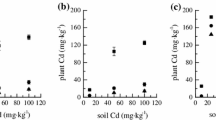
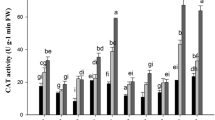
Abstract
Six barley cultivars widely differing for cadmium (Cd) tolerance, partitioning, and translocation were analyzed in relation to their thiol metabolism. Results indicated that Cd tolerance was not clearly related to the total amount of Cd absorbed by plants, resulting instead closely dependent on the capacity of the cultivars to trap the metal into the roots. Such behaviors suggested the existence of root mechanisms preserving shoots from Cd-induced oxidative damages, as indicated by the analysis of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances—diagnostic indicators of oxidative stress—whose increases in the shoots were negatively related to Cd root retention and tolerance. Cd exposure differentially affected glutathione (GSH) and phytochelatin (PC) levels in the tissues of each barley cultivar. The capacity to produce PCs appeared as a specific characteristic of each barley cultivar, since it did not depend on Cd concentration in the roots and resulted negatively related to the concentration of the metal in the shoots, indicating the existence of a cultivar-specific interference of Cd on GSH biosynthesis, as confirmed by the existence of close positive linear relationships between the effect of Cd on GSH levels and PC accumulation in both roots and shoots. The six barley cultivars also differed for their capacity to load Cd ions into the xylem, which was negatively related to PC content in the roots. Taken as a whole, these data indicated that the different capacity of each cultivar to maintain GSH homeostasis under Cd stress may strongly affect PC accumulation and, thus, Cd tolerance and translocation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter MF, Omelon CR, Gordon RA, Moser D, Macfie SM (2013) Localization and chemical speciation of cadmium in the roots of barley and lettuce. Environ Exp Bot 100:10–19
Alloway BJ, Steinnes E (1999) Anthropogenic addition of cadmium to soils. In: McLaughlin MJ, Singh BR (eds) Cadmium in soil and plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 97–123
Assunção AGL, Bookum WM, Nelissen HJM, Vooijs R, Schat H, Ernst WHO (2003) Differential metal-specific tolerance and accumulation patterns among Thlaspi caerulescens populations originating from different soil types. New Phytol 159:411–419
Bei HS, Ammami ZH, Rifa YT, Arrabi MH, Amza SH (2012) Phenotypic diversity analysis for salinity tolerance of Tunisian barley populations (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Arid Land Stud 22:57–60
Cakmak I, Welch RM, Hart J, Norvell WA, Oztürk L, Kochian LV (2000) Uptake and retranslocation of leaf-applied cadmium (109Cd) in diploid, tetraploid and hexaploid wheats. J Exp Bot 51:221–226
Cesco S, Mimmo T, Tonon G, Tomasi N, Pinton R, Terzano R, Neumann G, Weisskopf L, Renella G, Landi L, Nannipieri P (2012) Plant-borne flavonoids released into the rhizosphere: impact on soil bio-activities related to plant nutrition. A review. Biol Fertil Soils 48:123–149
Chaabane R, El Felah M, Ben Salah H, Ben Naceur M, Abdelly C, Ramla D, Nada A, Saker M (2009) Molecular characterization of Tunisian barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genotypes using microsatellites (SSRs) markers. Eur J Sci Res 36:6–15
Chen F, Wang F, Zhang G, Wu F (2008) Identification of barley varieties tolerant to cadmium toxicity. Biol Trace Elem Res 121:171–179
Clarke JM, Norvell WA, Clarke FR, Buckley WT (2002) Concentration of cadmium and other elements in the grain of near-isogenic durum lines. Can J Plant Sci 82:27–33
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88:1707–1719
Clemens S, Aarts MGM, Thomine S, Verbruggen N (2013) Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci 18:92–99
Cobbett CS (2000) Phytochelatins and their roles in heavy metal detoxification. Plant Physiol 123:825–832
Del Buono D, Mimmo T, Terzano R, Tomasi N, Cesco S (2014) Effect of cadmium on antioxidative enzymes, glutathione content, and glutathionylation in tall fescue. Biol Plant. doi:10.1007/s10535-014-0412-y
