Abstract
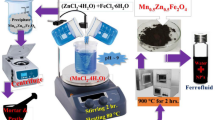
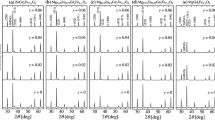
In this work, a series of PEGylated manganese-zinc ferrite mixed (PEG-Mn1-xZnxFe2O4) nanoparticles with varying concentrations of zinc ions (x = 0.0, 0.25, 0.4, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0) were synthesized using a solvothermal approach to investigate their physicochemical and magnetic hyperthermia properties through a range of analytical techniques, including TEM, XRF, XRD, FTIR, VSM, and magnetic hyperthermia. The PEG-Mn1-xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles exhibited a nearly spherical shape and diameters less than 30 nm. The particle size decreased from 27 to 11.6 nm with an increasing amount of zinc (x = 0.0–0.5). The saturation magnetization (MS) value decreased with the rising Zn content, ranging from 77.8 to 30.7 emu/g. The addition of zinc led to a reduction in the specific absorption rate (SAR) of the material. This decrease in the SAR parameter was associated with a decline in the intrinsic loss power (ILP) value, varying from 0.264 nH m2/kg for MnFe2O4 to 0.037 nH m2/kg for ZnFe2O4. Consequently, these PEG-Mn1-xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles exhibit potential as candidates for magnetic fluid hyperthermia applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
L.H. Reddy, J.L. Arias, J. Nicolas, P. Couvreur, Magnetic nanoparticles: design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 112, 5818–5878 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300068p
A. Akbarzadeh, M. Samiei, S. Davaran, Magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7(1), 144 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276x-7-144
S. Laurent, J.-L. Bridot, L.V. Elst, R.N. Muller, Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Future Med. Chem. 2, 427–449 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.09.164
M. Colombo, S. Carregal-Romero, M.F. Casula, L. Gutiérrez, M.P. Morales, I.B. Böhm, W.J. Parak, Biological applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 4306 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs15337h
M.J. Ansari et al., Synthesis and stability of magnetic nanoparticles. Bionanoscience. 12, 627–638 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-022-00947-5
A. Ali, T. Shah, R. Ullah et al., Review on recent progress in magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and diverse applications. Front. Chem. 9, 629054 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.629054
M.I. Anik, M.K. Hossain, I. Hossain et al., Recent progress of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: a review. Nano Select. 2, 1146–1186 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202000162
A. Singh, S.K. Sahoo, Magnetic nanoparticles: a novel platform for cancer theranostics. Drug Discov. Today 19, 474–481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2013.10.005
X.L. Liu, H.M. Fan, Innovative magnetic nanoparticle platform for magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic fluid hyperthermia applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 4, 38–46 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2013.12.010
Y. Cohen, S.Y. Shoushan, Magnetic nanoparticles-based diagnostics and theranostics. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 4, 672–681 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.01.006
P. Das, M. Colombo, D. Prosperi, Recent advances in magnetic fluid hyperthermia for cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B 171, 42–55 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.10.051
Z. Hedayatnasab, F. Abnisa, W.M.A.W. Daud, Review on magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic nanofluid hyperthermia application. Mater. Des. 123, 174–196 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.036
S. Laurent, S. Dutz, U.O. Häfeli, M. Mahmoudi, Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: focus on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 166, 8–23 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.04.003
C.S.S.R. Kumar, F. Mohammad, Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 9, 789–808 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2011.03.008
F. Vurro, M. Gerosa, A. Busato et al., Doped ferrite nanoparticles exhibiting self-regulating temperature as magnetic fluid hyperthermia antitumoral agents, with diagnostic capability in magnetic resonance imaging and Magnetic Particle Imaging. Cancers 14(20), 5150 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205150
J. Kurian, B.B. Lahiri, M.J. Mathew et al., High magnetic fluid hyperthermia efficiency in copper ferrite nanoparticles prepared by solvothermal and hydrothermal methods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 538, 168233 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168233
A. Bhardwaj, K. Parekh, N. Jain, In vitro hyperthermic effect of magnetic fluid on cervical and breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 15249 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71552-3
D. Ortega, Q.A. Pankhurst, Magnetic hyperthermia, in Nanoscience: volume 1: nanostructures through chemistry. ed. by P. O’Brien (Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2013), pp.60–88. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781849734844-00060
L. Arias, J. Pessan, A. Vieira, T. Lima, A. Delbem, D. Monteiro, Iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications: a perspective on synthesis, drugs, antimicrobial activity, and toxicity. Antibiotics. 7(2), 46 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7020046
E.A. Périgo, G. Hemery, O. Sandre, D. Ortega, E. Garaio, F. Plazaola, F.J. Teran, Fundamentals and advances in magnetic hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2, 041302 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4935688
