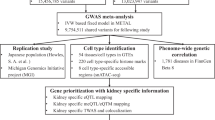
Abstract
Background
The pathogenesis of urolithiasis is multi-factorial and genetic factors have been shown to play a significant role in the development of urolithiasis. We tried to apply genome-wide Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis and figure out reliable gene susceptibility of urolithiasis from the largest samples to date in two independent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) database of European ancestry.
Methods
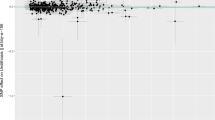
We extracted summary statistics of expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) from eQTLGen consortium. Urolithiasis phenotype information was obtained from both FinnGen Biobank and UK Biobank. Multiple two-sample MR analysis with a Bonferroni-corrected P threshold (P < 2.5e-06) was conducted. The primary endpoint was the causal effect calculated by random-effect inverse variance weighted (IVW) method. Sensitivity analysis, volcano plots, scatter plots, and regional plots were also performed and visualized.
Results
After multiple MR tests between 19942 eQTLs and urolithiasis phenotype from both cohorts, 30 common eQTLs with consistent effect size direction were found to be causally associated with urolithiasis risk. Finally only one gene (LMAN2) was simultaneously identified among all top significant eQTLs from both FinnGen Biobank (beta = 0.6758, se = 0.0327, P = 6.775e-95) and UK Biobank (beta = 0.0044, se = 0.0009, P = 2.417e-06). We also found that LMAN2 was with the largest beta effect size on urolithiasis phenotype from the two cohorts.
Conclusion
We for the first time implemented genome-wide MR analysis to investigate the genetic susceptibility of urolithiasis in general population of European ancestry. Our results provided novel insights into common genetic variants of urinary stone disease, which was of great help to subsequent researches.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Singh P, Enders FT, Vaughan LE, Bergstralh EJ, Knoedler JJ, Krambeck AE, Lieske JC, Rule AD (2015) Stone composition among first-time symptomatic kidney stone formers in the community. Mayo Clin Proc 90(10):1356–1365
Coe FL, Worcester EM, Evan AP (2016) Idiopathic hypercalciuria and formation of calcium renal stones. Nat Rev Nephrol 12(9):519–533
Lede L, Liang Z, Kaiwen X, ** J, Zhongyu J, Yu L, Hong L, Kunjie W (2022) Does combined lithotripter show superior stone-success rate than ultrasonic or pneumatic device alone during percutaneous nephrolithotrotomy? A meta-analysis. Int J Surg 98:106223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.106223
Singh P, Harris PC, Sas DJ, Lieske JC (2022) The genetics of kidney stone disease and nephrocalcinosis. Nat Rev Nephrol 18(4):224–240
Howles SA, Thakker RV (2020) Genetics of kidney stone disease. Nat Rev Urol 17(7):407–421
Dickson FJ, Sayer JA (2020) Nephrocalcinosis: a review of monogenic causes and insights they provide into this heterogeneous condition. Int J Mol Sci 21(1):369
Ehlayel AM, Copelovitch L (2019) Update on dent disease. Pediatr Clin North Am 66(1):169–178
De Matteis MA, Staiano L, Emma F, Devuyst O (2017) The 5-phosphatase OCRL in Lowe syndrome and Dent disease 2. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(8):455–470
Rungroj N, Nettuwakul C, Sawasdee N, Sangnual S, Deejai N, Misgar RA, Pasena A, Khositseth S, Kirdpon S, Sritippayawan S, Vasuvattakul S, Yenchitsomanus PT (2018) Distal renal tubular acidosis caused by tryptophan-aspartate repeat domain 72 (WDR72) mutations. Clin Genet 94(5):409–418
Jobst-Schwan T, Klämbt V, Tarsio M, Heneghan JF, Majmundar AJ, Shril S, Buerger F, Ottlewski I, Shmukler BE, Topaloglu R, Hashmi S, Hafeez F, Emma F, Greco M, Laube GF, Fathy HM, Pohl M, Gellermann J, Milosevic D, Baum MA, Mane S, Lifton RP, Kane PM, Alper SL, Hildebrandt F (2020) Whole exome sequencing identified ATP6V1C2 as a novel candidate gene for recessive distal renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int 97(3):567–579
