Abstract
Background
The impact of catheter ablation (CA) on the long-term clinical outcomes in atrial fibrillation (AF) are unclear due to limited cohort investigations.
Methods
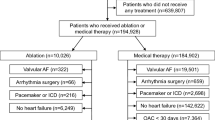
The Fushimi AF Registry is a community-based prospective survey of patients with AF in Fushimi-ku, Kyoto, Japan. Of 4465 patients enrolled between March 2011 and July 2019, analyses were performed on 2639 patients (492 patients who underwent CA and 2147 patients who received standard rhythm- and/or rate-control drug therapy at baseline). We compared the baseline characteristics and the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: the composite of cardiovascular death, heart failure hospitalization, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke or systemic embolism), and all-cause mortality during the follow-up using propensity score matching.
Results
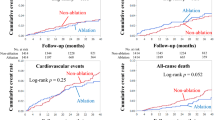
After entering 20 covariates in the current matching analysis, 342 patients who underwent CA and 342 matched patients who received drug therapy, with a median follow-up of 1865 days, were included. The patients who underwent CA were significantly associated with lower incidence of MACE (hazard ratio (HR) 0.56, 95% confidential interval (CI) 0.36–0.86; P = 0.0077), and all-cause mortality (HR 0.47, 95% CI 0.29–0.75; P = 0.0016).
Conclusion
CA was associated with lower incidences of MACE and all-cause mortality for patients with AF as compared with those who received drug therapy. The most common event of MACE in patients who underwent CA was heart failure hospitalization.
Clinical trial registration
URL: http://www.umin.ac.jp/ctr/index.htm
Unique identifier
UMIN000005834.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, Leip EP, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Murabito JM, Kannel WB, Benjamin EJ (2003) Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure and their joint influence on mortality. Circulation 107:2920–2925
Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D (1998) Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death. Circulation 98:946–952
Krahn AD, Manfreda J, Tate RB, Mathewson FA, Cuddy TE (1995) The natural history of atrial fibrillation: incidence, risk factors and prognosis in the Manitoba Follow-up Study. Am J Med 98:476–484
Singh SN, Tang XC, Singh BN, Dorian P, Reda DJ, Harris CL, Fletcher RD, Sharma SC, Atwood JE, Jacobson AK, Lewis HD Jr, Lopez B, Raisch DW, Ezekowitz MD, SAFE-T Investigators (2006) Quality of life and exercise performance in patients in sinus rhythm versus persistent atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:721–730
Dorian P, Paquette M, Newman D, Green M, Connolly SJ, Talajic M, Roy D (2002) Quality of life improves with treatment in the Canadian Trial of Atrial Fibrillation. Am Heart J 143:984–990
Wyse DG, Waldo AL, DiMarco JP, Domanski MJ, Rosenberg Y, Schron EB, Kellen JC, Greene HL, Mickel MC, Dalquist JE, Corley SD, Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) (2002) A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 347:1825–1833
Corley SD, Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Domanski MJ, Geller N, Greene HL, Josephson RA, Kellen JC, Klein RC, Krahn AD, Mickel M, Mitchell LB, Nelson JD, Rosenberg Y, Schron E, Shemanski L, Waldo AL, Wyse DG, AFFIRM Investigators (2004) Relationships between sinus rhythm, treatment, and survival in the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Study. Circulation 109:1509–1513
Wilber DJ, Pappone C, Neuzil P, De Paola A, Marchlinski F, Natale A, Macle L, Daoud EG, Calkins H, Hall B, Reddy V, Augello G, Reynolds MR, Vinekar C, Liu CY, Berry SM, Berry DA, ThermoCool AF Trial Investigators (2010) Comparison of antiarrhythmic drug therapy and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 303:333–340