Dunbar KR, McLaughlin MJ, Reid RJ (2003) The uptake and partitioning of cadmium in two cultivars of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J Exp Bot 54:349–354
Grant CA, Buckley WT, Bailey LD, Selles F (1998) Cadmium accumulation in crops. Can J Plant Sci 78:1–17
Grant CA, Clarke JM, Duguid S, Chaney RL (2008) Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. Sci Total Environ 390:301–310
Griffith OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106:207–212
Grill E, Winnacker E-L, Zenk MH (1987) Phytochelatins, a class of heavy metal-binding peptides from plants, are functionally analogous to metallothioneins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:439–443
Guo YL, Schulz R, Marschner H (1995) Genotypic differences in uptake and distribution of cadmium and nickel in plants. Angew Bot 69:42–48
Gwozdz EA, Przymusinski R, Rucinska R, Deckert J (1997) Plant cell responses to heavy metals: molecular and physiological aspects. Acta Physiol Plant 19:459–465
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611
Jarvis SC, Jones LHP, Hopper MJ (1976) Cadmium uptake from solution by plants and its transport from roots to shoots. Plant Soil 44:179–191
Khan DH, Duckett JG, Frankland B, Kirkham JB (1984) An X-ray microanalytical study of the distribution of cadmium in roots of Zea mays L. J Plant Physiol 115:19–28
Lancilli C, Giacomini B, Lucchini G, Davidian J-C, Cocucci M, Sacchi GA, Nocito FF (2014) Cadmium exposure and sulfate limitation reveal differences in the transcriptional control of three sulfate transporter (Sultr1;2) genes in Brassica juncea. BMC Plant Biol 14:132
Lombi E, Zhao FJ, Dunham SJ, McGrath SP (2000) Cadmium accumulation in population of Thlaspi caerulescens and Thlaspi goesingense. New Phytol 145:11–20
Lozano-Rodríguez E, Hernández LE, Bonay P, Carpena-Ruiz RO (1997) Distribution of Cd in shoot and root tissues of maize and pea plants: physiological disturbances. J Exp Bot 48:123–128
McLaughlin M, Parker DR, Clarke JM (1999) Metals and micronutrients—food safety issues. Field Crop Res 60:143–163
Mendoza-Cózatl DG, Moreno-Sánchez R (2006) Control of glutathione and phytochelatin under cadmium stress. Pathway modeling for plants. J Theor Biol 238:919–936
Mills RF, Peaston KA, Runions J, Williams LE (2012) HvHMA2, a P1B-ATPase from barley, is highly conserved among cereals and functions in Zn and Cd transport. PLoS One 7:e42640
Nocito FF, Lancilli C, Crema B, Fourcroy P, Davidian J-C, Sacchi GA (2006) Heavy metal stress and sulfate uptake in maize roots. Plant Physiol 141:1138–1148
Nocito FF, Lancilli C, Giacomini B, Sacchi GA (2007) Sulfur metabolism and cadmium stress in higher plants. Plant Stress 1:142–156
Nocito FF, Espen L, Crema B, Cocucci M, Sacchi GA (2008) Cadmium induces acidosis in maize root cells. New Phytol 179:700–711
Nocito FF, Lancilli C, Dendena B, Lucchini G, Sacchi GA (2011) Cadmium retention in rice roots is influenced by cadmium availability, chelation and translocation. Plant Cell Environ 34:994–1008
Palacios OA, Bashan Y, de-Bashan LE (2014) Proven and potential involvement of vitamins in interactions of plants with plant growth-promoting bacteria—an overview. Biol Fertil Soils 50:415–432
Persson DP, Hansen TH, Holm PE, Schjoerring JK, Hansen HCB, Nielsen J, Cakmak I, Husted S (2006) Multi-elemental speciation analysis of barley genotypes differing in tolerance to cadmium toxicity using SEC-ICP-MS and ESI-TOF-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 21:996–1005
Puig S, Peñarrubia L (2009) Placing metal micronutrients in context: transport and distribution in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:299–306
Rauser WE (1987) Compartmental efflux analysis and removal of extracellular cadmium from roots. Plant Physiol 85:62–65
Rauser WE (2003) Phytochelatin-based complexes bind various amounts of cadmium in maize seedlings depending on the time of exposure, the concentration of cadmium and the tissue. New Phytol 158:269–278
Rauser WE, Meuwly P (1995) Retention of cadmium in roots of maize seedlings. Role of complexation by phytochelatins and related thiol peptides. Plant Physiol 109:195–202
Rea PA, Vatamaniuk OK, Rigden DJ (2004) Weeds, worms, and more. Papain’s long-lost cousin, phytochelatin synthase. Plant Physiol 136:2463–2474