Enerbäck S, Nilsson D, Edwards N, Heglind M, Alkanderi S, Ashton E, Deeb A, Kokash FEB, Bakhsh ARA, Van’t Hoff W, Walsh SB, D’Arco F, Daryadel A, Bourgeois S, Wagner CA, Kleta R, Bockenhauer D, Sayer JA (2018) Acidosis and deafness in patients with recessive mutations in FOXI1. J Am Soc Nephrol 29(3):1041–1048
D’Ambrosio V, Azzarà A, Sangiorgi E, Gurrieri F, Hess B, Gambaro G, Ferraro PM (2021) Results of a gene panel approach in a cohort of patients with incomplete distal renal tubular acidosis and nephrolithiasis. Kidney Blood Press Res 46(4):469–474
Bourgeois S, Bettoni C, Baron S, Wagner CA (2018) Haploinsufficiency of the mouse Atp6v1b1 gene leads to a mild acid-base disturbance with implications for kidney stone disease. Cell Physiol Biochem 47(3):1095–1107
Bergwitz C, Miyamoto KI (2019) Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapy. Pflugers Arch 471(1):149–163
De Paolis E, Scaglione GL, De Bonis M, Minucci A, Capoluongo E (2019) CYP24A1 and SLC34A1 genetic defects associated with idiopathic infantile hypercalcemia: from genotype to phenotype. Clin Chem Lab Med 57(11):1650–1667
Amar A, Majmundar AJ, Ullah I, Afzal A, Braun DA, Shril S, Daga A, Jobst-Schwan T, Ahmad M, Sayer JA, Gee HY, Halbritter J, Knöpfel T, Hernando N, Werner A, Wagner C, Khaliq S, Hildebrandt F (2019) Gene panel sequencing identifies a likely monogenic cause in 7% of 235 Pakistani families with nephrolithiasis. Hum Genet 138(3):211–219
Kang SJ, Lee R, Kim HS (2019) Infantile hypercalcemia with novel compound heterozygous mutation in SLC34A1 encoding renal sodium-phosphate cotransporter 2a: a case report. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 24(1):64–67
Policastro LJ, Saggi SJ, Goldfarb DS, Weiss JP (2018) Personalized intervention in monogenic stone formers. J Urol 199(3):623–632
Martin-Higueras C, Torres A, Salido E (2017) Molecular therapy of primary hyperoxaluria. J Inherit Metab Dis 40(4):481–489
Singh P, Chebib FT, Cogal AG, Gavrilov DK, Harris PC, Lieske JC (2020) Pyridoxine responsiveness in a Type 1 primary hyperoxaluria patient with a rare (Atypical) AGXT gene mutation. Kidney Int Rep 5(6):955–958
Garrelfs SF, Rumsby G, Peters-Sengers H, Erger F, Groothoff JW, Beck BB, Oosterveld MJS, Pelle A, Neuhaus T, Adams B, Cochat P, Salido E, Lipkin GW, Hoppe B, Hulton SA, OxalEurope Consortium (2019) Patients with primary hyperoxaluria type 2 have significant morbidity and require careful follow-up. Kidney Int. 96(6):1389–1399
Greed L, Willis F, Johnstone L, Teo S, Belostotsky R, Frishberg Y, Pitt J (2018) Metabolite diagnosis of primary hyperoxaluria type 3. Pediatr Nephrol 33(8):1443–1446
Weigert A, Martin-Higueras C, Hoppe B (2018) Novel therapeutic approaches in primary hyperoxaluria. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 23(4):349–357
Li Y, Lu X, Yu Z, Wang H, Gao B (2023) Meta-data analysis of kidney stone disease highlights ATP1A1 involvement in renal crystal formation. Redox Biol 61:102648
Ye QL, Wang DM, Wang X, Zhang ZQ, Tian QX, Feng SY, Zhang ZH, Yu DX, Ding DM, **e DD (2021) Sirt1 inhibits kidney stones formation by attenuating calcium oxalate-induced cell injury. Chem Biol Interact 25(347):109605
Wang X, Zhang Y, Han S, Chen H, Chen C, Ji L, Gao B (2020) Overexpression of miR-30c-5p reduces cellular cytotoxicity and inhibits the formation of kidney stones through ATG5. Int J Mol Med 45(2):375–384
Wang XF, Zhang BH, Lu XQ, Wang RQ (2019) Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor gene silencing inhibits the development of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and formation of a calcium oxalate crystal in renal tubular epithelial cells in mice with kidney stones via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 234(2):1567–1577
Sayer JA (2017) Progress in understanding the genetics of calcium-containing nephrolithiasis. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(3):748–759
