologic factors associated with recurrence in low- and high-grade parotid cancers. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E1788–E1793
Janik S, Faisal M, Marijić B et al (2022) Prognostic factors in mammary analogue secretory carcinomas of the parotid gland: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 44(3):792–804
Amini A, Waxweiler TV, Brower JV et al (2016) Association of adjuvant chemoradiotherapy vs radiotherapy alone with survival in patients with resected major salivary gland carcinoma: data from the national cancer data base. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 142(11):1100–1110
Osborn V, Givi B, Lee A et al (2017) Characterization, treatment and outcomes of salivary ductal carcinoma using the National Cancer Database. Oral Oncol 71:41–46
Honda K, Tanaka S, Shinohara S et al (2018) Survival in patients with parotid gland carcinoma - Results of a multi-center study. Am J Otolaryngol 39(1):65–70
Dahan LS, Giorgi R, Vergez S et al (2021) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of salivary glands: a French Network of Rare Head and Neck Tumors (REFCOR) prospective study of 292 cases. Eur J Surg Oncol 47(6):1376–1383
Wei ZG, Peng XC, He Y et al (2021) Survival outcomes in patients with parotid gland carcinoma treated with postoperative therapies using risk stratification. Head Neck 43(8):2488–2496
Jia MQ, Gao M, Ye P et al (2022) Survival outcome of salivary gland carcinoma: a 50-year retrospective study with long-term follow-up. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 80(12):2003–2014
Conley J, Arena S (1963) Parotid gland as a focus of metastasis. Arch Surg 87:757–764
Batsakis JG (1983) Pathology consultation. Parotid gland and its lymph nodes as metastatic sites. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 92(2):209–210
McKean ME, Lee K, McGregor IA (1985) The distribution of lymph nodes in and around the parotid gland: an anatomical study. Br J Plast Surg 38(1):1–5
Sönmez Ergün S, Gayretli O, Büyükpınarbaşılı N et al (2014) Determining the number of intraparotid lymph nodes: postmortem examination. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 42(5):657–660
Klussmann JP, Ponert T, Mueller RP et al (2008) Patterns of lymph node spread and its influence on outcome in resectable parotid cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 34(8):932–937
Lim CM, Gilbert MR, Johnson JT et al (2014) Clinical significance of intraparotid lymph node metastasis in primary parotid cancer. Head Neck 36(11):1634–1637
Nisa L, Salmina C, Dettmer MS et al (2015) Implications of intraglandular lymph node metastases in primary carcinomas of the parotid gland. Laryngoscope 125(9):2099–2106
Guntinas-Lichius O, Thielker J, Robbins KT et al (2021) Prognostic role of intraparotid lymph node metastasis in primary parotid cancer: systematic review. Head Neck 43(3):997–1008
Stenner M, Molls C, Luers JC et al (2012) Occurrence of lymph node metastasis in early-stage parotid gland cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(2):643–648
Pisani P, Ramponi A, Pia F (1996) The deep parotid lymph nodes: an anatomical and oncological study. J Laryngol Otol 110(2):148–150
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB et al (2017) The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. Cancer J Clin 67(2):93–99
Seethala RR, Altemani A, Ferris RL et al (2019) Data Set for the reporting of carcinomas of the major salivary glands: explanations and recommendations of the guidelines from the international collaboration on cancer reporting. Arch Pathol Lab Med 143(5):578–586
Sood S, McGurk M, Vaz F (2016) Management of salivary gland tumours: United Kingdom national multidisciplinary guidelines. J Laryngol Otol 130(S2):S142-s149
Olsen KD, Quer M, de Bree R et al (2017) Deep lobe parotidectomy-why, when, and how? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(12):4073–4078
Niu X, Fang Q, Liu F (2019) Role of intraparotid node metastasis in mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the parotid gland. BMC Cancer 19(1):417
Wu J, Fang Q, Liu F et al (2020) Intraparotid node metastases in adults with parotid mucoepidermoid cancer: an indicator of prognosis? Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58(5):525–529
Lombardi D, Tomasoni M, Paderno A et al (2021) The impact of nodal status in major salivary gland carcinoma: a multicenter experience and proposal of a novel N-classification. Oral Oncol 112:105076
Kouka M, Koehler B, Buentzel J et al (2022) Role of intraparotid and neck lymph node metastasis in primary parotid cancer surgery: a population-based analysis. Cancers (Basel) 14(12):2822
Cho JK, Lim BW, Kim EH et al (2016) Low-grade salivary gland cancers: treatment outcomes, extent of surgery and indications for postoperative adjuvant radiation therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 23(13):4368–4375
Ghosh-Laskar S, Murthy V, Wadasadawala T et al (2011) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the parotid gland: factors affecting outcome. Head Neck 33(4):497–503
Zenga J, Parikh AS, Emerick KS et al (2018) Close margins and adjuvant radiotherapy in acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144(11):1011–1016
Richter SM, Friedmann P, Mourad WF et al (2012) Postoperative radiation therapy for small, low-/intermediate-grade parotid tumors with close and/or positive surgical margins. Head Neck 34(7):953–955
Haderlein M, Scherl C, Semrau S et al (2016) High-grade histology as predictor of early distant metastases and decreased disease-free survival in salivary gland cancer irrespective of tumor subtype. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E2041–E2048
Nam SJ, Roh JL, Cho KJ et al (2016) Risk factors and survival associated with distant metastasis in patients with carcinoma of the salivary gland. Ann Surg Oncol 23(13):4376–4383
Ali S, Bryant R, Palmer FL et al (2015) Distant metastases in patients with carcinoma of the major salivary glands. Ann Surg Oncol 22(12):4014–4019
Mimica X, McGill M, Hay A et al (2020) Distant metastasis of salivary gland cancer: Incidence, management, and outcomes. Cancer 126(10):2153–2162
Benchetrit L, Mehra S, Mahajan A et al (2022) Major salivary gland cancer with distant metastasis upon presentation: patterns, outcomes, and imaging implications. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 167(2):305–315
Pastorino U, Buyse M, Friedel G et al (1997) Long-term results of lung metastasectomy: prognostic analyses based on 5206 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 113(1):37–49
Girelli L, Locati L, Galeone C et al (2017) Lung metastasectomy in adenoid cystic cancer: Is it worth it? Oral Oncol 65:114–118
Tchekmedyian V, Sherman EJ, Dunn L et al (2019) Phase II study of lenvatinib in patients with progressive, recurrent or metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 37(18):1529–1537
Fushimi C, Tada Y, Takahashi H et al (2018) A prospective phase II study of combined androgen blockade in patients with androgen receptor-positive metastatic or locally advanced unresectable salivary gland carcinoma. Ann Oncol 29(4):979–984
Takahashi H, Tada Y, Saotome T et al (2019) Phase II trial of trastuzumab and docetaxel in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive salivary duct carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 37(2):125–134
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The experimental protocol was established, according to the ethical guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration, and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Written informed consent was obtained from individual or guardian participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., He, Y., Li, H. et al. Intraparotid node metastasis affects the long-term survival of patients with resectable recurrent parotid gland carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 5547–5555 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08142-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08142-2