Abstract
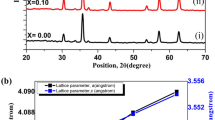
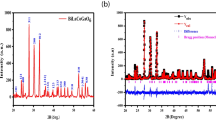
Polycrystalline ceramic samples of BiFe1−xZnxO3 (x = 0.00 and 0.05) have been prepared by sol–gel synthesis method. The formation of the compound has been checked by the X-ray analysis and confirmed the observed data by matching with the standard data (ICSD-97591). The Rietveld analysis confirmed the rhombohedral symmetry with space group R3c. The average crystallite size calculated by the Scherrer method is well matching with that calculated by Williamson–Hall plot method and is of the order of nanometre range. The two- and three-dimensional surface morphology has been measured using atomic force microscopy. The dielectric parameters, including dielectric constant, impedance, etc., have been measured and explained using the universal dielectric response model. The electrical modulus study explains the transport behaviour of the materials. The activation energies calculated by the dc conductivity measurement and the I–V characteristics indicate that both the materials show semiconducting behaviour. Thermal analysis has been used to check the high temperature phase transition and thermal stability of the materials. The room temperature FTIR spectra measured in the fingerprint region (750 cm−1 to 400 cm−1) explains the molecular symmetry of the materials. All the results have been discussed in detail.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Han, Y. Ma, C. Quan, N. Gao, Q. Zhang, W. Mao, W. Huang, Substitution-driven structural, optical and magnetic transformation of Mn, Zn doped BiFeO3. Ceram. Int. 41(2), 2476–2483 (2015)
A.S. Bhalla, R. Guo, R. Roy, The perovskite structure—a review of its role in ceramic science and technology. Mater. Res. Innov. 4(1), 3–26 (2000)
R. Chakraborty, S. Mukherjee, S. Mukherjee, Effect of zinc do** on phase evolution and characterization of nanocrystalline bismuth ferrite synthesized by chemical solution route. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 53(1), 57–65 (2017)
W. Eerenstein, M. Wiora, J.L. Prieto, J.F. Scott, N.D. Mathur, Giant sharp and persistent converse magnetoelectric effects in multiferroic epitaxial heterostructures. Nat. Mater. 6(5), 348–351 (2007)
N.A. Spaldin, M. Fiebig, The renaissance of magnetoelectric multiferroics. Science 309(5733), 391–392 (2005)
P. Bongurala, V. Gorige, Structural, magnetic and electric properties of multiferroic NiFe2O4–BaTiO3 composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 477, 350–355 (2019)
A. Testino, L. Mitoseriu, V. Buscaglia, M.T. Buscaglia, I. Pallecchi, A.S. Albuquerque, P. Nanni, Preparation of multiferroic composites of BaTiO3–Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26(14), 3031–3036 (2006)
B. Sarkar, B. Dalal, V. Dev Ashok, K. Chakrabarti, A. Mitra, S.K. De, Magnetic properties of mixed spinel BaTiO3–NiFe2O4 composites. J. Appl. Phys. 115(12), 123908 (2014)
M. Khan, A. Mishra, J. Shukla, P. Sharma, Structural, optical and electrical properties of BaTiO3–NiFe2O4 based multifunctional composites, in AIP Conference Proceedings 2142(1), 160012-1–160012-5 (2019)
N.A. Benedek, C.J. Fennie, Why are there so few perovskite ferroelectrics? J. Phys. Chem. C 117(26), 13339–13349 (2013)
L.H. Yin, Y.P. Sun, F.H. Zhang, W.B. Wu, X. Luo, X.B. Zhu, R.L. Zhang, Magnetic and electrical properties of Bi0.8Ca0.2Fe1−xMnxO3. J. Alloys Compd. 488(1), 254–259 (2009)
C. Ederer, N.A. Spaldin, Weak ferromagnetism and magnetoelectric coupling in bismuth ferrite. Phys. Rev. B 71(6), 060401 (2005)
H. Wadati, J. Okamoto, M. Garganourakis, V. Scagnoli, U. Staub, Y. Yamasaki, M. Kawasaki, Origin of the large polarization in multiferroic YMnO3 thin films revealed by soft-and hard-X-ray diffraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(4), 047203 (2012)
W. Eerenstein, N.D. Mathur, J.F. Scott, Multiferroic and Magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442(7104), 759–765 (2006)
V. K. Jha, M. Roy, S. N. Alam, Experimental studies of structural, electrical and thermal properties of multifunctional BiFeO3 ceramic, in AIP Conference Proceedings 2104(1), 020020(1–5) (2019).
