Abstract
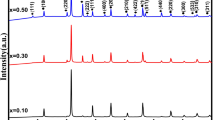
Multiferroic composites having composition (1 − x) BaTiO3–(x) BaFe12O19 (x = 0.50, 0.60, 0.70) were synthesized by the conventional solid-state reaction method. These composites constitute BaTiO3 as the ferroelectric phase and BaFe12O19 as the ferromagnetic phase. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to analyze the formation of crystal structure and phase purity. The formation of individual phases took place without evolving any chemical reaction in all the prepared samples, which evidences the good synthesis of composite ceramics. The presence of characteristic symmetry consisting of tetragonal (P4mm) and hexagonal (P63/mmc) was confirmed by the Rietveld refinement of XRD data. The effect of alternate concentration variation of the component ceramics has been analyzed over the dielectric, electric, and magnetic properties of the composites prepared. The dielectric constant (ε') and dielectric loss (tanδ) were recorded in the frequency and temperature domain and these have been observed to follow Maxwell Wagner’s dispersive behaviour. The dielectric relaxation and conduction mechanism were analyzed with the help of complex impedance spectroscopy (CIS). In Nyquist plots, two semi-circles, whose centres lie below the real axis, were observed for all the prepared samples. Magnetization (M) versus magnetic field (H) loops, recorded at room temperature shows, gradual increase with the increase in ferrite content. These hysteresis loops were fitted by the law of approach to saturation (LAS) and values of various magnetic parameters were evaluated. The gradual enhancement in the values of magnetic parameters may be attributed to an increase in the ferromagnetic phase component.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
H. Hou, S. Qian, I. Takeuchi, Materials, physics and systems for multicaloric cooling. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 633–652 (2022)
S. Nadupalli, F. Yan, E. Erdem, Low-temperature surface phase transitions in multiferroic BiFeO3 nanocrystals probed via electron paramagnetic resonance. J. Phys. Chem. C 44, 24596–24604 (2021)
B. Deka, Y.W. Lee, I.R. Yoo, D.W. Gwak, J. Cho, H.C. Song, J.J. Choi, B.D. Hahn, C.W. Ahn, K.H. Cho, Designing ferroelectric/ferromagnetic composite with giant self-biased magnetoelectric effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 192901 (2019)
Y.S. Teh, J. Li, K. Bhattacharya, Understanding the morphotropic phase boundary of perovskite solid solutions as a frustrated state. Phys. Rev. B 103, 144201 (2021)
U. Ozgur, Y. Alivov, H. Morkoc, Microwave Ferrites, Part 2: passive components and electrical tuning. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 20, 911–952 (2009)
N. Hur, S. Park, P.A. Sharma, J.S. Ahn, S. Guha, S.W. Cheong, Electric polarization reversal and memory in a multiferroic material induced by magnetic fields. Nature 429, 392–395 (2004)
W. Eerenstein, N.D. Mathur, J.F. Scott, Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442, 759–765 (2006)
M.P. Singh, W. Prellier, C. Simon, B. Raveau, Magnetocapacitance effect in perovskite-superlattice based multiferroics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 022505 (2005)
Y.T. Zhang, C.C. Wang, M. He, H.B. Lu, Interfacial contributions to magnetocapacitance in La0.05Tb0.95MnO3/La0.67Sr0.33MnO3/SrTiO3 heterojunctions. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42, 055309 (2009)
C.W. Nan, Magnetoelectric effect in composites of piezoelectric and piezomagnetic phases. Phy. Rev. B 50, 6082–6088 (1994)
D.R. Patil, S.A. Lokare, S.S. Chougule, B.K. Chougule, Dielectric and magnetic properties of xNiFe2O4+(1–x)Ba0.9Sr0/1TiO3 composites. Physica B 400, 77–82 (2007)
J. Qiu, L. Lana, H. Zhang, M. Gub, Microwave absorption properties of nanocomposite films of BaFe12O19 and TiO2 prepared by sol-gel method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 133, 191–194 (2006)
A. Srinivas, M.M. Raja, D. Sivaprahasam, P. Saravanan, Enhanced ferroelectricity and magnetoelectricity in 0.75BaTiO3–0.25BaFe12O19 by spark plasma sintering. Process. Appl. Ceram. 7, 29–35 (2013)
A. Srinivasa, T. Karthik, R. Gopalan, V. Chandrasekaran, Improved magnetoelectricity by uniaxial magnetic field pressed and sintered composites in BaTiO3 (x)–BaFe12O19 (1–x) system (x = 0.8, 0.6). Mater. Sci. Eng. B 172, 289–293 (2010)
M. Fahmi, A.B. Zzolkepli, Z. Zainuddin, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of barium titanate and magnesium ferrite composites. Sains Malays. 46(6), 967–973 (2017)
C.C. Yang, Y.J. Gung, C.C. Shih, W.C. Hung, K.H. Wub, Synthesis, infrared and microwave absorbing properties of (BaFe12O19+BaTiO3)/polyaniline composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 933–938 (2011)
