Abstract
Introduction
The main purpose of this retrospective, non-randomized, case series study was to evaluate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of distal humerus fractures (DHFs) in a consecutive series of elderly patients operatively treated by two surgeons, and second, to identify proper indications for two elderly age ranges and two fracture pattern groups.
Materials and methods
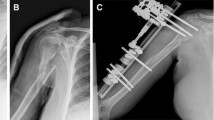
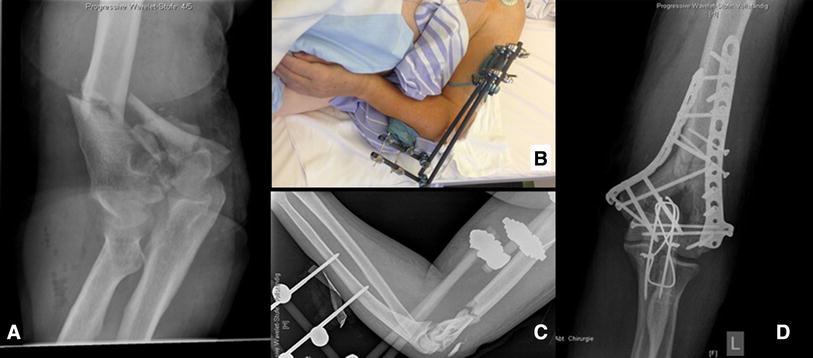
From January 2009 to June 2014, 51 patients (pts) underwent open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) using the locking compression plate (LCP) distal humerus plate (DHP) system at our institution. Medical records and radiographs were retrospectively assessed. Patients were divided into 3 groups according to gender, age (pts <85 years, pts ≥85 years) and AO classification (13-B1-B2-C1-C2 or 13-C3). All subjects completed MEPS, Quick-DASH and SF-36 PCS/MCS scores at final follow-up, and statistical analysis was performed.
Results
36 patients (20 women, 16 men), mean age 80.3 years, with AO type 13-B and 13-C DHFs were included with a mean follow-up of 56 months (range 24–92). The most common mechanism of trauma was a fall from ground level (55.6%). The mean MEPS was 78.9 points, Quick-DASH 28.4, SF-36 PCS 48.3 and MCS 48.9. There was statistically significant evidence that having a 13-C3 fracture leads to worse results in MEPS, Quick-DASH and SF-36. The female gender correlates with worse results in SF-36. The patients ≥85 years had a worse prognosis according to Quick-DASH and SF-36, while the AO 13-C3 pattern obtained the worst ROM outcomes versus AO 13 B1-B2-C1-C2 (normal ROM 0°–140°): mean ROM 24°–114° vs 10°–130°, mean flexion deficit 26° vs 10°, mean extension deficit 24° vs 10°, respectively). Complications were presents in 36.1% of patients, overall belonging to the AO type 13-C fracture pattern and to the group ≥85 years.
Conclusion
These study data seem to confirm our hypothesis that plate fixation for DHFs guarantees adequate fracture osteosynthesis and satisfactory functional outcomes at medium to long-term follow-up, not only in elderly patients, but also in octogenarian osteoporotic patients (≥85 years) with 13-C1 and 13-C2 fracture patterns, while an alternative solution should be considered for type C3 fractures, even in a primary trauma setting.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang TL, Chiu FY, Chuang TY, Chen TH (2005) The results of open reduction and internal fixation in elderly patients with severe fractures of the distal humerus: a critical analysis of the results. J Trauma 58:62–69
Srinivasan K, Agarwal M, Matthews SJE, Giannoudis PV (2005) Fractures of the distal humerus in the elderly. Is internal fixation the treatment of choice? Clin Orthop Relat Res 434:222–230
Chiarissoux JL, Mabit C, Fourastier J (2008) Comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus in elderly patients. Rev Chir Orthop 94S:36–62
Proust J, Oksman A, Charissoux JL, Mabic C, Arnaud JP (2007) Intra-articular fracture of the distal humerus: outcome after osteosynthesis in patients over 60. Rev Chir Orthop 93:798–806
Ducrot G, Bonnomet F, Adam P, Ehlinger M (2013) Treatment of distal humerus fractures with LCP DHP ™ locking plates in patients older than 65 years. Orthop Traum Surg Res 99:145–154
Charissoux JL, Vergnenegre G, Pelissier M, Fabre T, Mansat P, The SOFCOT (2013) Epidemiology of distal humerus fractures in the elderly. Orthop Traum Surg Res 99:765–769
Bégué T (2014) Articular fractures of the distal humerus. Orthop Traum Surg Res 100S:55–63
Kannus P, Sievanen M, Jarvinen T, Pakkari J (2005) Prevention of falls and consequent injuries in elderly people. Lancet 366:1885–1893
Pidhorz L, Alligand-Perrin P, De Keating E, Fabre T, Mansat P (2013) Distal humerus fractures in the elderly: does conservative treatment still have a role? Orthop Traum Surg Res 99:903–907
Miller AN, Beingnesser DM (2013) Intra-articular distal humerus fractures. Orthop Clin North Am 44:35–45