** J, Chen Y, **g J, Zhang Y, Liang C, Hao Z, Zhang L (2019) Sirtuin 3 suppresses the formation of renal calcium oxalate crystals through promoting M2 polarization of macrophages. J Cell Physiol 234(7):11463–11473
Lu H, Sun X, Jia M, Sun F, Zhu J, Chen X, Chen K, Jiang K (2021) Rosiglitazone suppresses renal crystal deposition by ameliorating tubular injury resulted from oxidative stress and inflammatory response via promoting the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and shifting macrophage polarization. Oxid Med Cell Longev 14(2021):5527137
Sun L, Zou LX, Wang J, Chen T, Han YC, Zhu DD, Zhuo SC (2018) Mucin 4 gene silencing reduces oxidative stress and calcium oxalate crystal formation in renal tubular epithelial cells through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in nephrolithiasis rat model. Kidney Blood Press Res 43(3):820–835
Sun Y, Liu Y, Guan X, Kang J, Wang X, Liu Q, Li D, Xu H, Tao Z, Deng Y (2020) Atorvastatin inhibits renal inflammatory response induced by calcium oxalate crystals via inhibiting the activation of TLR4/NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. IUBMB Life 72(5):1065–1074
Võsa U, Claringbould A, Westra HJ, Bonder MJ, Deelen P, Zeng B, Kirsten H, Saha A, Kreuzhuber R, Yazar S, Brugge H, Oelen R, de Vries DH, van der Wijst MGP, Kasela S, Pervjakova N, Alves I, Favé MJ, Agbessi M, Christiansen MW, Jansen R, Seppälä I, Tong L, Teumer A, Schramm K, Hemani G, Verlouw J, Yaghootkar H, Sönmez Flitman R, Brown A, Kukushkina V, Kalnapenkis A, Rüeger S, Porcu E, Kronberg J, Kettunen J, Lee B, Zhang F, Qi T, Hernandez JA, Arindrarto W, Beutner F, BIOS Consortium, i2QTL Consortium, Dmitrieva J, Elansary M, Fairfax BP, Georges M, Heijmans BT, Hewitt AW, Kähönen M, Kim Y, Knight JC, Kovacs P, Krohn K, Li S, Loeffler M, Marigorta UM, Mei H, Momozawa Y, Müller-Nurasyid M, Nauck M, Nivard MG, Penninx BWJH, Pritchard JK, Raitakari OT, Rotzschke O, Slagboom EP, Stehouwer CDA, Stumvoll M, Sullivan P, ‘t Hoen PAC, Thiery J, Tönjes A, van Dongen J, van Iterson M, Veldink JH, Völker U, Warmerdam R, Wijmenga C, Swertz M, Andiappan A, Montgomery GW, Ripatti S, Perola M, Kutalik Z, Dermitzakis E, Bergmann S, Frayling T, van Meurs J, Prokisch H, Ahsan H, Pierce BL, Lehtimäki T, Boomsma DI, Psaty BM, Gharib SA, Awadalla P, Milani L, Ouwehand WH, Downes K, Stegle O, Battle A, Visscher PM, Yang J, Scholz M, Powell J, Gibson G, Esko T, Franke L (2021) Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat Genet 53(9):1300–1310
Elsworth B, Lyon M, Alexander T, Liu Yi, Matthews P, Hallett J, Bates P, Palmer Tom, Haberland V, Smith GD, Zheng J, Haycock P, Gaunt TR, Hemani G (2020) The MRC IEU OpenGWAS data infrastructure. bioRxiv 08(10):244293
Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, Wade KH, Haberland V, Baird D, Laurin C, Burgess S, Bowden J, Langdon R, Tan VY, Yarmolinsky J, Shihab HA, Timpson NJ, Evans DM, Relton C, Martin RM, Davey Smith G, Gaunt TR, Haycock PC (2018) The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 30(7):e34408
Lyon M, Andrews SJ, Elsworth B, Gaunt TR, Hemani G, Marcora E (2020) The variant call format provides efficient and robust storage of GWAS summary statistics. bioRxiv 4:280
Kurki MI, Karjalainen J, Palta P, Sipilä TP, Kristiansson K, Donner KM, Reeve MP, Laivuori H, Aavikko M, Kaunisto MA, Loukola A, Lahtela E, Mattsson H, Laiho P, Della Briotta Parolo P, Lehisto AA, Kanai M, Mars N, Rämö J, Kiiskinen T, Heyne HO, Veerapen K, Rüeger S, Lemmelä S, Zhou W, Ruotsalainen S, Pärn K, Hiekkalinna T, Koskelainen S, Paajanen T, Llorens V, Gracia-Tabuenca J, Siirtola H, Reis K, Elnahas AG, Sun B, Foley CN, Aalto-Setälä K, Alasoo K, Arvas M, Auro K, Biswas S, Bizaki-Vallaskangas A, Carpen O, Chen CY, Dada OA, Ding Z, Ehm MG, Eklund K, Färkkilä M, Finucane H, Ganna A, Ghazal A, Graham RR, Green EM, Hakanen A, Hautalahti M, Hedman ÅK, Hiltunen M, Hinttala R, Hovatta I, Hu X, Huertas-Vazquez A, Huilaja L, Hunkapiller J, Jacob H, Jensen JN, Joensuu H, John S, Julkunen V, Jung M, Junttila J, Kaarniranta K, Kähönen M, Kajanne R, Kallio L, Kälviäinen R, Kaprio J; FinnGen; Kerimov N, Kettunen J, Kilpeläinen E, Kilpi T, Klinger K, Kosma VM, Kuopio T, Kurra V, Laisk T, Laukkanen J, Lawless N, Liu A, Longerich S, Mägi R, Mäkelä J, Mäkitie A, Malarstig A, Mannermaa A, Maranville J, Matakidou A, Meretoja