M. Valant, A.K. Axelsson, N. Alford, Peculiarities of a solid-state synthesis of multiferroic polycrystalline BiFeO3. Chem. Mater. 19(22), 5431–5436 (2007)
Z. Chen, J. Hu, Z. Lu, X. He, Low-temperature preparation of lanthanum-doped BiFeO3 crystallites by a sol–gel-hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 37(7), 2359–2364 (2011)
F. Bhadala, L. Suthar, M. Roy, Structural, dielectric and thermal properties of 0.25BFO-0.75CTO composite, in AIP Conference Proceedings 2100(1), 020144(1–6) (2019).
M. Roy, S. Jangid, S.K. Barbar, P. Dave, Electrical and magnetic properties of BiFeO3 multiferroic ceramics. J. Magn. 14(2), 62–65 (2009)
Q. Xu, H. Zai, D. Wu, Y.K. Tang, M.X. Xu, The magnetic properties of BiFeO3 and Bi(Fe0.95Zn0.05)O3. J. Alloys Compd. 485(1–2), 13–16 (2009)
F. Bhadala, L. Suthar, M. Roy, V. K. Jha, Dielectric and transport properties of CaTiO3, in AIP Conference Proceedings 1953(1), 050028-1–050028-6 (2018)
L. Suthar, V.K. Jha, F. Bhadala, M. Roy, S. Sahu, S.K. Barbar, Studies on structural, electrical, thermal and magnetic properties of YFeO3 ceramic. Appl. Phys. A 123(10), 668 (2017)
F. Bhadala, L. Suthar, M. Roy, Study of structural, dielectric and optical properties of zinc doped bismuth ferrite, in AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2220, no. 1 (2020), pp. 040026-1–040026-6
Y. Yoneda, Y. Kitanaka, Y. Noguchi, M. Miyayama, Electronic and local structures of Mn-doped BiFeO3 crystals. Phys. Rev. B 86(18), 184112 (2012)
F. Bhadala, V.K. Jha, L. Suthar, M. Roy, Synthesis, structural, electrical and thermal properties of ScFeO3 ceramic. Am. J. Mod. Phys. 6(6), 132–139 (2017)
H. Bouaamlat, N. Hadi, N. Belghiti, H. Sadki, M. Naciri Bennani, F. Abdi, M. Abarkan, Dielectric properties, AC conductivity, and electric modulus analysis of bulk ethylcarbazole-terphenyl. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 8689150(1-8) (2020)
W. Cao, R. Gerhardt, Calculation of various relaxation times and conductivity for a single dielectric relaxation process. Solid State Ionics 42(3–4), 213–221 (1990)
R. Singh, R.P. Tandon, V.S. Panwar, S. Chandra, Low-frequency ac conduction in lightly doped polypyrrole films. J. Appl. Phys. 69(4), 2504–2511 (1991)
J. M. Stevels, The electrical properties of glass, in Electrical Conductivity II/Elektrische Leitungsphänomene II (Springer, Berlin, 1957), pp. 350–391.
