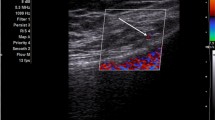
Abstract
Objective
Intra-articular steroid injection has been widely used in the management of symptomatic osteoarthritis; however, its frequent use is avoided since there is an increase in the incidence of articular infection and several mechanical side effects such as cartilage breakdown and loss of elasticity of the articular cartilage. For these reasons, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs instead of corticosteroids can be considered for intra-articular injection. On this basis, we investigated the effects and safety of ultrasound-guided intra-articular ketorolac versus corticosteroid injection for patients with osteoarthritis of the hip.
Materials and methods
This retrospective study included 98 patients with diagnoses of hip osteoarthritis who underwent ultrasound-guided intra-articular ketorolac or corticosteroid injection. Fifty patients who received ultrasound-guided intra-articular corticosteroid injection were administered a mixture of 0.5 % lidocaine and triamcinolone. Forty-eight patients who received ultrasound-guided intra-articular ketorolac injection were administered 0.5 % lidocaine and ketorolac. Outcome measurement was assessed using the Harris hip score and verbal numeric pain scale, which were evaluated before the injections and at 1, 3 and 6 months following the injection. Univariate analysis (using the x 2 test) and multiple logistic regression analysis were performed to evaluate the relationship between the possible outcome predictors (injected medications, patients’ age, gender, pain duration and Kellgren-Lawrence classification) and the therapeutic effects.
Results
The Harris hip score and verbal numeric pain scale were improved at 1, 3 and 6 months after the injection in both groups. No statistical differences in the Harris hip score and verbal numeric pain scale were observed between the groups. The success rate was also not significantly different among the time periods of 1, 3 and 6 months. Multiple logistic regression and univariate analysis showed that injected medications patients’ age, gender, pain duration and Kellgren-Lawrence classification were not independent predictors of successful outcome at midterm follow-up.
Conclusion
The treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip with intra-articular ketorolac injection is as effective as that with intra-articular corticosteroid injection. Intra-articular ketorolac injection can be considered useful for patients with contraindications to using corticosteroids.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oliveria SA, Felson DT, Reed JI, Cirillo PA, Walker AM. Incidence of symptomatic hand, hip and knee osteoarthritis among patients in health maintenance organizations. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1134–41.
Wilson MG, Michet CJ, Ilstrup DM, Melton LJ. Idiopathic osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. A population-based incidence study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1990;65:1214–21.
Conrozier T, Chappuis-Cellier C, Richard M, Mathieu P, Richard S, Vignon E. Increased serum C-reactive protein levels by immunonephelometry in patients with rapidly destructive hip osteoarthritis. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1998;65:759–65.
Spector TD, Hart DJ, Nandra D, et al. Low-level increases in serum C-reactive protein are present in early osteoarthritis of the knee and predict progressive disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:723–7.
Braun HJ, Wilcox-Fogel N, Kim HJ, Pouliot MA, Harris AH, Dragoo JL. The effect of local anesthetic and corticosteroid combinations on chondrocyte viability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(9):1689–95.
Qvistgaard E, Christensen R, Torp-Pedersen S, Bliddal H. Intra-articular treatment of hip osteoarthritis: a randomized trial of hyaluronic acid, corticosteroid, and isotonic saline. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2006;14:163–70.
Meenagh G, Filippucci E, Iagnocco A, Delle Sedie A, Riente L, Bombardieri S, et al. Ultrasound imaging in osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25:172–5.
Desai A, Ramankutty S, Board T, Raut V. Intraarticular steroid infiltration increase the rate of infection in subsequent total knee replacements? Knee. 2009;16:262–4.
Jones AC, Pattrick M, Doherty S, Doherty M. Intraarticular hyaluronic acid compared to intraarticular triamcinolone hexacetonide in inflammatory knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 1995;3:269–73.
Unlu Z, Ay K, Tuzun C. Comparison of intra-articular tenoxicam and oral tenoxicam for pain and physical functioning in osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25(1):54–61.
Suominen MM, Tulamo RM, Anttila MO, et al. Effects of intra-articular injections of bufexamac suspension in healthy horses. Am J Vet Res. 2001;62:1629–35.
Shapiro PS, Rohde RS, Froimson MI, et al. The effect of local corticosteroid or ketorolac exposure on histologic and biomechanical properties of rabbit tendon and cartilage. Hand (New York). 2007;2:165–72.
Riggin CN, Tucker JJ, Soslowsky LJ, Kuntz AF. Intra-articular tibiofemoral injection of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug has no detrimental effects on joint mechanics in a rat model. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(11):1512–9.
Galán-Herrera JF, Poo JL, Maya-Barrios JA, de Lago A, Oliva I, González-de la Parra M, et al. Bioavailability of two sublingual formulations of ketorolac tromethamine 30 mg: a randomized, open-label, single-dose, two-period crossover comparison in healthy Mexican adult volunteers. Clin Ther. 2008;30:1667–74.
Calmet J, Esteve C, Boada S, Giné J. Analgesic effect of intraarticular ketorolac in knee arthroscopy: comparison of morphine and bupivacaine. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2004;12:552–5.
Dogan N, Erdem AF, Gundogdu C, Kursad H, Kizilkaya M. The effects of ketorolac and morphine on articular cartilage and synovium in the rabbit knee joint. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004;82:502–5.
Bianchi S, Zamorani MP. US-guided interventional procedures. In: Bianchi S, Martinoli C, editors. Ultrasound of the musculoskeletal system. 1st ed. Berlin: Springer; 2007. p. 891–917.
Diraçoğlu D, Alptekin K, Dikici F, Balci HI, Ozçakar L, Aksoy C. Evaluation of needle positioning during blind intra-articular hip injections for osteoarthritis: fluoroscopy versus arthrography. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;90:2112–5.