S.W. Cheong, M. Mostovoy, Multiferroic: a magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat. Mater. 6(1), 13–20 (2007)
H. Pfeiffer, R.W. Chantrell, P. Görnert, W. Schüppel, E. Sinn, M. Rösler, Properties of barium hexaferrite powders for magnetic recording. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 125, 373–376 (1993)
H. Kojima, Chapter 5 Fundamental properties of hexagonal ferrites with magnetoplumbite structure. Handb. Magn. Mater. 3, 305–391 (1982)
R. Pattanayak, R. Muduli, R.K. Panda, T. Dash, P. Sahu, S. Raut, S. Panigrahi, Investigating the effect of multiple grains–grain interfaces on electric and magnetic properties of [50 wt% BaFe12O19–50 wt% Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3] composite system. Physica B 485, 67–77 (2016)
K. Tanwar, D.S. Gyan, P. Gupta, S. Pandey, O. Parkash, D. Kumar, “Investigation of crystal structure, microstructure and low-temperature magnetic behaviour of Ce4+ and Zn2+ co-doped barium hexaferrite (BaFe12O19). RSC Adv. 8, 19600–19609 (2018)
H.M. Sung, C.J. Chen, W.S. Ko, H.C. Lin, Fine powder ferrite for multilayer chip inductors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 30, 4906–4908 (1984)
J. Rodriguez, Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by Neutron Powder Diffraction + FullProf. Phys. B. 192, 55–69 (1993)
Y. Cao, K. Zhu, J. Liu, J. Qiu, Fabrication of BaTiO3 nanoparticles and its formation mechanism using the high-temperature mixing method under hydrothermal conditions. Adv. Powder Technol. 25, 853–858 (2014)
J. Krishna-Murthy, C. Mitra, S. Ram, A. Venimadhav, Temperature-dependent magnetic and dielectric properties of M-type hexagonal BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 545, 225–230 (2012)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32(5), 751–767 (1976)
V.V. Gudkov, M.N. Sarychev, S. Zherlitsyn, I.V. Zhevstovskikh, N.S. Averkiev, D.A. Vinnik, S.A. Gudkova, R. Niewa, M. Dressel, L.N. Alyabyeva, B.P. Gorshunov, I.B. Bersuker, Sub-lattice of Jahn-Teller centres in hexaferrite crystal. Sci. Reports 10, 7076 (2020)
D.A. Vinnik, D.A. Zherebtsov, L.S. Mashkovtseva, S. Nemrava, N.S. Perov, A.S. Semisalova, I.V. Krivtsov, L.I. Isaenko, G.G. Mikhailov, R. Niewa, Ti-Substituted BaFe12O19 Single Crystal Growth and Characterization. Cryst. Growth Des. 14, 5834–5839 (2014)
S. Dagar, A. Hooda, S. Khasa, M. Malik, Structural refinement, investigation of dielectric and magnetic properties of NBT doped BaFe12O19 novel composite system. J. Alloys Compd. 826, 154214 (2020)
M.J. Iqbal, M.N. Ashiq, Comparative studies of SrZrxMnxFe12-2xO19 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation and sol-gel combustion methods. Scr. Mater. 56, 145–148 (2007)
I.A. Auwal, B. Ünal, A. Baykal, U. Kurtan, M.D. Amir, A. Yıldız, M. Sertkol, Electrical and Dielectric Properties of Y3+Substituted Barium Hexaferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 1813–1826 (2017)
K. Momma, F. Izumi, Vesta: a three-dimensional visualization system for electronic and structural analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41, 653–658 (2008)
A. J. Blake, W. Clegg, J. M. Cole, J. S.O. Evans, P. Main, S. Parsons, D. J. Watkin, Crystal structure analysis principles and practice second edition. IUCr (2009)
O. Singh, A. Agarwal, S. Sanghi, J. Singh, Variation of crystal structure, magnetization, and dielectric properties of Nd and Ba co-doped BiFeO3 multiferroics. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 16, 119–129 (2018)
K.W. Wagner, The distribution of relaxation times in typical dielectrics. Ann. Phys. 40, 818 (1993)
C.G. Koops, On the Dispersion of Resistivity and Dielectric Constant of Some Semiconductors at Audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. B 83, 121 (1951)
J.C. Anderson, Dielectrics, Spottiswoode (Ballantyne & Co Ltd., London, 1964)
A. Jain, Y.G. Wang, N. Wang, Y. Li, F.L. Wang, Tuning the dielectric, ferroelectric and electromechanical properties of Ba0.83Ca0.10Sr0.07TiO3–MnFe2O4 multiferroic composites. Ceram. Int. 46, 7576–7585 (2020)
H.B. Lu, X.Y. Zhang, Influence of the relaxation of Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars polarization and dc conductivity on the dielectric behaviours of nylon 1010. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 054104 (2006)
S. Katlakuntaa, P. Rajua, S.S. Meena, S. Srinath, R. Sandhya, P. Kuruva, S.R. Murthy, Multiferroic properties of microwave sintered BaTiO3-SrFe12O19 composites. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 448, 323–326 (2014)