T, Mozaffari SV, Niemi MEK, Niemi M, Niiranen T, O Donnell CJ, Obeidat ME, Okafo G, Ollila HM, Palomäki A, Palotie T, Partanen J, Paul DS, Pelkonen M, Pendergrass RK, Petrovski S, Pitkäranta A, Platt A, Pulford D, Punkka E, Pussinen P, Raghavan N, Rahimov F, Rajpal D, Renaud NA, Riley-Gillis B, Rodosthenous R, Saarentaus E, Salminen A, Salminen E, Salomaa V, Schleutker J, Serpi R, Shen HY, Siegel R, Silander K, Siltanen S, Soini S, Soininen H, Sul JH, Tachmazidou I, Tasanen K, Tienari P, Toppila-Salmi S, Tukiainen T, Tuomi T, Turunen JA, Ulirsch JC, Vaura F, Virolainen P, Waring J, Waterworth D, Yang R, Nelis M, Reigo A, Metspalu A, Milani L, Esko T, Fox C, Havulinna AS, Perola M, Ripatti S, Jalanko A, Laitinen T, Mäkelä TP, Plenge R, McCarthy M, Runz H, Daly MJ, Palotie A (2023) FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 613(7944):508-518.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05473-8. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Erratum in: Nature. 2023 Feb 24;: PMID: 36653562; PMCID: PMC9849126
Lin L, Wang W, **ao K, Guo X, Zhou L (2023) Genetically elevated bioavailable testosterone level was associated with the occurrence of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Endocrinol Invest 46(10):2095–2102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02060-0
Lede L, Kang N, Liyuan X, Liao P, **ang L (2024) SGLT2 inhibition and three urological cancers: Up-to-date results. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3797
Lede L, Yaxiong T, Kang N, **ang L, Xu H (2024) Investigating the causal associations between metabolic biomarkers and the risk of kidney cancer. Commun Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-024-06114-8
Canela VH, Bledsoe SB, Lingeman JE, Gerber G, Worcester EM, El-Achkar TM, Williams JC Jr (2021) Demineralization and sectioning of human kidney stones: a molecular investigation revealing the spatial heterogeneity of the stone matrix. Physiol Rep 9(1):e14658
Grams ME, Surapaneni A, Chen J, Zhou L, Yu Z, Dutta D, Welling PA, Chatterjee N, Zhang J, Arking DE, Chen TK, Rebholz CM, Yu B, Schlosser P, Rhee EP, Ballantyne CM, Boerwinkle E, Lutsey PL, Mosley T, Feldman HI, Dubin RF, Ganz P, Lee H, Zheng Z, Coresh J (2021) Proteins Associated with Risk of Kidney Function Decline in the General Population. J Am Soc Nephrol 32(9):2291–2302
Kiernan E, Surapaneni A, Zhou L, Schlosser P, Walker KA, Rhee EP, Ballantyne CM, Deo R, Dubin RF, Ganz P, Coresh J, Grams ME (2023) Alterations in the circulating proteome associated with albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.0000000000000108
Hara-Kuge S, Ohkura T, Ideo H, Shimada O, Atsumi S, Yamashita K (2002) Involvement of VIP36 in intracellular transport and secretion of glycoproteins in polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells. J Biol Chem 277(18):16332–16339
Acknowledgements
We express our thanks to those people who have contributed to the IEU GWAS database project and the MRC Integrative Epidemiology Unit (IEU) at the University of Bristol. Sincere thanks also go to the many GWAS consortia who have made the GWAS data that they generated publicly available, and many members of the IEU who have contributed to curating these data. In addition, we want to acknowledge the participants and investigators of the eQTLGen consortium and FinnGen study.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of study: L L, Y M, and Z L. Acquisition of data: L L, Y M, Z L, L L, and Q H. Data analysis and/or interpretation: L L, Y M, and Z L. Drafting of manuscript and/or critical revision: L L and Y M. Approval of final version of manuscript: L L, Y M, Z L, L L, Q H, and L Z.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1:
(PDF 1479 KB)
Supplementary file 2:
(XLSX 254 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Ma, Y., Li, Z. et al. Genetic susceptibility of urolithiasis: comprehensive results from genome-wide analysis. World J Urol 42, 230 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-024-04937-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-024-04937-y