Abstract
Purpose
We investigated the hypothesis that increasing fMRI temporal resolution using a multiband (MB) gradient echo-echo planar imaging (GRE-EPI) pulse sequence provides fMRI language maps of higher statistical quality than those acquired with a traditional GRE-EPI sequence.
Methods
This prospective study enrolled 29 consecutive patients receiving language fMRI prior to a potential brain resection for tumor, AVM, or epilepsy. A 4-min rhyming task was performed at 3.0 Tesla with a traditional GRE-EPI pulse sequence (TR = 2000, TE = 30, matrix = 64/100%, slice = 4/0, FOV = 24, slices = 30, time points = 120) and an additional MB GRE-EPI pulse sequence with an acceleration factor of 6 (TR = 333, TE = 30, matrix 64/100%, slice = 4/0, FOV = 24, time points = 720). Spatially filtered t statistical maps were generated. Volumes of interest (VOIs) were drawn around activations at Broca’s, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, Wernicke’s, and the visual word form areas. The t value maxima were measured for the overall brain and each of the VOIs. A paired t test was performed for the corresponding traditional and MB GRE-EPI measurements.
Results
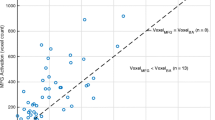
The mean age of subjects was 42.6 years old (18–75). Sixty-two percent were male. The average overall brain t statistic maxima for the MB pulse sequence (t = 15.4) was higher than for the traditional pulse sequence (t = 9.3, p = < .0001). This also held true for Broca’s area (p < 0.0001), Wernicke’s area (p < .0001), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (p < .0001), and the visual word form area (p < .0001).
Conclusion
A MB GRE-EPI fMRI pulse sequence employing high temporal resolution provides clinical fMRI language maps of greater statistical significance than those obtained with a traditional GRE-EPI sequence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stippich C, Rapps N, Dreyhaupt J, Durst A, Kress B, Nennig E, Tronnier VM, Sartor K (2007) Localizing and lateralizing language in patients with brain tumors: feasibility of routine preoperative functional MR imaging in 81 consecutive patients. Radiology. 243(3):828–836
Agarwal S, Sair HI, Gujar S, Pillai JJ (2019) Language map** with fMRI: current standards and reproducibility. Top Magn Reson Imaging 28(4):225–233
Murphy K, Bodurka J, Bandettini PA (2007) How long to scan? The relationship between fMRI temporal signal to noise ratio and necessary scan duration. NeuroImage. 34(2):565–574
Feinberg DA, Setsompop K (2013) Ultra-fast MRI of the human brain with simultaneous multi-slice imaging. J Magn Reson 229, 90:–100
Larkman DJ, Hajnal JV, Herlihy AH, Coutts GA, Young IR, Ehnholm G (2001) Use of multicoil arrays for separation of signal from multiple slices simultaneously excited. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(2):313–317
Barth M, Breuer F, Koopmans PJ, Norris DG, Poser BA (2016) Simultaneous multislice (SMS) imaging techniques. Magn Reson Med 75(1):63–81
Moeller S, Yacoub E, Olman CA, Auerbach E, Strupp J, Harel N, Uğurbil K (2010) Multiband multislice GE-EPI at 7 tesla, with 16-fold acceleration using partial parallel imaging with application to high spatial and temporal whole-brain fMRI. Magn Reson Med 63(5):1144–1153
Thanh Vu A, Jamison K, Glasser MF, Smith SM, Coalson T, Moeller S et al (2017) Tradeoffs in pushing the spatial resolution of fMRI for the 7T Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage. 154:23–32
Demetriou L, Kowalczyk OS, Tyson G, Bello T, Newbould RD, Wall MB (2018) A comprehensive evaluation of increasing temporal resolution with multiband-accelerated protocols and effects on statistical outcome measures in fMRI. NeuroImage. 176:404–416
Black DF, Vachha B, Mian A, Faro SH, Maheshwari M, Sair HI, Petrella JR, Pillai JJ, Welker K (2017) American Society of Functional Neuroradiology-recommended fMRI paradigm algorithms for presurgical language assessment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38(10):E65–e73
Cox RW (1996) AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res 29(3):162–173
Krasnow B, Tamm L, Greicius MD, Yang TT, Glover GH, Reiss AL, Menon V (2003) Comparison of fMRI activation at 3 and 1.5 T during perceptual, cognitive, and affective processing. Neuroimage. 18(4):813–826
Smith SM, Beckmann CF, Andersson J, Auerbach EJ, Bijsterbosch J, Douaud G, Duff E, Feinberg DA, Griffanti L, Harms MP, Kelly M, Laumann T, Miller KL, Moeller S, Petersen S, Power J, Salimi-Khorshidi G, Snyder AZ, Vu AT, Woolrich MW, Xu J, Yacoub E, Uğurbil K, van Essen D, Glasser MF, WU-Minn HCP Consortium (2013) Resting-state fMRI in the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage. 80:144–168
Smitha KA, Arun KM, Rajesh PG, Joel SE, Venkatesan R, Thomas B, Kesavadas C (2018) Multiband fMRI as a plausible, time-saving technique for resting-state data acquisition: study on functional connectivity map** using graph theoretical measures. Magn Reson Imaging 53:1–6
Todd N, Moeller S, Auerbach EJ, Yacoub E, Flandin G, Weiskopf N (2016) Evaluation of 2D multiband EPI imaging for high-resolution, whole-brain, task-based fMRI studies at 3T: sensitivity and slice leakage artifacts. NeuroImage 124(Pt A):32–42
Siegel JS, Power JD, Dubis JW, Vogel AC, Church JA, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2014) Statistical improvements in functional magnetic resonance imaging analyses produced by censoring high-motion data points. Hum Brain Mapp 35(5):1981–1996
Stöcker T, Schneider F, Klein M, Habel U, Kellermann T, Zilles K, Shah NJ (2005) Automated quality assurance routines for fMRI data applied to a multicenter study. Hum Brain Mapp 25(2):237–246
Geissler A, Gartus A, Foki T, Tahamtan AR, Beisteiner R, Barth M (2007) Contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) as a quality parameter in fMRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 25(6):1263–1270
Welvaert M, Rosseel Y (2013) On the definition of signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio for FMRI data. PLoS One 8(11):e77089
Cauley SF, Polimeni JR, Bhat H, Wald LL, Setsompop K (2014) Interslice leakage artifact reduction technique for simultaneous multislice acquisitions. Magn Reson Med 72(1):93–102
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mark, I.T., Black, D.F., DeLone, D.R. et al. Higher temporal resolution multiband fMRI provides improved presurgical language maps. Neuroradiology 63, 439–445 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02569-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02569-8