Morillo CA, Verma A, Connolly SJ, Kuck KH, Nair GM, Champagne J, Sterns LD, Beresh H, Healey JS, Natale A, RAAFT-2 Investigators (2014) Radiofrequency ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (RAAFT-2): a randomized trial. JAMA 311:692–700
Jones DG, Haldar SK, Hussain W, Sharma R, Francis DP, Rahman-Haley SL, McDonagh TA, Underwood SR, Markides V, Wong T (2013) A randomized trial to assess catheter ablation versus rate control in the management of persistent atrial fibrillation in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 61:1894–1903
Packer DL, Mark DB, Robb RA, Monahan KH, Bahnson TD, Poole JE, Noseworthy PA, Rosenberg YD, Jeffries N, Mitchell LB, Flaker GC, Pokushalov E, Romanov A, Bunch TJ, Noelker G, Ardashev A, Revishvili A, Wilber DJ, Cappato R, Kuck KH, Hindricks G, Davies DW, Kowey PR, Naccarelli GV, Reiffel JA, Piccini JP, Silverstein AP, Al-Khalidi HR, Lee KL, CABANA Investigators (2019) Effect of catheter ablation vs antiarrhythmic drug therapy on mortality, stroke, bleeding, and cardiac arrest among patients with atrial fibrillation: The CABANA randomized clinical trial. JAMA 321:1261–1274
Mark DB, Anstrom KJ, Sheng S, Piccini JP, Baloch KN, Monahan KH, Daniels MR, Bahnson TD, Poole JE, Rosenberg Y, Lee KL, Packer DL, CABANA Investigators (2019) Effect of catheter ablation vs medical therapy on quality of life among patients with atrial fibrillation: The CABANA randomized clinical trial. JAMA 321:1275–1285
Chang CH, Lin JW, Chiu FC, Caffrey JL, Wu LC, Lai MS (2014) Effect of radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation on morbidity and mortality: a nationwide cohort study and propensity score analysis. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 7:76–82
Lin YJ, Chao TF, Tsao HM, Chang SL, Lo LW, Chiang CE, Hu YF, Hsu PF, Chuang SY, Li CH, Chung FP, Chen YY, Wu TJ, Hsieh MH, Chen SA (2013) Successful catheter ablation reduces the risk of cardiovascular events in atrial fibrillation patients with CHA2DS2-VASc risk score of 1 and higher. Europace 15:676–684
Hunter RJ, McCready J, Diab I, Page SP, Finlay M, Richmond L, French A, Earley MJ, Sporton S, Jones M, Joseph JP, Bashir Y, Betts TR, Thomas G, Staniforth A, Lee G, Kistler P, Rajappan K, Chow A, Schilling RJ (2012) Maintenance of sinus rhythm with an ablation strategy in patients with atrial fibrillation is associated with a lower risk of stroke and death. Heart 98:48–53
Pappone C, Rosanio S, Augello G, Gallus G, Vicedomini G, Mazzone P, Gulletta S, Gugliotta F, Pappone A, Santinelli V, Tortoriello V, Sala S, Zangrillo A, Crescenzi G, Benussi S, Alfieri O (2003) Mortality, morbidity, and quality of life after circumferential pulmonary vein ablation for atrial fibrillation: outcomes from a controlled nonrandomized long-term study. J Am Coll Cardiol 42:185–197
Akao M, Chun YH, Wada H, Esato M, Hashimoto T, Abe M, Hasegawa K, Tsuji H, Furuke K, Fushimi AF Registry Investigators (2013) Current status of clinical background of patients with atrial fibrillation in a community-based survey: The Fushimi AF Registry. J Cardiol 61:260–266
Akao M, Chun YH, Esato M, Abe M, Tsuji H, Wada H, Hasegawa K, Fushimi AF Registry Investigators (2014) Inappropriate use of oral anticoagulants for patients with atrial fibrillation. Circ J 78:2166–2172
An Y, Esato M, Ishii M, Iguchi M, Masunaga N, Tsuji H, Wada H, Hasegawa K, Ogawa H, Abe M, Lip GYH, Akao M (2018) Clinical characteristics and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation receiving rhythm-control therapy: the Fushimi AF Registry. Heart Vessels 33:1534–1546
Ogawa S, Yamashita T, Yamazaki T, Aizawa Y, Atarashi H, Inoue H, Ohe T, Ohtsu H, Okumura K, Katoh T, Kamakura S, Kumagai K, Kurachi Y, Kodama I, Koretsune Y, Saikawa T, Sakurai M, Sugi K, Tabuchi T, Nakaya H, Nakayama T, Hirai M, Fukatani M, Mitamura H, J-RHYTHM Investigators (2009) Optimal treatment strategy in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circ J 73:242–248