A.E. Deatsch, B.A. Evans, Heating efficiency in magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 354, 163–172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.11.006
H. Etemadi, G.P. Plieger, Magnetic fluid hyperthermia based on magnetic nanoparticles: physical characteristics, historical perspective, clinical trials, technological challenges, and recent advances. Adv. Ther. 3(11), 2000061 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adtp.202000061
S. Healy, A.F. Bakuzis, P.W. Goodwill et al., Clinical magnetic hyperthermia requires integrated magnetic particle imaging. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 14(3), e1779 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1779
J.A. Fuentes-García, A. Carvalho-Alavarse et al., Simple sonochemical method to optimize the heating efficiency of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. ACS Omega 5, 26357–26364 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02212
D.D. Andhare, S.R. Patade, M.V. Khedkar et al., Intensive analysis of uncoated and surface modified Co–Zn nanoferrite as a heat generator in magnetic fluid hyperthermia applications. Appl. Phys. A 128, 502 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05648-0
I. Sharifi, H. Shokrollahi, S. Amiri, Ferrite-based magnetic nanofluids used in hyperthermia applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 903–915 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.10.017
W. Zhang, X. Yu, H. Li, D. Dong, X. Zuo, C. Wu, Magnetic nanoparticles with low Curie temperature and high heating efficiency for self-regulating temperature hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 489, 165382 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165382
K.K. Kefeni, T.A.M. Msagati, T.T.I. Nkambule, B.B. Mamba, Spinel ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites for biomedical applications and their toxicity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 107, 110314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110314
P. Thakur, D. Chahar, S. Taneja, N. Bhalla, A. Thakur, A review on MNZN ferrites: synthesis, characterization and applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 15740–15763 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.287
A.K. Gupta, M. Gupta, Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomater. 26, 3995–4021 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012
R.D. Piazza et al., PEGlatyon-SPION surface functionalization with folic acid for magnetic hyperthermia applications. Mater. Res. Express. 7, 015078 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6700
S. Hatamie, P.-J. Shih, M. Soufi-Zomorod et al., Hyperthermia response of pegylated magnetic graphene nanocomposites for heating applications and accelerate antibacterial activity using magnetic fluid hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. A 126, 276 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3454-3
J.S. Suk, Q. Xu, N. Kim, J. Hanes, L.M. Ensign, Pegylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. 99, 28–51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.09.012
Z. Shaterabadi, G. Nabiyouni, M. Soleymani, Physics responsible for heating efficiency and self-controlled temperature rise of magnetic nanoparticles in magnetic hyperthermia therapy. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 133, 9–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.10.001
A. Apostolov, I. Apostolova, J. Wesselinowa, Specific absorption rate in Zn-doted ferrites for self-controlled magnetic hyperthermia. Eur. Phys. J. B. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2019-90567-2
A. Makridis, K. Topouridou, M. Tziomaki, D. Sakellari, K. Simeonidis, M. Angelakeris, O. Kalogirou, In vitro application of Mn-ferrite nanoparticles as novel magnetic hyperthermia agents. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2, 8390–8398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tb01017e
J. **e et al., High-performance PEGylated Mn–Zn ferrite nanocrystals as a passive-targeted agent for magnetically induced cancer theranostics. Biomaterials 35, 9126–9136 (2014)
Y. Qu et al., Enhanced magnetic fluid hyperthermia by micellar magnetic nanoclusters composed of MnxZn1-XFe2O4 nanoparticles for induced tumor cell apoptosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 16867–16879 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am5042934
X.L. Liu et al., Synthesis of ferromagnetic Fe0.6Mn0.4O nanoflowers as a new class of magnetic theranostic platform for in vivo T1–T2 dual-mode magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic hyperthermia therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 5, 2092–2104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201600357
H. Wu, L. Song, L. Chen, Huang et al., Injectable thermosensitive magnetic nanoemulsion hydrogel for multimodal-imaging-guided accurate thermoablative cancer therapy. Nanoscale 9(42), 16175–16182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr02858j
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (State assignment in the field of scientific activity, № FENW-2023-0019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, supervision: AVS. Investigation, visualization, writing—original draft, writing – review & editing: MKA, MAB, VOD and OEP. Validation: MKA, OEP, and AVS. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Omoush, M.K., Bryleva, M.A., Dmitriev, V.O. et al. Heating efficiency of PEGylated Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. A 130, 160 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07337-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07337-6