Abstract
Objectives
To compare the efficacy and safety of localization of small pulmonary nodules with microcoil and hookwire prior to surgical resection.
Methods
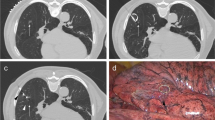
A total of 112 patients who underwent preoperative computed tomography (CT)-guided localization of small pulmonary nodules were enrolled in this single-center retrospective non-randomized cohort study between June 2016 and June 2017. Seventy-nine patients who underwent percutaneous localization with microcoils formed the microcoil group; the remaining 33 patients underwent percutaneous localization with hookwires (hookwire group). The primary outcomes were the success and complication rates of the procedure. Student’s t test was used for continuous variables, whereas chi-square analysis and logistic regression were used for dichotomous variables.
Results
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) was successfully performed in all cases, without conversion to thoracotomy. The localization success rate was 94.9% (75/79) in the microcoil group and 93.9% (31/33) in the hookwire group (p = 0.836). Hookwire group (p = 0.000) and nodule location of the lower lobe (p = 0.012) were associated with an increased incidence of pneumothorax. Hookwire group (p = 0.027) and decreased nodule diameter (p = 0.024) were associated with an increased incidence of moderate to severe chest pain, as well as an increased incidence of overall complications.
Conclusions
Although the deployment of the microcoil was more complex and required more time than hookwire placement, microcoil localization was associated with fewer complications.
Key Points
• CT-guided percutaneous localization using a microcoil and that using a hookwire are equally effective for localizing small pulmonary nodules prior to resection with video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery.
• Lung nodule localization using a microcoil was associated with fewer complications than localization using a hookwire.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- VATS:
-
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery
References
Gould MK, Tang T, Liu IL et al (2015) Recent trends in the identification of incidental pulmonary nodules. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 192:1208–1214
Rivera MP, Mahta AC, Wahidi MM (2013) Establishing the diagnosis of lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 143:142–165
Suzuki K, Nagai K, Yoshida J et al (1999) Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for small indeterminate pulmonary nodules: indications for preoperative marking. Chest 115:563–568
Kondo R, Yoshida K, Hamanaka K et al (2009) Intraoperative ultrasonographic localization of pulmonary ground-glass opacities. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 138:837–842
Su TH, Fan YF, ** L, He W, Hu LB (2015) CT-guided localization of small pulmonary nodules using adjacent microcoil implantation prior to video-assisted thoracoscopic surgical resection. Eur Radiol 25:2627–2633
Park CH, Han K, Hur J et al (2017) Comparative effectiveness and safety of preoperative lung localization for pulmonary nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest 151:316–328
Mack MJ, Gordon MJ, Postma TW et al (1992) Percutaneous localization of pulmonary nodules for thoracoscopic lung resection. Ann Thorac Surg 53:1123–1124
Powell TI, Jangra D, Clifton JC et al (2004) Peripheral lung nodules: fluoroscopically guided video-assisted thoracoscopic resection after computed tomography-guided localization using platinum microcoils. Ann Surg 240:481–489
Lenglinger FX, Schwarz CD, Artmann W (1994) Localization of pulmonary nodules before thoracoscopic surgery: value of percutaneous staining with methylene blue. AJR Am J Roentgenol 163:297–300
Moon SW, Wang YP, Jo KH et al (1999) Fluoroscopy-aided thoracoscopic resection of pulmonary nodule localized with contrast media. Ann Thorac Surg 68:1815–1820
Watanabe K, Nomori H, Ohtsuka T, Kaji M, Naruke T, Suemasu K (2006) Usefulness and complications of computed tomography-guided lipiodol marking for fluoroscopy-assisted thoracoscopic resection of small pulmonary nodules: experience with 174 nodules. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 132:320–324
Chella A, Lucchi M, Ambrogi MC et al (2000) A pilot study of the role of TC-99 radionuclide in localization of pulmonary nodular lesions for thoracoscopic resection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 18:17–21
