Abstract
Background
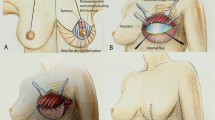
Nipple reconstruction in implant-based breast reconstruction remains challenging, as the remaining thin skin envelope results in a less projected neo-nipple with a reduced volume. This study presents a modified top-hat flap technique with rolled dermal grafts from the dog-ears of lateral wings for augmenting reconstructed nipples during implant-based breast reconstruction.
Methods
Between April 2011 and December 2014, among 34 patients who underwent immediate post-mastectomy reconstruction with a direct silicone implant, nipple reconstruction was performed using the modified top-hat flap technique in only 21 patients (group A), whereas 13 patients underwent the modified top-hat flap technique with rolled dermal grafts from the dog-ears of lateral wings (group B). The projection and width of the neo-nipple were measured at the time of surgery and at 1 year post-surgery, respectively.
Results
All modified top-hat flaps were successful without any complications. The mean nipple projections at the time of surgery were 0.75 ± 0.107 cm (range 0.5–0.9 cm) and 1.29 ± 0.064 cm (range 1.2–1.4 cm) in groups A and B, respectively (p < 0.001). The mean nipple widths at the time of surgery were 0.90 ± 0.184 cm (range 0.6–1.2 cm) and 1.43 ± 0.076 cm (range 1.3–1.5 cm) in groups A and B, respectively (p < 0.001). The maintenance of nipple projection and width was significantly increased in group B compared with group A.
Conclusion
The modified top-hat flap technique with rolled dermal grafts from the dog-ears of lateral wings is a useful and easy method to expand and augment the volume of reconstructed nipples in implant-based breast reconstruction.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Losken A, Mackay GJ, Bostwick J 3rd (2001) Nipple reconstruction using the C-V flap technique: a long-term evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg 108:361–369
Cheng MH, Rodriguez ED, Smartt JM, Cardenas-Mejia A (2007) Nipple reconstruction using the modified top hat flap with banked costal cartilage graft: long-term follow-up in 58 patients. Ann Plast Surg 59:621–628
Chia HL, Wong M, Tan BK (2014) Nipple reconstruction with rolled dermal graft support. Arch Plast Surg 41:158–162
Jabor MA, Shayani P, Collins DR Jr, Karas T, Cohen BE (2002) Nipple-areola reconstruction: satisfaction and clinical determinants. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:457–463 (discussion 64-65)
Wellisch DK, Schain WS, Noone RB, Little JW 3rd (1987) The psychological contribution of nipple addition in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 80:699–704
Nahabedian MY (2007) Nipple reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 34:131–137 (abstract vii)
Hammond DC, Khuthaila D, Kim J (2007) The skate flap purse-string technique for nipple-areola complex reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:399–406
Eskenazi L (1993) A one-stage nipple reconstruction with the “modified star” flap and immediate tattoo: a review of 100 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 92:671–680
Eng JS (1996) Bell flap nipple reconstruction—a new wrinkle. Ann Plast Surg 36:485–488
Guerra AB, Khoobehi K, Metzinger SE, Allen RJ (2003) New technique for nipple areola reconstruction: arrow flap and rib cartilage graft for long-lasting nipple projection. Ann Plast Surg 50:31–37
Cheng MH, Ho-Asjoe M, Wei FC, Chuang DC (2003) Nipple reconstruction in Asian females using banked cartilage graft and modified top hat flap. Br J Plast Surg 56:692–694
Elizabeth Clark S, Turton E (2014) The CC-V flap: a novel technique for augmenting a C-V nipple reconstruction using a free dermal graft. World J Plast Surg 3:8–12
El-Ali K, Dalal M, Kat CC (2009) Modified C-V flap for nipple reconstruction: our results in 50 patients. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62:991–996
Banducci DR, Le TK, Hughes KC (1999) Long-term follow-up of a modified Anton–Hartrampf nipple reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 43:467–469 (discussion 9-70)
Few JW, Marcus JR, Casas LA, Aitken ME, Redding J (1999) Long-term predictable nipple projection following reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1321–1324
Shestak KC, Gabriel A, Landecker A, Peters S, Shestak A, Kim J (2002) Assessment of long-term nipple projection: a comparison of three techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:780–786
Kroll SS (1999) Nipple reconstruction with the double-opposing tab flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:511–514 (discussion 5-7)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All examinations and procedures in the present study have been approved by our institutional ethics committee (UUH 2016-01-003-002) and have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Kim, S.I., Ha, W. et al. Augmentation of the Nipples Reconstructed with Modified Top-Hat Flap Using Dermal Grafts in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Comparative Study. Aesth Plast Surg 41, 800–805 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0806-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0806-2