Margules KR. Fluoroscopically directed steroid instillation in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis: safety and efficacy in 510 cases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2449–50.
Plant MJ, Borg AA, Dziedzic K, Saklatvala J, Dawes PT. Radiographic patterns and responses to corticoid hip injections. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997;56:476–80.
Qvistgaard E, Kristoffersen H, Terslev L, Danneskiold-Samsøe B, Torp-Pedersen S, Bliddal H. Guidance by ultrasound of intra-articular injections in the knee and hip joints. Ostoarthr Cartil. 2001;9:512–7.
Caglar-Yagci H, Unsal S, Yagci I, Dulgeroglu D, Ozel S. Safety and efficacy of ultrasound guided intra-articular hylan G-F 20 injection in osteoarthritis of the hip: a pilotstudy. Rheumatol Int. 2005;25:341–4.
Migliore A, Martin LS, Alimonti A, Valenti C, Tormenta S. Efficacy and safety of viscosupplementation by ultrasound guided intra-articular injection in osteoarthritis of the hip. Ostoarthr Cartil. 2003;11:305–6.
Smith J, Hurdle MF, Weingarten TN. Accuracy of sonographically guided intra-articular injections in the native adult hip. J Ultrasound Med. 2009;28:329–35.
Altman R, Alarcón G, Appelrouth D, Bloch D, Borenstein D, Brandt K, et al. The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34:505–14.
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16:494–502.
Mahomed NN, Arndt DC, McGrory BJ, Harris WH. The Harris hip score: comparison of patient self-report with surgeon assessment. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16:575–80.
Garellick G, Malchau H, Herberts P. Specific or general health outcome measures in the evaluation of total hip replacement. A comparison between the Harris hip score and the Nottingham Health Profile. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 1998;80:600–6.
Hartrick CT, Kovan JP, Shapiro S. The numeric rating scale for clinical pain measurement: a ratio measure? Pain Pract. 2003;3:310–6.
Kili S, Wright I, Jones RS. Change in Harris hip score in patients on the waiting list for total hip replacement. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2003;85:269–71.
Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:626–34.
Felson DT. Clinical practice. Osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:841–8.
Bonnet CS, Walsh DA. Osteoarthritis, angiogenesis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44:7–16.
Haywood L, McWilliams DF, Pearson CI, et al. Inflammation and angiogenesis in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2173–7.
Ledingham J, Regan M, Jones A, Doherty M. Factors affecting radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995;54:53–8.
Belcher C, Fawthrop F, Bunning R, Doherty M. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in synovial fluids from normal, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis knees. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996;55:230–6.
Kontinnen YT, Kemppinen P, Segerberg M, Hukkanen M, Rees R, Santavirta S. Peripheral and spinal neural mechanisms in arthritis with particular reference to treatment of inflammation and pain. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:965–82.
Creamer P. Intra-articular corticosteroid injections in osteoarthritis: do they work and if so, how? Ann Rheum Dis. 1997;56:634–6.
Hameed F, Ihm J. Injectable medications for osteoarthritis. Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;4:75–81.
Weinstein RS. Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis. Endocrine. 2012;41:183–90.
Reuben SS, Connelly NR. Postoperative analgesia for outpatient arthroscopic knee sugery with intraarticular bupivacaine and ketorolac. Anesth Analg. 1995;80:1154–7.
Min KS, St Pierre P, Ryan PM, Marchant BG, Wilson CJ. Arrington EDA double-blind randomized controlled trial comparing the effects of subacromial injection with corticosteroid versus NSAID in patients with shoulder im**ement syndrome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(5):595–601.
Makela A, Kuusi T, Schroder T. Inhibition of serum phospholipase-A2 in acute pancreatitis by pharmacological agents in vitro. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1997;57:401–7.
Buchbinder R, Green S, Youd JM. Corticosteroid injections for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;1, CD004016. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004016. Review.
Larsen A, Dale K, Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by the standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn. 1977;18:481–91.
Jones A, Doherty M. Intra-articular corticosteroids are effective in osteoarthritis but there are no clinical predictors of response. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996;55:829–32.
Deshmukh AJ, Panagopoulos G, Alizadeh A, Rodriguez JA, Klein DA. Intra-articular hip injection: does pain relief correlate with radiographic severity of osteoarthritis? Skelet Radiol. 2011;40:1449–54.
Migliore A, Massafra U, Bizzi E, Lagana B, Germano V, Piscitelli P, et al. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid (MW 1,500-2,000 kDa; HyalOne) in symptomatic osteoarthritis of the hip: a prospective cohort study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131:1677–88.
Sawyer GA, Anderson BC, Raukar NP, Fadale PD. Intramuscular ketorolac injections in the athlete. Sports Health. 2012;4(4):319–27.
Feldman HI, Kinman JL, Berlin JA, et al. Parenteral ketorolac: the risk for acute renal failure. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126:193–9.
Douketis JD, Berger PB, Dunn AS, et al. The perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 suppl):299S–339.
Strom BL, Berlin JA, Kinman JL, et al. Parenteral ketorolac and risk of gastrointestinal and operative site bleeding: a post marketing surveillance study. JAMA. 1996;275(5):376–82.
Lee SC, Rha DW, Chang WH. Rapid analgesic onset of intra-articular hyaluronic acid with ketorolac in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2011;24(1):31–8.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ki Deok Park and Tai Kon Kim contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, K.D., Kim, T.K., Bae, B.W. et al. Ultrasound guided intra-articular ketorolac versus corticosteroid injection in osteoarthritis of the hip: a retrospective comparative study. Skeletal Radiol 44, 1333–1340 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2174-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2174-9