Korner J, Lill H, Muller LP, Rommens PM, Schneider E, Linke B (2003) The LCP-concept in the operative treatment of distal humerus fractures. Biological, biomechanical and surgical aspects. Injury 34:B20–B30
Morrey BF, Adams RA (1995) Semiconstrained elbow replacement for distal humeral non union. J Bone Jt Surg 77B:67–72
Korner J, Lill H, Muller LP (2005) Distal humerus fractures in elderly patients: results after open reduction and internal fixation. Osteoporos Int 16(Suppl. 2):S73–S79
Holdsworth BJ, Mossad MM (1990) Fractures of the adult distal humerus. Elbow function after internal fixation. J Bone Jt Surg Br 72:362–365
Armstrong AD, Yamaguchi K (2004) Total elbow anthroplasty and distal humerus elbow fractures. Hand Clin 20:475–483
Charissoux JL, Mabit C, Fourastier J, Beccari R, Emily S, Cappelli M, Malingue E, Mansat P, Hubert L, Proust J, Bratu D, Veillard D, Grandmaison FL, Apard T, Martinel V, Bonnevialle N (2008) Comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus in elderly patients. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 94:S36–S62
Nauth A, McKee MD, Ristevski B, Hall J, Schemitsch EH (2011) Distal humeral fractures in adults. J Bone Jt Surg Am 93:686–700
Vennettilli M, Athwal GS (2012) Parallel versus orthogonal plating for distal humerus fractures. J Hand Surg Am 37:819–820
Schmidt-Horlohéa KH, Bonkb A, Wildea P, Beckera L, Hoffmann R (2013) Promising results after the treatment of simple and complex distal humerus type C fractures by angular-stable double-plate osteosynthesis. Orthop Traum Surg Res 99:531–541
McKee MD, Veillette CJH, Hall JA, Schemitsch EH, Wild LM (2009) Multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial of open reduction and internal fixation versus total elbow arthroplasty for displaced intra-articular distal humeral fractures in elderly patients. J Shoulder Elb Surg 18:3–12
Sanchez-Sotelo J (2012) Distal humeral fractures: role of internal fixation and elbow arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am 94(6):556–558
Obert L, Ferrier M, Jacquot A, Mansat P, Sirveaux F, Clavert P, Charissoux JL, Pidhorz L, Fabre T (2013) Distal humerus fractures in patients over 65: complications. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(8):909–913
Lawrence TM, Ahmadi Shahryar, Morrey BF, Sanchez-Sotelo J (2014) Wound complications after distal humerus fracture fixation: incidence, risk factors and outcome. J Shoulder Elb Surg 23:258–264
Daabiss M (2011) American Society of Anaesthesiologists physical status classification. Indian J Anaesth 55(2):111–115
Ring D, Gulotta L, Chin K, Jupiter JB (2004) Olecranon osteotomy for exposure of fractures and nonunions of the distal humerus. J Orthop Trauma 18(7):446–449
Steinitz A, Sailer J, Rikli D (2016) Distal humerus fractures: a review of current therapy concepts. Curr Rev Mus Med 9:199–206
Marsh JL, Slongo TF, Agel J, Broderick JS, Creevey W, DeCoster TA, Prokuski L, Sirkin MS, Ziran B, Henley B, Audigé L (2007) Fracture and dislocation classification compendium—2007: orthopaedic trauma association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma 21(10 Suppl):S1–133
Morrey BF, An KN (2009) Functional evaluation of the elbow. In: Morrey BF (ed) The elbow and its disorders, 4th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 80–91 (ISBN 978-1-4160-2902-1)
Beaton DE, Wright JG, Katz JN, The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (2005) Development of the QuickDASH: comparison of three item-reduction approaches. J Bone Jt Surg 87A(5):1038–1046
Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD (1992) The MOS 36-items short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care 30:473–483
Hausman M, Panozzo A (2004) Treatment of distal humerus fractures in the elderly. Clin Orthop Rel Res 425:55–63
Garcia JA, Mykula R, Stanley D (2002) Complex fractures of the distal humerus in the elderly: the role of total elbow replacement as primary treatment. J Bone Jt Surg 84B:812–816
Prasad N, Dent C (2008) Outcome of total elbow replacement for distal humerus fractures in the elderly: a comparison of primary surgery and surgery after failed internal fixation or conservative treatment. J Bone Jt Surg 90B:343–348
