Abstract
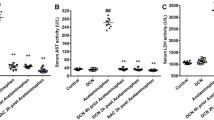
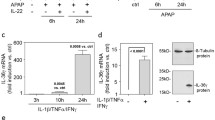
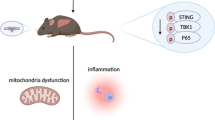
Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose can lead to acute, severe kidney injury, which has recently attracted considerable attention among researchers and clinicians. Unfortunately, there are no well-established treatments for APAP-induced renal injury, and the molecular mechanism of APAP-induced kidney injury is still unclear. Herein, we explored the protective effects of interleukin (IL)-22 on APAP-induced renal injury and the underlying molecular basis. We found that IL-22 could significantly alleviate the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction, reducing APAP-induced renal tubular epithelial cell (TEC) death in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, IL-22 could downregulate the APAP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mature IL-1β release in kidney injury. Additionally, the APAP-mediated upregulation of the serum levels of IL-18, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β was obviously decreased, suggesting IL-22 has inhibitory effects on inflammatory responses. Conclusively, our study demonstrated that IL-22 exerted ameliorative effects on APAP-induced kidney injury by alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction and NLRP3 inflammasome activation, suggesting that IL-22 represents a potential therapeutic approach to treat APAP-induced kidney injury.
Key Points
• IL-22 could ameliorate APAP that triggered oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
• IL-22 could reduce APAP that caused inflammatory responses.

Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad ST, Arjumand W, Nafees S, Seth A, Ali N, Rashid S, Sultana S (2012) Hesperidin alleviates acetaminophen induced toxicity in Wistar rats by abrogation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Toxicol Lett 208:149–161
Athuraliya TN, Jones AL (2009) Prolonged N,acetylcysteine therapy in late acetaminophen poisoning associated with acute liver failure-a need to be more cautious? Crit Care 13:144
Bertolini A, Ferrari A, Ottani A, Guerzoni S, Tacchi R, Leone S (2006) Paracetamol: new vistas of an old drug. CNS Drug Rev 12:250–275
Bessems JG, Vermeulen NP (2001) Paracetamol (acetaminophen)-induced toxicity: molecular and biochemical mechanisms, analogues and protective approaches. Crit Rev Toxicol 31:55–138
Bonavia A, Singbartl K (2018) A review of the role of immune cells in acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol 33:1629–1639
Borghi M, De Luca A, Puccetti M, Jaeger M, Mencacci A, Oikonomou V, Pariano M, Garlanda C, Moretti S, Bartoli A, Sobel J, van de Veerdonk FL, Dinarello CA, Netea MG, Romani L (2015) Pathogenic NLRP3 Inflammasome activity during Candida infection is negatively regulated by IL-22 via activation of NLRC4 and IL-1Ra. Cell Host Microbe 18:198–209
Boutis K, Shannon M (2001) Nephrotoxicity after acute severe acetaminophen poisoning in adolescents. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 39:441–445
Chen W, Zhang X, Fan J, Zai W, Luan J, Li Y, Wang S, Chen Q, Wang Y, Liang Y, Ju D (2017) Tethering interleukin-22 to apolipoprotein A-I ameliorates mice from acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Theranostics 7:4135–4148
Chen Y, ** S, Teng X, Hu Z, Zhang Z, Qiu X, Tian D, Wu Y (2018a) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:6717212
Chen W, Luan J, Wei G, Zhang X, Fan J, Zai W, Wang S, Wang Y, Liang Y, Nan Y, Yin C, Li Y, Liu ML, Ju D (2018b) In vivo hepatocellular expression of interleukin-22 using penetratin-based hybrid nanoparticles as potential anti-hepatitis therapeutics. Biomaterials 187:66–80
Cohen SD, Pumford NR, Khairallah EA, Boekelheide K, Pohl LR, Amouzadeh HR, Hinson JA (1997) Selective protein covalent binding and target organ toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 143:1–12
Eyerich S, Eyerich K, Cavani A, Schmidt-Weber C (2010) IL-17 and IL-22: siblings, not twins. Trends Immunol 31:354–361
Gronke K, Hernández PP, Zimmermann J, Klose CSN, Kofoed-Branzk M, Guendel F, Witkowski M, Tizian C, Amann L, Schumacher F, Glatt H, Triantafyllopoulou A, Diefenbach A (2019) Interleukin-22 protects intestinal stem cells against genotoxic stress. Nature 566:249–253
Hou Q, Ye L, Liu H, Huang L, Yang Q, Turner JR, Yu Q (2018) Lactobacillus accelerates ISCs regeneration to protect the integrity of intestinal mucosa through activation of STAT3 signaling pathway induced by LPLs secretion of IL-22. Cell Death Differ 25:1657–1670
Hua H, Ge X, Wu M, Zhu C, Chen L, Yang G, Zhang Y, Huang S, Zhang A, Jia Z (2018) Rotenone protects against acetaminophen-induced kidney injury by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation. Kidney Blood Press Res 43:1297–1309
Jaeschke H (2018) Mechanisms of sterile inflammation in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Cell Mol Immunol 15:74–75
Kandiş H, Erkan ME, Yildirim U, Güneş H, Erbaş M, Yildirim HA, Gezer S, Kara IH (2011) Comparison of the effects of N-acetyl cysteine and erdosteine in rats with renal injury caused by paracetamol intoxication. Hum Exp Toxicol 30:1350–1358
Lazerow SK, Abdi MS, Lewis JH (2005) Drug-induced liver disease 2004. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 21:283–292
