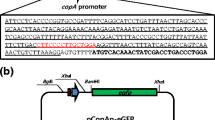
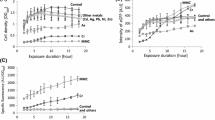
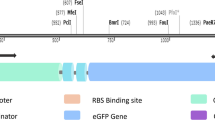
Abstract
Despite the large number of bioreporters developed to date, the ability to detect heavy metal(loid)s with bioreporters has thus far been limited owing to the lack of appropriate genetic systems. We here present a novel approach to modulate the selectivity and sensitivity of microbial whole-cell bioreporters (WCBs) for sensing metal(loid)s via the znt-operon from Escherichia coli, which were applied to quantify the bioavailability of these contaminants in environmental samples. The WCB harboring the fusion gene zntAp::egfp was used as a microbial metal(loid) sensor, which was turned on by the interaction between ZntR and metal(loid) ions. This design makes it possible to modulate the selectivity and sensitivity to metal(loid)s simply by changing the metal-binding property of ZntR and by disrupting the metal efflux system of E. coli, respectively. In fact, the E. coli cell-based bioreporter harboring zntAp::egfp showed multi-target responses to Cd(II), Hg(II), and Zn(II). However, the WCBs showed responses toward only Cd(II) and Hg(II) when the amino acid sequence of the metal-binding loop of ZntR was changed to CNHEPGTVCPIC and CPGDDSADC, respectively. Moreover, the sensitivity toward both Cd(II) and Hg(II) was enhanced when copA, which is known to export copper and silver, was deleted. Thus, our findings provide a strong foundation for expanding the target of WCBs from the currently limited number of genetic systems available.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belkin S (2003) Microbial whole-cell sensing systems of environmental pollutants. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(3):206–212
Bjerketorp J, Håkansson S, Belkin S, Jansson JK (2006) Advances in preservation methods: kee** biosensor microorganisms alive and active. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17(1):43–49
Branco R, Cristóvão A, Morais PV (2013) Highly sensitive, highly specific whole-cell bioreporters for the detection of chromate in environmental samples. PLoS One 8(1):e54005
Brocklehurst KR, Hobman JL, Lawley B, Blank L, Marshall SJ, Brown NL, Morby AP (1999) ZntR is a Zn (II)-responsive MerR-like transcriptional regulator of zntA in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 31(3):893–902
Changela A, Chen K, Xue Y, Holschen J, Outten CE, O'Halloran TV, Mondragón A (2003) Molecular basis of metal-ion selectivity and zeptomolar sensitivity by CueR. Science 301(5638):1383–1387
Close DM, Ripp S, Sayler GS (2009) Reporter proteins in whole-cell optical bioreporter detection systems, biosensor integrations, and biosensing applications. Sensors 9(11):9147–9174
Daunert S, Barrett G, Feliciano JS, Shetty RS, Shrestha S, Smith-Spencer W (2000) Genetically engineered whole-cell sensing systems: coupling biological recognition with reporter genes. Chem Rev 100(7):2705–2738
DeLano WL (2002) PyMOL
Franke S, Grass G, Nies DH (2001) The product of the ybdE gene of the Escherichia coli chromosome is involved in detoxification of silver ions. Microbiology 147(4):965–972
Good L, Nazar RN (1992) An improved thermal cycle for two-step PCR-based targeted mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 20(18):4934
Harms H, Wells MC, van der Meer JR (2006) Whole-cell living biosensors—are they ready for environmental application? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70(3):273–280
Hong H, Park W (2014) TetR repressor-based bioreporters for the detection of doxycycline using Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter oleivorans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(11):5039–5050
Hynninen A, Tõnismann K, Virta M (2010) Improving the sensitivity of bacterial bioreporters for heavy metals. Bioengineered bugs 1(2):132–138
Hynninen A, Virta M (2009) Whole-cell bioreporters for the detection of bioavailable metals. Whole Cell Sensing System II. Springer, pp 31–63
Ibáñez MM, Checa SK, Soncini FC (2015) A single serine residue determines selectivity to monovalent metal ions in metalloregulators of the MerR family. J Bacteriol 197(9):1606–1613
Juhasz AL, Smith E, Weber J, Rees M, Rofe A, Kuchel T, Sansom L, Naidu R (2006) In vivo assessment of arsenic bioavailability in rice and its significance for human health risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect 114(12):1826–1831
Kang Y, Lee W, Kim S, Jang G, Kim B-G, Yoon Y (2018) Enhancing the copper-sensing capability of Escherichia coli-based whole-cell bioreporters by genetic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(3):1513–1521
Magrisso S, Erel Y, Belkin S (2008) Microbial reporters of metal bioavailability. Microb Biotechnol 1(4):320–330
Merulla D, Buffi N, Beggah S, Truffer F, Geiser M, Renaud P, van der Meer JR (2013) Bioreporters and biosensors for arsenic detection. Biotechnological solutions for a world-wide pollution problem. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(3):534–541
Nivens DE, McKnight T, Moser S, Osbourn S, Simpson M, Sayler G (2004) Bioluminescent bioreporter integrated circuits: potentially small, rugged and inexpensive whole-cell biosensors for remote environmental monitoring. J Appl Microbiol 96(1):33–46
Rensing C, Mitra B, Rosen BP (1997) The zntA gene of Escherichia coli encodes a Zn (II)-translocating P-type ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(26):14326–14331
Walker DJ, Clemente R, Roig A, Bernal MP (2003) The effects of soil amendments on heavy metal bioavailability in two contaminated Mediterranean soils. Environ Pollut 122(2):303–312
Wang D, Hosteen O, Fierke CA (2012) ZntR-mediated transcription of zntA responds to nanomolar intracellular free zinc. J Inorg Biochem 111:173–181
Yagur-Kroll S, Belkin S (2011) Upgrading bioluminescent bacterial bioreporter performance by splitting the lux operon. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(4):1071–1082
Yoon Y, Kang Y, Chae Y, Kim S, Lee Y, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2016a) Arsenic bioavailability in soils before and after soil washing: the use of Escherichia coli whole-cell bioreporters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(3):2353–2361
Yoon Y, Kang Y, Lee W, Kim S, Oh K, Kim B (2017) Modulating the properties of metal-sensing whole-cell bioreporters by interfering Escherichia coli metal homeostasis. J Microbiol Biotechnol
Yoon Y, Kim S, Chae Y, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2016b) Evaluation of bioavailable arsenic and remediation performance using a whole-cell bioreporter. Sci Total Environ 547:125–131
Yoon Y, Kim S, Chae Y, Kang Y, Lee Y, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2016c) Use of tunable whole-cell bioreporters to assess bioavailable cadmium and remediation performance in soils. PLoS One 11(5):e0154506
Yoon Y, Kim S, Chae Y, Kim SW, Kang Y, An G, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2016d) Simultaneous detection of bioavailable arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils using dual-sensing bioreporters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(8):3713–3722
Funding
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (2015R1C1A1A02037275 and 2017R1E1A1A01073894 to Y.Y.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article did not involve any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 124 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Y., Lee, W., Jang, G. et al. Modulating the sensing properties of Escherichia coli-based bioreporters for cadmium and mercury. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 4863–4872 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8960-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8960-2