Chalidis B, Dimitriou C, Papadopoulos P, Petsatodis G, Giannoudis PV (2009) Total elbow arthroplasty for the treatment of insufficient distal humerus fractures. A retrospective clinical study and review of the literature. Inj Int J Care Inj 40:582–590
Burkhart KJ, Nijs S, Mattyasovzky SG, Wouters R, Grouskza D, Nowak TE (2011) Distal humerus hemi-arthroplasty of the elbow for comminuted distal humeral fractures in the elderly patient. J Trauma 71:635–642
Frankle MA, Herscovici D, DiPasquale TG, Vasey MB, Sanders RW (2003) A comparison of open reduction and internal fixation and primary total elbow arthtroplasty in the treatment of intraarticular distal humerus fractures in women older than age 65. J Orthop Trauma 17(7):473–480
Leigey DF, Farrel DJ, Siska PA, Tarkin IS (2014) Bicolumnar 90-90 plating of low-energy distal humerus fractures in the elderly patient. Ger Orthop Surg Reab 5(3):122–126
Mansat P, Bonnevialle N, Rongières M, Bonnevialle P (2014) The role of total elbow arthroplasty in traumatology. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 100(6 Suppl):S293–S298
Clavert P, Ducrot G, Sirveaux F, Fabre T, Mansat P, The SOFCOT (2013) Outcomes of distal humerus fractures in patients above 65 years of age treated by plate fixation. Orthop Traum Surg Res 99:771–777
An KN, Hui FC, Morrey BF (1981) Muscles across the elbow joint: a biomechanical analysis. J Biomech 14:659–669
Morrey BF, Askew LJ, Chao EY (1981) A biomechanical study of normal functional elbow motion. J Bone Jt Surg Am 63:872–877
Raiss P, Rettig O, Wolf S (2007) Range of motion of shoulder and elbow in activities of daily life in 3D motion analysis. Z Orthop Unfall 145:493–498
Athwal GS, Hoxie SC, Rispoli DM (2009) Precontoured parallel plate fixation of AO/OTA type C distal humerus fractures. J Orthop Traum 23:575–580
Robinson CM, Hill RMF, Jacobs N, Dall G, Court-Brown CM (2003) Adult distal humeral metaphyseal fractures: epidemiology and results of treatment. J Orthop Trauma 17:38–47
Kamineni S, Morrey BF (2005) Distal humeral fractures treated with noncustom total elbow replacement. Surgical technique. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87:41–50
Prasad N, Ali A, Stanley D (2016) Total elbow arthroplasty for non-rheumatoid patients with a fracture of the distal humerus: a minimum ten-year follow-up. Bone Jt J 98B(3):381–386
Zhang Chi, Zhong Biao, Luo Cong-feng (2014) Comparing approaches to expose type C fractures of the distal humerus fit ORIF in elderly patients: six years clinical experience with both the triceps-sparing approach and olecranon osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134:803–811
Iselin LD, Mett T, Babst R, Jakob M, Rickli D (2014) The triceps reflecting approach (Bryan–Morrey) for distal humerus fracture osteosynthesis. Musculosk Disord 15:406
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Prof. Anna Chiara Frigo for her assistance with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SPS and CB: study concept and design; drafting the paper; NM and MB: data collection and statistical analysis; NM and CB: analysis and interpretation of data; PR and CI: study concept and final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki as revised in 2000. The patients received a thorough explanation of this study and gave their oral and written informed consent to be included in this analysis.
Informed consent
The patients gave their oral and written informed consent to the publication of their anonymous and clustered data and anonymous pictures.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this manuscript, and they have not received benefits or financial funds in support of this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biz, C., Sperotto, S.P., Maschio, N. et al. The challenging surgical treatment of closed distal humerus fractures in elderly and octogenarian patients: radiographic and functional outcomes with a minimum follow-up of 24 months. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137, 1371–1383 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2762-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2762-3