Lin Z, Wu F, Lin S, Pan X, ** L, Lu T, Shi L, Wang Y, Xu A, Li X (2014) Adiponectin protects against acetaminophen-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and acute liver injury by promoting autophagy in mice. J Hepatol 61:825–831
McGill MR, Sharpe MR, Williams CD, Taha M, Curry SC, Jaeschke H (2012) The mechanism underlying acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans and mice involves mitochondrial damage and nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Clin Invest 122:1574–1583
Mizoguchi A (2012) Healing of intestinal inflammation by IL-22. Inflamm Bowel Dis 18:1777–1784
Mulay SR, Anders HJ (2017) Crystal nephropathies: mechanisms of crystal-induced kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol 13:226–240
Ngo VL, Abo H, Maxim E, Harusato A, Geem D, Medina-Contreras O, Merlin D, Gewirtz AT, Nusrat A, Denning TL (2018) A cytokine network involving IL-36γ, IL-23, and IL-22 promotes antimicrobial defense and recovery from intestinal barrier damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E5076–E5085
Nikoopour E, Bellemore SM, Singh B (2015) IL-22, cell regeneration and autoimmunity. Cytokine 74:35–42
Reshi MS, Shrivastava S, Jaswal A, Sinha N, Uthra C, Shukla S (2017) Gold nanoparticles ameliorate acetaminophen induced hepato-renal injury in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 69:231–240
Saito C, Zwingmann C, Jaeschke H (2010) Novel mechanisms of protection against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice by glutathione and N-acetylcysteine. Hepatology 51:246–254
Shan S, Shen Z, Zhang C, Kou R, **e K, Song F (2019) Mitophagy protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biochem Pharmacol 169:113643
Tachiiri A, Imamura R, Wang Y, Fukui M, Umemura M, Suda T (2003) Genomic structure and inducible expression of the IL-22 receptor alpha chain in mice. Genes Immun 4:153–159
Ulinski T, Guigonis V, Dunan O, Bensman A (2004) Acute renal failure after treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Pediatr 163:148–150
Vivoli E, Cappon A, Milani S, Piombanti B, Provenzano A, Novo E, Masi A, Navari N, Narducci R, Mannaioni G, Moneti G, Oliveira CP, Parola M, Marra F (2016) NLRP3 inflammasome as a target of berberine in experimental murine liver injury: interference with P2X7 signalling. Clin Sci 130:1793–1806
Wang S, Li Y, Fan J, Zhang X, Luan J, Bian Q, Ding T, Wang Y, Wang Z, Song P, Cui D, Mei X, Ju D (2017) Interleukin-22 ameliorated renal injury and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Death Dis 8:e2937
Wang S, Fan J, Mei X, Luan J, Li Y, Zhang X, Chen W, Wang Y, Meng G, Ju D (2019) Interleukin-22 attenuated renal tubular injury in aristolochic acid nephropathy via suppressing activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Immunol 10:2277
Wolk K, Sabat R (2006) Interleukin-22: a novel T-cell and NK cell derived cytokine that regulates the biology of tissue cells. Cytokine Factor Rev 17:367–380
Wolk K, Kunz S, Witte E, Friedrich M, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2004) IL-22 increases the innate immunity of tissues. Immunity 21:241–254
Woolbright BL, Jaeschke H (2017) The impact of sterile inflammation in acute liver injury. J Clin Transl Res 3(Suppl 1):170–188
Xu MJ, Feng D, Wang H, Guan Y, Yan X, Gao B (2014) IL-22 ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting proximal tubule epithelium. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:967–977
Yan M, Huo Y, Yin S, Hu H (2018) Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol 17:274–283
Zai W, Chen W, Luan J, Fan J, Zhang X, Wu Z, Ding T, Ju D, Liu H (2018) Dihydroquercetin ameliorated acetaminophen-induced hepatic cytotoxicity via activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway and autophagy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:1443–1453
Zhang C, Feng J, Du J, Zhuo Z, Yang S, Zhang W, Wang W, Zhang S, Iwakura Y, Meng G, Fu YX, Hou B, Tang H (2018) Macrophage-derived IL-1α promotes sterile inflammation in a mouse model of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Cell Mol Immunol 15:973–982
Funding
The study was supported by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (31872746), National Nature Science Foundation of China (81773620), and Scientific Research Projects of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (201740140).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
**aobin Mei and Dianwen Ju designed the study; Yilan Shen, **n **, Wei Chen, Congrong Gao, Qi Bian, Jiajun Fan, and **gyun Luan carried out experiments; Congrong Gao, Zhiyong Guo, Hongrui Liu, and Zhonglian Cao analysed the data; Yilan Shen and Wei Chen drafted and revised the paper; all authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All animal experiments were conducted with the approval of the Ethics Committee of Fudan University School of Pharmacy.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., **, X., Chen, W. et al. Interleukin-22 ameliorated acetaminophen-induced kidney injury by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammatory responses. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 5889–5898 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10638-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10638-4