Austin PC (2011) An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivariate Behav Res 46:399–424
Gage BF, Waterman AD, Shannon W, Boechler M, Rich MW, Radford MJ (2001) Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 285:2864–2870
Japanese Society of Nephrology (2009) Evidence based practice guideline for the treatment of CKD. Clin Exp Nephrol 13:537–566
Beutler E, Waalen J (2006) The definition of anemia: what is the lower limit of normal of the blood hemoglobin concentration? Blood 107:1747–1750
Saliba W, Schliamser JE, Lavi I, Barnett-Griness O, Gronich N, Rennert G (2017) Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation is associated with reduced risk of stroke and mortality: A propensity score-matched analysis. Heart Rhythm 14:635–642
Allessie M, Ausma J, Schotten U (2002) Electrical, contractile and structural remodeling during atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 54:230–246
Daccarett M, Badger TJ, Akoum N, Burgon NS, Mahnkopf C, Vergara G, Kholmovski E, McGann CJ, Parker D, Brachmann J, Macleod RS, Marrouche NF (2011) Association of left atrial fibrosis detected by delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging and the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 57:831–838
Ogawa H, An Y, Ikeda S, Aono Y, Doi K, Ishii M, Iguchi M, Masunaga N, Esato M, Tsuji H, Wada H, Hasegawa K, Abe M, Lip GYH, Akao M, Fushimi AF Registry Investigators (2018) Progression from paroxysmal to sustained atrial fibrillation is associated with increased adverse events. Stroke 49:2301-2308
Marrouche NF, Brachmann J, Andresen D, Siebels J, Boersma Jordaens L, Merkely B, Pokushalov E, Sanders P, Proff J, Schunkert H, Christ H, Vogt J, Bänsch D, CASTLE-AF Investigators (2018) Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation with Heart Failure. N Engl J Med 378:417–427
Reynolds MR, Gunnarsson CL, Hunter TD, Ladapo JA, March JL, Zhang M, Hao SC (2012) Health outcomes with catheter ablation or antiarrhythmic drug therapy in atrial fibrillation. Cir Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 5:171–181
Darrat YH, Shah J, Elayi CS, Morales GX, Naditch-Brûlé L, Brette S, Taniou C, Kowey PR, Schwartz PJ (2017) Regional lack of consistency in the management of atrial fibrillation (from the RECORD-AF Trial). Am J Cardiol 119:47–51
An Y, Ogawa H, Yamashita Y, Ishii M, Iguchi M, Masunaga N, Esato M, Tsuji H, Wada H, Hasegawa K, Abe M, Lip GYH, Akao M (2019) Causes of death in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation: The Fushimi Atrial Fibrillation Registry. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes 5:35–42
Acknowledgment
We sincerely appreciate the efforts of all of the institutions participating in the registry and the clinical research coordinators (T. Shinagawa, M. Mitamura, M. Fukahori, M. Kimura, M. Fukuyama, C. Kamata and N. Nishiyama).
Funding
The Fushimi AF Registry is supported by research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis Pharma, MSD, Sanofi-Aventis and Takeda Pharmaceutical. This research is partially supported by the Practical Research Project for Life-Style related Diseases including Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes Mellitus from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED (19ek0210082h0003, 18ek0210056h0003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr Akao received lecture fees from Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer Healthcare, and Daiichi Sankyo. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the content of this paper to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esato, M., An, Y., Ogawa, H. et al. Major adverse cardiovascular events and mortality after catheter ablation in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation: The Fushimi AF Registry. Heart Vessels 36, 1219–1227 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01796-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01796-0