D.R. Patil, S.A. Lokare, S.S. Chougule, B.K. Chougule, Dielectric and magnetic properties of xNiFe2O4+(1–x)Ba0.9Sr0.1TiO3 composites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 400, 77–82 (2007)
D. Pandey, N. Singh, S.K. Mishra, Diffuse ferroelectric transition and relaxational dipolar freezing (Ba, Sr)TiO3:II Role of Sr concentration in the dynamics of freezing Ind. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 32, 616 (1994)
M.R. Bhandare, H.V. Jamadar, A.T. Pathan, B.K. Chougule, A.M. Shaikh, Dielectric properties of Cu substituted Ni0.5−xZn0.3Mg0.2Fe2O4 ferrites. J. Alloys Comp. 509, L113–L118 (2011)
A.A. Sattar, S.A. Rahman, Dielectric properties of rare earth substituted Cu–Zn ferrites. Phys. Stat. Sol(a) 200, 415–422 (2003)
Y.D. Kolekar, L.J. Sanchez, C.V. Ramana, Dielectric relaxations and alternating current conductivity in manganese substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 144106 (2014)
Z. Dong, Y. Pu, Z. Gao, P. Wang, X. Liu, Z. Sun, Fabrication, structure and properties of BaTiO3–BaFe12O19 composites with core-shell heterostructure. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 3513–3520 (2015)
P. Sarah, S.V. Suryanarayana, Magnetic properties of diphasic composites of LiFe5O8-BaTiO3. Indian J. Phys. 77, 449 (2003)
A. Verma, O.P. Thakur, C. Prakash, T.C. Goel, R.G. Mendiratta, Temperature dependence of electrical properties of nickel-zinc ferrites processed by the citrate precursor technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 116, 1–6 (2005)
D.K. Pradhan, R.N.P. Choudhary, C. Rinaldi, R.S. Katiyar, Effect of Mn substitution on electrical and magnetic properties of Bi0.9 La0.1FeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 024102 (2009)
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, Impedance and modulus spectroscopy of semiconducting BaTiO3 showing positive temperature coefficient of resistance. J. Appl. Phys. 66, 3850–3855 (1989)
M.A.L. Nobre, S. Lanfredi, Ferroelectric state analysis in the grain boundary of Na0.85Li0.15NbO3 ceramic. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 5557–5562 (2003)
I. D. Raistrick, J. R. Macdonald, and D. R. Franceschetti. "Impedance spectroscopy." Emphasizing Solid Mater. Syst. 27 (1987)
J.R. Macdonald, Note on the parameterization of the constant phase admittance element. Solid State Ion. 13, 147–149 (1984)
M.H. Khan, S. Pal, E. Bose, Room-temperature frequency-dependent complex impedance and conductivity behaviour of BaTiO3–La0.7Ca0.3MnO3 composites. Can. J. Phys. 91(12), 1029–1033 (2013)
S. Dagar, A. Hooda, S. Khasa, M. Malik, Rietveld refinement, dielectric and magnetic properties of NBT-Spinel ferrite composites. J. Alloys Compd 806, 737–752 (2019)
S.G.C. Fonseca, L.S. Neiva, M.A.R. Bonifácio, P.R.C. Dos Santos, U.C. Silva, J.B.L. De Oliveira, Tunable magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt and zinc ferrites Co1-xZnxFe2O4 synthesized by combustion route. Mater. Res. 21, 1–9 (2018)
L. Ju, C. Shi, L. Sun, Y. Zhang, H. Qin, J. Hu, Room-temperature magnetoelectric coupling in nanocrystalline Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 083909 (2014)
Z. Huai-Wu, L. Jie, S. Hua, Z. Ting-Chuan, L. Yang, Z. Zong-Liang, Chin. Phys. B 22, 117504 (2013)
S.A. Mathews, D. Rajan Babu, Analysis of the role of M-type hexaferrite-based materials in electromagnetic interference shielding. Curr. Appl. Phys. 29, 39–53 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful to DST, New Delhi for providing the XRD facility under the FIST Scheme to the department (SR/FST/PSI-089/2005). Anand Kumari is thankful to CSIR for the award of junior research fellowship (09/752/(0063)/2016-EMR-I). Ashish Agarwal and Sujata Sanghi are also thankful to DST, New Delhi for providing funds under the PURSE program vide grant number SR/PURSE Phase 2/40(G).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK was involved in the investigation, data curation, conceptualization and writing original draft, OS contributed to software visualization and validation, EA contributed to formal analysis and data curation, MC contributed to methodology and resources, VV contributed to resources and formal analysis, SS contributed in writing—review and editing, conceptualization and funding acquisition, AA contributed in supervision, project administration, writing original draft and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, A., Singh, O., Arya, E. et al. Crystal structure, dielectric and magnetic properties of (1 − x)BaTiO3-(x)BaFe12O19 (x = 0.50, 0.60, 0.70) multiferroic composites. Appl. Phys. A 129, 334 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06596-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06596-z