Gonfiotti A, Davini F, Vaggelli L et al (2007) Thoracoscopic localization techniques for patients with solitary pulmonary nodule: hookwire versus radio-guided surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 32:843–847
Kleedehn M, Kim DH, Lee FT et al (2016) Preoperative pulmonary nodule localization: a comparison of methylene blue and hookwire techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol 207:1334–1339
Caraceni A, Cherny N, Fainsinger R et al (2002) Pain measurement tools and methods in clinical research in palliative care: recommendations of an Expert Working Group of the European Association of Palliative Care. J Pain Symptom Manage 2002:239–255
Mayo JR, Clifton JC, Powell TI et al (2009) Lung nodules: CT-guided placement of microcoils to direct video-assisted thoracoscopic surgical resection. Radiology 250:576–585
Miyoshi K, Toyooka S, Gobara H et al (2009) Clinical outcomes of short hook wire and suture marking system in thoracoscopic resection for pulmonary nodules. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 36:378–382
Seo JM, Lee HY, Kim HK et al (2012) Factors determining successful computed tomography-guided localization of lung nodules. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 143:809–814
Omary RA, Bettmann MA, Cardella JF et al (2002) Quality improvement guidelines for the reporting and archiving of interventional radiology procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:879–881
Gagliano RA Jr, Reinschmidt JP, Murray SP, Casha LM, Tracy D, Collins GJ (1999) A novel method of transthoracic lung nodule localization. Curr Surg 56:410–412
Thaete FL, Peterson MS, Plunkett MB, Ferson PF, Keenan RJ, Landreneau RJ (1999) Computed tomography-guided wire localization of pulmonary lesions before thoracoscopic resection: results in 101 cases. J Thorac Imaging 14:90–98
Mullan BF, Stanford W, Barnhart W, Galvin JR (1999) Lung nodules: improved wire for CT-guided localization. Radiology 21:561–565
Dendo S, Kanazawa S, Ando A et al (2002) Preoperative localization of small pulmonary lesions with a short hook wire and suture system: experience with 168 procedures. Radiology 225:511–518
Ichinose J, Kohno T, Fujimori S, Harano T, Suzuki S (2013) Efficacy and complications of computed tomography-guided hook wire localization. Ann Thorac Surg 96:1203–1028
Hanauer M, Perentes JY, Krueger T et al (2016) Pre-operative localization of solitary pulmonary nodules with computed tomography-guided hook wire: report of 181 patients. J Cardiothorac Surg 11:1–7
Kha LC, Hanneman K, Donahoe L et al (2016) Safety and efficacy of modified preoperative lung nodule microcoil localization without pleural marking: a pilot study. J Thorac Imaging 31:15–22
Sharma A, McDermott S, Mathisen DJ, Shepard JO (2017) Preoperative localization of lung nodules with fiducial markers: feasibility and technical considerations. Ann Thorac Surg 103:1114–1120
Bolton WD, Howe H 3rd, Stephenson JE (2014) The utility of electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy as a localization tool for robotic resection of small pulmonary nodules. Ann Thorac Surg 98:471–476
Abbas A, Kadakia S, Ambur V, Muro K, Kaiser L (2017) Intraoperative electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopic localization of small, deep, or subsolid pulmonary nodules. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 153:1581–1590
Greenfield AL, Steiner RM, Liu JB et al (1997) Sonographic guidance for the localization of peripheral pulmonary nodules during thoracoscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:1057–1060
Wada H, Anayama T, Hirohashi K et al (2015) Thoracoscopic ultrasonography for localization of subcentimetre lung nodules. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 49:690–697
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Jian Gao.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Statistics and biometry
Huixin Liu (Department of Clinical Epidemiology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Bei**g, China), PhD, provided statistical advice for this study, and she is one of the authors.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• observational
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Gao, J., Chen, C. et al. Comparison between the application of microcoil and hookwire for localizing pulmonary nodules. Eur Radiol 29, 4036–4043 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5939-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5939-4