Abstract
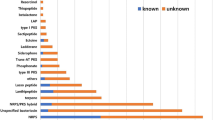
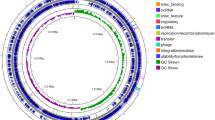
The increased prevalence of multidrug-resistant pathogens poses a significant clinical threat, and hence, the discovery of novel antibiotics is the need of the hour. Several attempts are being made worldwide to screen and identify newer antibiotics from various microbial sources. The genus Paenibacillus is known for its biosynthetic potential and metabolic versatility in producing several secondary metabolites. In this study, we isolated Paenibacillus alvei strain JR949 from the soil, which exhibited antimicrobial activity against Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The whole genome of this strain was sequenced using the Illumina platform. The genome mining of the draft genome sequence revealed a total of 31 biological gene clusters (BGCs) responsible for the synthesis of secondary metabolites. The construction of the similarity network of the BGCs and the comparative analysis with the genetically related strains aided the identification of metabolites produced by this strain. We identified BGCs coding for paenibactin, paenibacterin, anabaenopeptin NZ857, icosalide A/B, polymyxin, and bicornutinA1/A2 with 100% similarity. The BGCs with lower sequence similarity to paenibacterin, polymyxin B, colistin A/B, pellasoren, tridecaptin, pelgipeptin, and marthiapeptide were also identified. Furthermore, 13 putative NRPS BGCs, 3 NRPS-T1PKS hybrid clusters, a T1PKS, and a bacteriocin BGC were identified with very low similarity (≤ 25%) or no similarity with known antibiotics. Further experimental investigations may result in the discovery of novel antimicrobial drugs.




source genomes and the node shapes indicate the biosynthetic classes

Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’neill J (2016) Review on antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations, 2014. HM Government, London
World Health Organization (2001) WHO global strategy for containment of antimicrobial resistance (No. WHO/CDS/CSR/DRS/2001.2). World Health Organization, Geneva
Priest FG, Goodfellow M, Todd C (1988) A numerical classification of the genus Bacillus. J Gen Microbiol 134:1847–1882. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-134-7-1847
Grady EN, MacDonald J, Liu L, Richman A, Yuan ZC (2016) Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: a review. Microb Cell Fact 15:203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0603-7
Cochrane SA, Vederas JC (2016) Lipopeptides from Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp.: a gold mine of antibiotic candidates. Med Res Rev 36:4–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21321
He Z, Kisla D, Zhang L, Yuan C, Green-Church KB, Yousef AE (2007) Isolation and identification of a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain that coproduces a novel lantibiotic and polymyxin. Appl Environ Microb 73:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02023-06
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Jolley KA, Bliss CM, Bennett JS, Bratcher HB, Brehony C et al (2012) Ribosomal multilocus sequence ty**: universal characterization of bacteria from domain to strain. Microbiology (Reading) 158:1005–1015. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.055459-0
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Vallenet D, Calteau A, Dubois M, Amours P, Bazin A et al (2020) MicroScope: an integrated platform for the annotation and exploration of microbial gene functions through genomic, pangenomic and metabolic comparative analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 48:579–589. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz926
Zhang H, Yohe T, Huang L, Entwistle S, Wu P et al (2018) dbCAN2: a meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 46:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky418
Blin K, Shaw S, Steinke K, Villebro R, Ziemert N et al (2019) antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 47:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz310
Anand S, Prasad MVR, Yadav G, Kumar N, Shehara J et al (2010) SBSPKS: structure based sequence analysis of polyketide synthases. Nucleic Acids Res 38:487–496. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq340
Kautsar SA, Blin K, Shaw S, Navarro-Muñoz JC, Terlouw BR et al (2020) MIBiG 2.0: a repository for biosynthetic gene clusters of known function. Nucleic Acids Res 48:454–458. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz882
Navarro-Muñoz JC, Selem-Mojica N, Mullowney MW, Kautsar SA, Tryon JH et al (2020) A computational framework to explore large-scale biosynthetic diversity. Nat Chem Biol 16:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0400-9
Gu Z, Gu L, Eils R, Schlesner M, Brors B (2014) Circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 30:2811–2812. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu393
Csizmadia P (1999) Marvinsketch and marvinview: molecule applets for the world wide web. http://www.chemaxon.com
Bionda N, Pitteloud JP, Cudic P (2013) Cyclic lipodepsipeptides: a new class of antibacterial agents in the battle against resistant bacteria. Future Med Chem 5:1311–1330. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.13.86
Huang E, Yousef AE (2014) Paenibacterin, a novel broad-spectrum lipopeptide antibiotic, neutralises endotoxins and promotes survival in a murine model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced sepsis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 44:74–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.02.018
Olishevska S, Nickzad A, Déziel E (2019) Bacillus and Paenibacillus secreted polyketides and peptides involved in controlling human and plant pathogens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:1189–1215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9541-0
Li J, Nation RL, Turnidge JD, Milne RW, Coulthard K et al (2006) Colistin: the re emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect Dis 6:589–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70580-1
Qian CD, Liu TZ, Zhou SL, Ding R, Zhao WP et al (2012) Identification and functional analysis of gene cluster involvement in biosynthesis of the cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic pelgipeptin produced by Paenibacillus elgii. BMC Microbiol 12:197. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-197
Jangra M, Kaur M, Tambat R, Rana R, Maurya SK et al (2019) Tridecaptin M, a new variant discovered in mud bacterium, shows activity against colistin- and extremely drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63:e00338-e419. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00338-19
Zhou X, Huang H, Chen Y, Tan J, Song Y et al (2012) Marthiapeptide A, an anti-infective and cytotoxic polythiazole cyclopeptide from a 60 L scale fermentation of the deep sea-derived Marinactinospora thermotolerans SCSIO 00652. J Nat Prod 75:2251–2255. https://doi.org/10.1021/np300554f
Boros C, Smith CJ, Vasina Y, Che Y, Dix AB et al (2006) Isolation and Identification of the Icosalides-cyclic peptolides with selective antibiotic and cytotoxic activities. J Antibiot 59:486–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2006.68
Johnson BA, Anker H, Meleney FL (1945) Bacitracin: a new antibiotic produced by a member of the Bacillus subtilis group. Science 102:376–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.102.2650.376
Swierstra J, Kapoerchan V, Knijnenburg A, van Belkum A, Overhand M (2016) Structure, toxicity and antibiotic activity of gramicidin S and derivatives. Eur J Clin Microbiol 35:763–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2595-y
Wenzel M, Rautenbach M, Vosloo JA, Siersma T, Aisenbrey CHM et al (2018) The multifaceted antibacterial mechanisms of the pioneering peptide antibiotics tyrocidine and gramicidin S. mBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00802-18
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the UGC-NRCBS, DBT-IPLS, DST-PURSE, and DST-FIIST Programs of the School of Biological Sciences, Madurai Kamaraj University.
Funding
Madurai Kamaraj University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JR, RS, and RK: designed the experiments. PSP, BM, RS: performed experiments. PSP and JR: wrote the experiment. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pranav, P.S., Mahalakshmi, B., Sivakumar, R. et al. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of Paenibacillus alvei JR949 Revealed Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Coding for Novel Antimicrobials. Curr Microbiol 78, 1168–1176 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02393-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02393-0