T.T. Fang, C.P. Liu, Evidence of the internal domains for inducing the anomalously high dielectric constant of CaCu3Ti4O12. Chem. Mater. 17(20), 5167–5171 (2005)
C. Yang, C.Z. Liu, C.M. Wang, W.G. Zhang, J.S. Jiang, Magnetic and dielectric properties of alkaline earth Ca2+ and Ba2+ ions co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(8), 1483–1487 (2012)
M. Arshad, W. Khan, M. Abushad, M. Nadeem, S. Husain, A. Ansari, V.K. Chakradhary, Correlation between structure, dielectric and multiferroic properties of lead free Ni modified BaTiO3 solid solution. Ceram. Int. 46(17), 27336–27351 (2020)
W.K. Lee, J.F. Liu, A.S. Nowick, Limiting behavior of ac conductivity in ionically conducting crystals and glasses: a new universality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(12), 1559 (1991)
M.T. Rahman, C.V. Ramana, Impedance spectroscopic characterization of gadolinium substituted cobalt ferrite ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 116(16), 164108 (2014)
M.R. Biswal, J. Nanda, N.C. Mishra, S. Anwar, A. Mishra, Dielectric and impedance spectroscopic studies of multiferroic BiFe1−xNixO3. Adv. Mater. Lett. 5(9), 531–537 (2014)
H. Singh, A. Kumar, K.L. Yadav, Structural, dielectric, magnetic, magnetodielectric and impedance spectroscopic studies of multiferroic BiFeO3–BaTiO3 ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176(7), 540–547 (2011)
K. Abraham, A.K. Thomas, J. Thomas, K.V. Saban, Steady nature of dielectric behaviour in Sm1.5Sr0.5NiO4–CCTO composites. Mod. Electron. Mater. 5(4), 145–150 (2019)
F. Tian, Y. Ohki, Electric modulus powerful tool for analyzing dielectric behavior. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21(3), 929–931 (2014)
S.K. Tripathi, A. Gupta, M. Kumari, Studies on electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of PVdF–HFP–PMMA–NaI polymer blend electrolyte. Bull. Mater. Sci. 35(6), 969–975 (2012)
R.K. Mishra, D.K. Pradhan, R.N.P. Choudhary, A. Banerjee, Effect of yttrium on improvement of dielectric properties and magnetic switching behavior in BiFeO3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 20(4), 045218 (2008)
S. Hajra, S. Sahoo, T. Mishra, P.K. Rout, R.N.P. Choudhary, Studies of dielectric and electrical transport characteristics of BaTiO3–BiFeO3–CaSnO3 ternary system. Process. Appl. Ceram. 12(2), 164–170 (2018)
S. Sahoo, S. Hajra, M. De, R.N.P. Choudhary, Resistive, capacitive and conducting properties of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–BaTiO3 solid solution. Ceram. Int. 44(5), 4719–4726 (2018)
H. Matsuo, Y. Noguchi, M. Miyayama, Gap-state engineering of visible-light-active ferroelectrics for photovoltaic applications. Nat. Commun. 8(1), 1–8 (2017)
F. Bhadala, L. Suthar, P. Kumari, M. Roy, Rietveld refinement, morphological, vibrational, Raman, optical and electrical properties of Ca/Mn co-doped BiFeO3. Mater. Chem. Phys. 247(1–9), 122719 (2020)
A. Sasmal, S. Sen, P.S. Devi, Significantly suppressed leakage current and reduced band gap of BiFeO3 through Ba–Zr co-substitution: structural, optical, electrical and magnetic study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 254(1–26), 123362 (2020)
L. Suthar, F. Bhadala, M. Roy, The impact of Bi3+ substitution for Y3+ cation on structural, topographical, electrical and thermal behaviour of YFeO3. Ceram. Int. 45(16), 20891–20899 (2019)
L. Suthar, V.K. Jha, F. Bhadala, M. Roy, Synthesis, electrical and IR spectroscopy of calcium substituted yttrium ferrite ceramics. Mater. Today Proc. 26, 3353–3356 (2020)
H. Singh, K.L. Yadav, Structural, dielectric, vibrational and magnetic properties of Sm doped BiFeO3 multiferroic ceramics prepared by a rapid liquid phase sintering method. Ceram. Int. 41(8), 9285–9295 (2015)
Acknowledgement
FB is thankful to UGC for providing NET-JRF fellowship. LS is thankful for BSR fellowship. We are also thankful to Prof. N. Lakshmi, Prof. S. Kumar, Prof. M.S. Dhaka and Dr. P.K. Baroliya in hel** us in XRD, AFM, I-V and FTIR measurements, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhadala, F., Suthar, L. & Roy, M. Sequel of divalent zinc substitution on structural, electrical and thermal properties of bismuth ferrite ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 127, 320 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04383-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04383-2