Sanità di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Nagato Y, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Watanabe A, Akagi H (2012) Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol 53:213–224
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Watanabe A, Akagi H (2013) Functional relationship heavy metal P-type ATPases (OsHMA2 and OsHMA3) of rice (Oryza sativa) using RNAi. Plant Biotechnol 30:511–515
Schäfer HJ, Greiner S, Rausch T, Haag-Kerwer A (1997) In seedlings of the heavy metal accumulator Brassica juncea Cu2+ differentially affects transcript amounts for γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (γ-ECS) and metallothionein (MT2). FEBS Lett 404:216–220
Schneider S, Bergmann L (1995) Regulation of glutathione synthesis in suspension cultures of parsley and tobacco. Bot Acta 108:34–40
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2009) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14:43–50
Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H, Ogo Y, Senoura T, Nishizawa NK, Nakanishi H (2012) The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice. Plant Cell Environ 35:1948–1957
Tan J, Wang J, Chai T, Zhang Y, Feng S, Li Y, Zhao H, Liu H, Chai X (2013) Functional analyses of TaHMA2, a P1B-type ATPase in wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 11:420–431
Tukendorf A, Rauser WE (1990) Changes in glutathione and phytochelatins in roots of maize seedlings exposed to cadmium. Plant Sci 70:155–166
Turner AP (1994) The response of plants to heavy metals. In: Ross SM (ed) Toxic metals in soil-plant systems. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, pp 153–187
Ueno D, Yamaji N, Kono I, Huang CF, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2010) Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:16500–16505
Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T (2012) Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice 5:5
Uraguchi S, Mori S, Kuramata M, Kawasaki A, Arao T, Ishikawa S (2009) Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. J Exp Bot 60:2677–2688
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:364–372
Verkleij JAC, Koevoets P, Van’t Riet J, Bank R, Nijdam Y, Ernst WHO (1990) Poly(y-glutamylcysteinyl)glycines or phytochelatins and their role in cadmium tolerance of Silene vulgaris. Plant Cell Environ 13:913–921
Wagner GJ (1993) Accumulation of cadmium in crop plants and its consequences to human health. Adv Agron 51:173–212
Weigel HJ, Jäger HJ (1980) Subcellular distribution and chemical form of cadmium in bean plants. Plant Physiol 65:480–482
Wong CKE, Cobbett CS (2009) HMA P-type ATPases are the major mechanism for root-to-shoot Cd translocation in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 181:71–78
Wu FB, Zhang GP, Yu JS (2003) Genotypic differences in effect of Cd on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:1272–1281
Wu FB, Zhang GP, Dominy P, Wu HX, Bachir DML (2007) Differences in yield components and kernel Cd accumulation in response to Cd toxicity in four barley genotypes. Chemosphere 70:83–92
**ang C, Werner BL, Christensen EM, Oliver DJ (2001) The biological functions of glutathione revisited in Arabidopsis transgenic plants with altered glutathione levels. Plant Physiol 126:564–574
Zhu YL, Pilon-Smits EAH, Jouanin L, Terry N (1999a) Overexpression of glutathione synthetase in Indian mustard enhances cadmium accumulation and tolerance. Plant Physiol 119:73–79
Zhu YL, Pilon-Smits EAH, Tarun AS, Weber SU, Jouanin L, Terry N (1999b) Cadmium tolerance and accumulation in Indian mustard is enhanced by overexpressing γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Plant Physiol 121:1169–1177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sghayar, S., Ferri, A., Lancilli, C. et al. Analysis of cadmium translocation, partitioning and tolerance in six barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars as a function of thiol metabolism. Biol Fertil Soils 51, 311–320 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0977-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0977-9